Hello in this section we will define the post closing trial balance. When seeing the post closing trial balance, it’s easiest to look at it in comparison to the adjusted trial balance and consider where we are at in the accounting cycle in the accounting process. When we see these terms such as the adjusted trial balance and post closing trial balance, as well as an unadjusted trial balance, we’re really talking about the same type of thing. We’re talking about a trial balance, meaning we’re going to have the accounts with balances in them. And we’re going to have the amounts related to them. And of course, the debits and the credits will always remain in balance. If it is a trial balance, no matter the name, whether it be just a trial balance on an adjusted trial balance and adjusted trial balance or a post closing trial balance.
Posts with the trial balance tag
Closing Process Explained
Hello in this lecture we’re going to talk about the objectives of the closing process the closing process will happen after the financial statements have been created. So we will have done the journal entries where we will have compiled those journal entries into a trial balance, and then we will have made the financial statements. And then as of the end of the period in this case, we’re going to say as of December, when we move into the next time period, January, what we need to do is close out some of the temporary accounts those accounts including the income statement and the draws account so that we can start the new period from start in a similar way as if we were trying to see how many miles we could drive say in a month. If we wanted to Vince in December, and then see how many miles we’re going to drive in January of next year.
Bond Retirement
In this presentation, we will discuss the journal entries related to the retirement of bonds. the retirement of bonds just means that we’re going to pay off the bonds in some form or another at some time or another, meaning the bonds are going to go away. Typically, that’ll happen at the maturity date at the end of the bond. So for example, if we have a bond on these terms, with the face amount of 240, the issue price of 198 for 80, for 15 year bonds, they’re going to be semi annual. What would happen is when we put this on the books, we would put it on the books as cash we got for the 198, the bond payable on the books for 240, and then a discount. And then of course, over the life of the bond, we would be paying interest for that 15 year time period two times that’s 30 payments. And then at the end of this we would also be be amortizing out the discount to get rid of it, to make it go away to the interest and then By the end of this time period, the discount would be zero. And we would only be left with a bond on the books. In other words, at the maturity date, we would have something like this on our trial balance, the discount is now zero. And the bond is on the books at 240, which is the face amount of the bond, if it were a premium, it would be it would be the same in that we would be left with just the bond amount and the premium would be gone to zero. And now it’s just like anything else that we don’t have to deal with interest at this point or anything else, we just need to close out the bond. And so it’s just like any other liability, we’re just going to pay at the maturity date. That’s how we’re going to retire it. So this is a 240 credit, we’re going to make it go down by doing the opposite thing to it a debit, and we’re going to pay cash, cash is a debit balance, we need to make it go down. So we’re going to credit cash. So this is going to be our journal entry. We’ll debit the bond make go away, and then we’ll pay off the cash. When we post this then the bond payable will be here. Here, it’s going to go it’s a credit, we’re going to debit it, making it go away to zero, and then the cash has a debit balance, we’re going to credit it making the cash go down. So it’s a pretty straightforward journal entry.
02:12
The only confusing thing about this journal entry is that it happens at the end of the bond term. So when we’re talking about book questions, we often don’t get asked it because usually we’re concentrating on how to calculate the interest how to calculate the face amount of the bond, how to record the bond, how to amortize the the bond, discount or premium. And we don’t really typically get all the way to the end of the bond, the retirement the maturity date, to record the end transaction oftentimes, and it’s a pretty easy transaction if we were to do so. And it’s a lot easier to if we can actually see the trial balance. When you see the trial balance, you say, oh, there’s a liability there. We’re going to pay it just like we would if it were note payable at this time. It needs to go down and then we’re going to pay it off with cash. Now it is possible for us To have a callable bond that we’re going to retire before the end of the bond date before the maturity date. So in other words, in this case, we have the bond on the books of 240,000. And we have the discount of 338 748. And therefore, if we were to calculate the carrying amount, we’d have 240,000 minus 238 748, or two a one 252. This 201 252 is the carrying amount of this bond payable. This is something that we owe in the future. If we can pay it off at this point in time for some cash that’s going to be less than this amount, then we’re going to have a gain resulting in a gain. And if we are paying it off early for something more than this, we’re going to have a loss. So let’s see what that’s going to look like.
