Corporate Finance PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will discuss Statement of Cash Flows Get ready, it’s time to take your chance with corporate finance statement of cash flows. So remember when we’re thinking about the financial statements, we can think about them as answering two major questions to users of the financial statements. For examples, if we’re thinking about investing to the company in some type of way, and are using the financial statements to help us make a decision with regards to that, we want to know where does the company stand at this point in time, what’s basically their worth at this point in time. For that we get help from the balance sheet, which is going to give us the assets liabilities, equity, assets, minus liabilities equals equity, which is basically the book value as of a point in time.
Posts with the component tag
Segment Reporting Overview
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will give an overview of segment reporting, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, overview segment reporting. So when we think about segment reporting, we’re thinking about a company breaking that company into the segments. And when we think about the segments, two questions we want to consider are what is a segment? How does one qualify or how does a segment qualify as a segment and once qualifying for a segment, then what are going to be the financial reporting that needs to be done for the segment? So three characteristics of an operating segment, the component units, business activities, generate revenue and incur expenses. So the component unit that unit you can think about like a separate unit incurs revenue and has expenses including any revenue or expenses in transactions with other business units of the company? So we’re including the transactions if you’re thinking about it as a different segment, a different unit? You’re thinking okay, they have revenue and expenses with In the revenue worth, we’re also including any revenue or expenses, in transactions with other business units of the company. So you’re kind of thinking about a segment as being somewhat autonomous in and of itself here, and therefore having its own basically revenue and expenses, although it can be connected to other segments, the component units, operating results are regularly reviewed by the entities Chief Operating mark, operating decision maker.
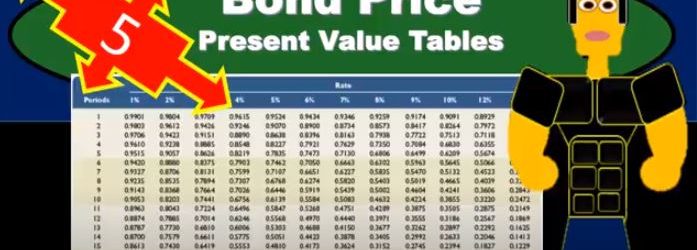
Bond Price Present Value Tables
In this presentation, we will calculate the bond price using present value tables. Remember that the bonds is going to be a great tool for understanding the time value of money. Because of those two cash flow streams we have when with relation to bonds, meaning we’re going to pay the bond back the face amount of the bond, and we’re going to have the income stream. And those are going to be perfect for us to think about time value of money, how to calculate time value of money, our goal being to get a present value of those two streams. So we’re going to think of those two streams separately generally, and present value each of them to find out what the present value of the bond will be. We can do that at least three or four different ways. We can do that with a formula actually doing the math on it. We can do it now, which is probably more popular. Now. Do it with a calculator or with tables in Excel, I would prefer Excel or we can use just tables pre formatted tables. The goal here the point is to really understand what we’re doing in terms of what what is happening, what can it tell it? What can it tell us, and then understand that these different methods are all doing the same thing.
Perpetual & Periodic Inventory Systems
In this presentation, we will compare and contrast the perpetual and periodic inventory systems as we track inventory through the accounting process. First, we’re going to look at the perpetual system, the system we typically think of when recording transactions that deal with inventory. So if a transaction doesn’t say it’s using a periodic or perpetual system, you probably want to default to the perpetual system. We have here the owner, we have the customer, we’re saying that we’re selling this inventory this Inc for a cost of 8450. To the customer, the customer is not paying cash but pain, an IOU to the owner. Typically, under a perpetual system. We break this out into two components one, the IOU, or the accounts receivable or sales component. The component similar to what would be seen if we were not selling merchandise but a service company.