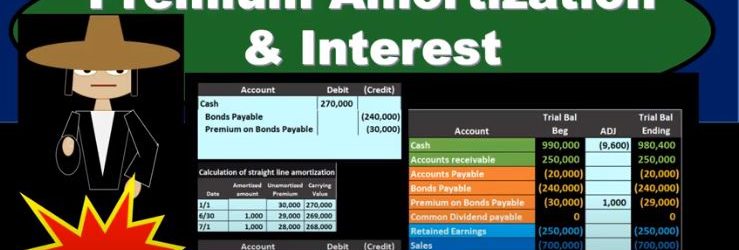
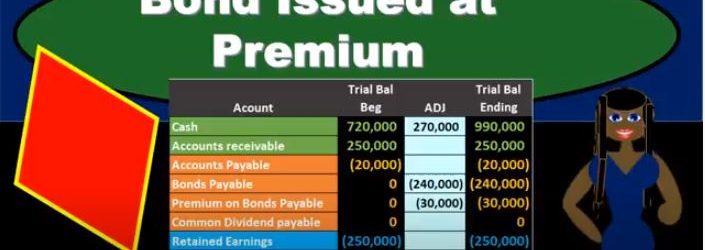
In this presentation, we will discuss the amortization of a bond premium and the recording of interest expense on bonds. This is going to be our starting point. This is the initial transaction in order to get the bonds on the books. Here’s our data down here we’ve got the number of years we’ve got the face amount of the bonds, we’ve got the issue price 270, we see that the interest on the market rate is different than the contract rate. The result then is that cash is going to be increased by the 217. The bonds payable went on the books for the face amount of the bond, the amount that’s on the bonds of the 240, which is a liability. And then we have the premium being the difference increasing the premium here by the 30. The 240 plus 230 is going to be equal to the 270,000 carrying amount book value of the bonds. Now we’re going to go through the process of recording the interest we can see that this is going to have 15 years bonds, we’re going to pay the bonds semi annually. So we’re going to have to record the interest on them. And we’re gonna have to reduce this premium in some way as well. Remember, at the end of the bonds, we’re not going to pay back the 270. We’re only going to pay back 240. So how are we going to get rid of that the premium on the bond and why are we going to do it in the way we will. We’ll start off by amortize in the premium using a straight line the method. Note that the effective method is the preferred method for amortize in a premium for generally accepted accounting principles, but the straight line method will be appropriate in some cases, if the difference is going to be a non material. And the straight line method is a simplified method and it’s easy for us to see what is going on. So we’ll start off with the straight line method.