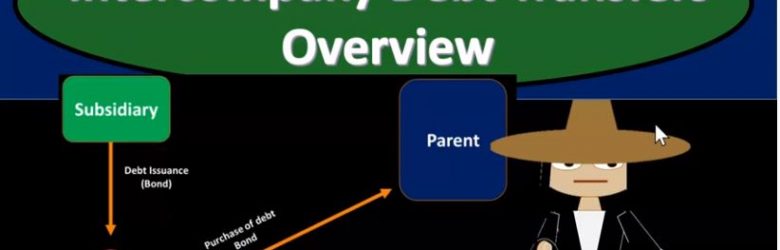
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will give an overview of intercompany debt transfers. In other words within the concept of our consolidation process where we have parent subsidiary relationships we have intercompany debt debt going from one entity to the other, from parent to the subsidiary or subsidiary to the parent could be in the form of, of notes payable or in the form of bonds payable, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. When we think of intercompany debt, we can break it out basically into two categories intercompany debt the debt from one to the other from parent to subsidiary or subsidiary to parent, two categories, one direct intercompany debt transfer and the other is the indirect intercompany debt transfer.
Posts with the indirect tag
Direct & Indirect Control
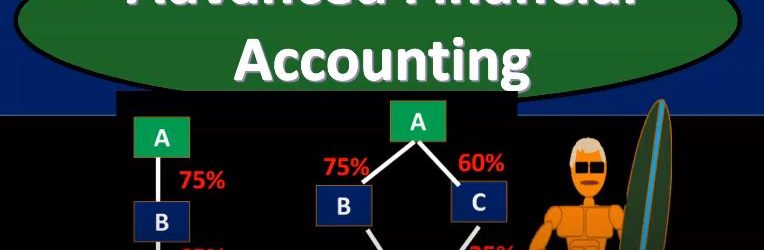
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to talk about the concepts of direct and indirect control. If you’re ready to account with advanced financial accounting, we want to consider these concepts within the context of financial statements and consolidation. So you’ll recall that when we have consolidated financial statements, the idea is to put two financial statements together when one company has basically control over another company that being defined typically by having more than 51% interest because if you have more than 51%, then you have basically a voting share for you to vote on anything, then of course, you would win the vote at that point in time. So let’s consider then direct control and indirect control direct control when one company has a majority of another company’s stock common stock. So that would be a situation where you got a and b, one company has a majority interest over 51% control is pretty easy to see at that point. When you start to get into indirect control. This can get more complicated things can get more confusing here. So indirect control, one company’s common stock is owned by one or more other companies that are under common control. So this can get a lot more detailed structure in terms of what is going to constitute control. So for example, if we have direct control, then you have just simply a parent subsidiary type of relationship. And, you know, the parent has more than 51% of the subsidiary, interest common stock. So and that could happen if we have to, we could still have a little bit more complexity here, where we have two subsidiaries, right. But they’re both going to be consolidated in this case, because there’s 75% over 51% direct control is parent over as one direct control over as to here because it’s over the 51%. So both of these cases would be direct control.
Consolidation When there is Complex Ownership Structure
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we’re going to discuss a consolidation that when there is a complex ownership structure, so more complex ownership structure comparing the direct ownership, which is what we’ve normally been dealing with, with structures such as multi level ownership and reciprocal ownership, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. Normally, when we think about our consolidation structure, we’re dealing with a direct ownership situation which looks like this direct ownership type of situation, it gets more complex. Of course, if we have more complex type of ownership structures, such as a multiple multi level ownership structure where we have a parent owning a subsidiary, that basically we have an indirect ownership, let’s say in another subsidiaries, that’s going to be more complex for us to deal with or if we have a situation where we have reciprocal ownership, where the parent has ownership a controlling interest in s, but as also has some ownership in p, right. We’ve been dealing with basically P parent company owning portion of S. So if we talk about direct ownership we’re talking about the parent has, as has controlling interest in every subsidiary. So that’s going to be of course, this situation.