In this presentation, we’re going to record a sale on account. In other words, we can also call that a sale on credit. In other words, the form that we’re going to be using in QuickBooks will be to record an invoice. Let’s get into it with Intuit QuickBooks Online now. Here we are in our get great guitars file, we’re going to record an invoice. We’ve seen this in the past, so we’re going to do it a bit faster here. If we go to our flowchart from the desktop version, we’re going to be recording the invoice the difference between an invoice and the sales receipt is that we have not yet received payment.
00:31
This will typically happen when we do the work before we get paid and then basically build a client or send out the invoice and that means the accounts receivable will be going up with regards to the invoice as opposed to cash or undeposited funds going up with regards to the Create sales receipt. So let’s go back to the QuickBooks desktop. I’m going to be down in the 100% no zooming in because I wanted to not mess up the invoice or anything like that as we go into it. We’re going to be going to the center invoice so the new and then send an invoice.
01:03
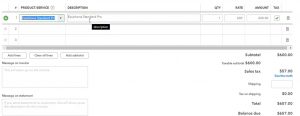
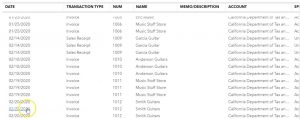
This invoice is going to music stuff stores. So we’re going to type in music stuff store music, and there it is, but we have that one down below. So that’s the one we’re going to be picking up. The date is going to be 219. So I’m just going to select a plus button here to get to the 19th. The invoice number populates on its own, which is nice. We’re going to then go down to the product. It’s going to be on Epiphone standard pro and Epiphone standard Pro, Epiphone standard. So there it is an Epiphone standard Pro, ESP, that’s the one we’re going to be picking, it is subject to sales tax, because it’s going to be an inventory item. And so there we have it, the $600 we’re applying the sales tax, this is calculated in California, the 57.
01:48
You could adjust the number to match our number with this see the math here and you can you can override it if you so choose if you want to match our problem and you have some other state for some reason. Then you can go down below and we have the total being the 657. So what’s going to happen with this every time we do the invoice, we’re going to think okay, invoice means the accounts receivable is going to go up, then the other side’s going to go to sales, but sales is only going to go up by the 600, rather than the AR is going up by the 657, the difference is going to go to sales tax because the statement is collect $57 more to give to them. And that’s a liability. And then the inventory is going to go down by an amount not on this form, but driven by the item.
02:31
So the infant so the system knows what it should be going down by but it’s not on the actual form, we could look it up by looking at the inventory reports. And then the cost of goods sold is going to be going up which is an expense account related to the same number that inventory is going to be going down by now let’s record another one. So we’re going to instead of saying Save and Close I’m going to select the drop down which is more like a drop up and we’re going to say Save and new I’m going to make a save and new and go directly into another invoice that we will be creating This one for Smith guitars. So we’re going to scroll back up top to the customer field. I’m looking for Smith Smith guitars.
03:07
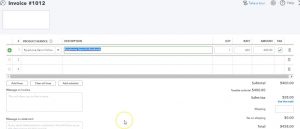
So as I do we have them we do there they are Smith, I know them. They’re good customer, they’re good people. So we’re going to tab through this will make the invoice date as of the 20th. And so there we have that, then we’re going to go down to the product and service and this one’s going to be an Epiphone semi hollow body. So let’s see if I can find that one. We want an Epiphone semi hollow body, that’s the one so nice guitar, that’s a good one. So we’re going to say all right, that’s going to be the $400. It is going to be taxable. So we have the 400. Down here, the tax being calculated at the $38. Again, you could change it if you want to just for the purposes of the practice problem.
03:47
What’s going to happen when we record this? Well, it’s an invoice accounts receivable is going to go up by the 437. Sales is going to go up by the 400. The amount we get to keep the difference is the amount of state made is charged in order to give to the Which is 38, which is going to go into a liability inventory is going to go down by some amount that’s not on this form, but is known by the system because of the item that we put in cost of goods sold and expense is going to be going up by that same amount. Let’s record it and check them out.
04:15
So I’m going to this time, I’m going to say Save and Close. Instead of saving news, I’m going to take the drop down, which is really kind of a drop up, and we’re going to go to save and close, then we’re going to open up our trusty trial balance. And we’ll do a quick review on this with the trusty trial balance. I mean, I didn’t close it saved it, I believe, but it didn’t close it, I don’t think anyways, I’ll close it here, then I’m going to go to the reports on the left will type in trial balance. That’s what we want to look at now the trial balance, which is trustee, and we’ll go into that, and then we’re going to change the dates up top. We’re going to go back up top changing the dates from a 10120 to 1230 120. January through December 2020. Run that report.
04:57
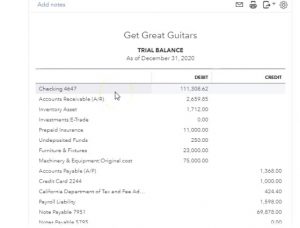
Then I’m going to close the hamburger up Because I don’t think we need to do anything else and we don’t need to duplicate the tab. This time I’m going to hold down Control, scroll up a bit to get to the 125. That’s where I like to be. And then the accounts receivable just to review this. Let’s go into the accounts receivable we have two invoices that we put into the AR now increasing for music store stuff and Smith guitars, there’s the two invoices for the gross amount or the total amount of the invoice. Let’s go on back and go back. The other side I would think of going to the sales which would be on the income statement, which is on the bottom of the trustee trial balance. There’s the sale we want to pick up the sales for the products.
05:39
So this is going to be the sales item we need. If we then scroll down to the bottom of that transaction detail we see those two invoices once again however this time for a bit less of an amount, the amount that we actually charged for on the sticker price form not including the sales tax if a state made us add to the sticker price, then we’re going to go back and look for that added amount. This statement is add to the sticker price that’s going to be in a liability, which is up top or kind of in the middle of the trial balance, it goes assets and then liabilities. And there’s the 424 14. If we select that and scroll back down, we’re going to see those invoices once again and the sales tax related to them broken out into their component parts.
06:20
Going back up top, we’re not quite done yet, we’re pretty close. But we also know that the inventory went down because we sold a guitar and that’s the stuff we sell, that’s our inventory and it went down so we’re going to go to the inventory assets go into the inventory assets. Scrolling back down, we see our two invoices once again, they are going down not by any amount that we recognize. I didn’t see that on the invoice at all. It’s not on the invoice but it is driven by the invoice.
06:44
The system knows what it is because we entered the service items related to them. Scrolling back up top, what’s the other side to that inventory going down? It’s the cost of goods sold and expense account going up. The cost of goods sold represents us consuming the inventory in order to generate revenue So we’re going to go back down. There’s the other side of those reflecting these expense accounts going up. What’s the effect on net income? The difference between the sales the sales that we’ve recorded, increasing, and the difference in the expense Cost of Goods Sold increasing is going to be the net effect on net income.