Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to talk about the consolidation process with a differential we’re going to look at the component parts with a simple example a simple calculation, you’re ready to account with advanced financial accounting, consolidation with differential example. So here’s going to be the basic scenario for many of the practice problems we will be looking with. We have P and S, there’s going to be a parent subsidiary relationship in which we will be making consolidated financial statements. How did this situation take place what constituted this situation, we’re going to say that in this example, P is purchasing the stocks of S. So notice they’re purchasing the stocks of s and therefore negotiating the stock price, which we’re going to say is $1,000 here. Now to simplify this example, you first want to think about this as p purchasing 100% of the stock of s for $1,000. And then once they have control, anything over 51% would then be controlled.
Posts with the fair tag
Consolidation When There is a Book & Fair Value Difference
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to take a look at a consolidation process when there is a book and fair value difference. In other words, we’ll have a consolidation. We have two companies, we have a parent subsidiary type of relationship, and the parent has a controlling interest of the subsidiary. Therefore consolidation is what we’re going to be doing. That means we’re going to take two separate sets of books combine them together as if they were one. And we had some complications with the fact that when the purchase took place, there was a difference between the book value and the fair value, what will be the effect of that difference on the consolidation process, elimination entry example. So when we consider this difference, we want to think about what’s going on with the parents books and the subsidiaries books and then what would be the process to consolidate them and what type of problems would be caused if there was a difference between the book and fair value of the net assets so the parents books investment accounts starts out containing the acquisition costs at the fair market value of net assets and goodwill, so we have, that’s basically what’s going to be on the parents books, right. And we’re thinking here typically have an equity method being used. So we have the parents books, we have the subsidiary books that we’re gonna have to consolidate together, and then do our elimination entries. And on the parents books, you’re accounting for the subsidiaries.
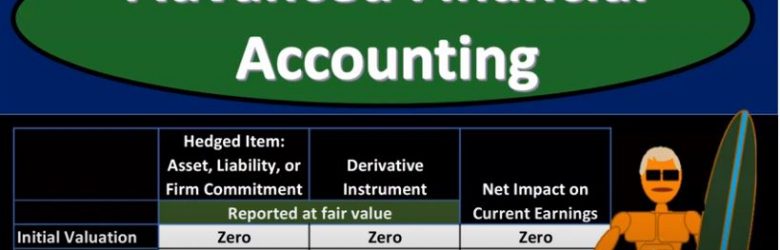
Forward Exchange Financial Instruments
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss forward exchange of financial instruments get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, forward exchange financial instruments let’s start off with some definitions starting off with financial instrument itself will be either cash evidence of ownership or a contract that imposes on one entity on contractual obligation to deliver cash or another instrument and conveys to the second entity, the contractual right to receive cash or another financial instrument. That of course, being the most complex component here. So let’s read that one more time. The financial instrument a contract that imposes on one entity a contractual obligation to deliver either cash or another instrument and conveys to the second party the second party in this item, the second entity, the contractual right to of course, receive the cash or another financial instrument derivative. So a derivative, financial instrument or other contract whose value is derived from some other item that has a value that varies over time. So let’s think about that one more time again, derivative financial instruments or other contracts whose value is derived from, they’re going to get the value from some other item that has a value. That is that varies over time, meaning of course, that it will be changing over time. So let’s think about the derivative characteristics. And then we’ll apply these to the component of what we’re considering here. foreign currency and foreign currency transactions in terms of typically foreign currency type hedge transactions.
Acquisition Accounting Bargain Purchase
This presentation we’re going to continue on with our discussion of acquisition accounting, and this time focusing in on a bargain purchase, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. First off, we can basically think of the bargain purchase as the opposite of goodwill. So in a prior presentation, we talked about the concept of goodwill within an acquisition, which would be resulting if the fair market value of the amount that was given like basically the purchasing price was greater than the fair market value of the net assets. So in other words, we take we look at the books of the company that’s being acquired, we’ve revalue their assets and liabilities to be on a fair market value, then assets minus liabilities, the equity section, the net assets now at a fair market value, we take a look at that. And if there’s a consideration that’s given that is greater than that amount, that then would result in goodwill. Now goodwill is quite common, because it’s unlikely even if you even if you re assess all the assets and liabilities to their fair value. Then you would typically think that the price would either be that that would be given the the amount that would be exchanged, the fair market value of the consideration would be the same as the assets minus the liabilities at fair market value, or more, because there’s some type of goodwill, that’s going to be that’s going to be in the organization. Now, you might be thinking, Well, what what if it was the opposite? What if you took the fair market value of the net assets, and the amount that was given the exchange amount was less than the fair market value? Now that could happen, but just note that that’s a lot more unusual.
Acquisition Accounting Goodwill
In this presentation, we’re going to continue on with our discussion of acquisition accounting, this time focusing in on the concept of goodwill. Get ready, because it’s time to account with advanced financial accounting. First question is, what is goodwill. So it’s an intangible factors that allow a business to earn above average profits. So the way you might want to think about that is the first thing about a business that isn’t being purchased and sold. If you just got one business that started from scratch, they just started doing business, they started earning revenue, then you can look at their financial statements, they got the they got the balance sheet, assets minus liabilities is the book value of the company, and then the income statement, which is their performance. Now, if you were to say, Hey, is this company worth more than their equity than their assets minus the liabilities than their net assets? In other words, if it is, then you’re saying hey, there must be some intangible factor that’s not really on the balance sheet that would explain the reason why the you know the value of them because most likely through Profit generation, after the the perceived ability, the likely ability to earn profit in the future is greater than just what’s on the balance sheet assets minus liabilities. So you would think then that many companies, if a company is doing well, then there’s going to be some kind of intangible factor there. That’s not basically on the balance sheet that basically explains why the company is doing better than then just the value of the company being assets minus liabilities. So in other words, if we were to purchase the company, you would think that you would purchase it for their assets minus the liabilities, that’s what they consist of, that’s breaking them down to their parts.