03:52
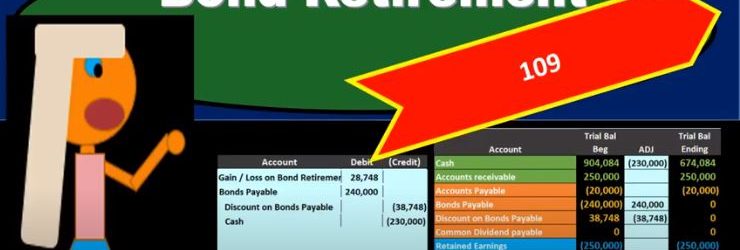
The gain or loss can be confusing here. When we’re talking about a bond. It’s easier to get to that point by just doing the journaling So if we have all this information, especially if we have the trial balance, because then we can see what accounts are debited and credited on the trial balance or which accounts have a debit or credit balance, then it’s a lot easier for us to construct the journal entry. So the first is going to be given to us, we’re going to say that the cash that we’re paying is 230,000. That’s gonna have to just be given in the problem because that’s the callable price that’s how much we’re able to purchase these bonds for. So cash is going to go down because remember, we are buying them back basically, or we’re we’re paying them off early before the maturity date. So it’s going to be 230. Then we’re going to say that the bond payable has to go off the books. Now the bond payables on the books at 240,000, we can see it’s a liability, it has a credit balance. So to take it off the books, we do the opposite thing to it, a debit for whatever it needs to be to make it go to zero, the discount. Same thing we need to do whatever we need to do to make it go to zero because it’s Gotta go away. So when we construct the journal entry, we just know that we just got to do whatever we need to do to make it go to zero. If you have a trial balance in front of you, that’s easy to do, because we can see the discounts on the books at a debit. And we need to do the opposite to make it go down, which is a credit. If you’re looking at a book problem that doesn’t give you a trial balance, and just tells you that the bond is on the books at a discount, then you got to think through it. And one way to think through it might be to say, well, the bonds is a liability, it must be a credit, that discount means that we’re making the bond go down, because it must be decreasing, we’re having it less than the state, the face amount, the sticker price.
05:40
And since it’s a credit, the thing that makes a credit go down would be a debit. So that discount must be a debit because these two are really combined together. And a discount means that we we really the net of the two are below the face amount price, so this must be a debit. So if it were a premium, then this amount be increasing or greater than the face amount, and it would be a credit normal balance. Once we know that this is a, this is a debit normal balance for a discount, then we can do the opposite thing to it to credit it to make it go down. And then of course, we just need to figure out what the difference is we’ve got credits of 230,038 748 minus the 240. Debit means we need a 28 748 debit. And that of course, in this case, I’m going to say it’s a gain loss account here because it could have gone either way. But if it’s a debit here, then it’s on the income statement. That’s going to be a loss. And you just got to basically start to be able to recognize that why would that be a loss? Well, you can think through that. We paid 230 versus the carrying value, or you can also just think well, if it’s a debit on the income statement, It’s acting more like an expense, meaning expenses have debit balances, they go up in the debit direction, and they bring net income down.
07:08
Revenue has a credit balance, it brings net income up. This is acting like a, an expense because it’s a debit balance. If we debit the income statement, it’s going to make net income go down, that means it must be a loss rather than a gain, which we would think would make net income go up. So the other way we can think about this is to is remember, the carrying value is going to be the 240,000 minus the 38 748. So this is kind of a value that we owe on the bond. And it’s a liability, that’s kind of the value we owe and we paid more than the value that we owe. So that’s going to be a loss in this case. And that’s another way you can think through it being a loss. So if we post this out, then we’re going to say that the gain or loss 28 748 Here, making the income statement accounts go up, kind of like an expense bringing net income down. The bond payable will be posted here, it’s going to make the bond payable go to zero. That’s why we are retiring. It’s making it go away. And then we’ve got the discount, it’s going to make the discount go to zero because we’re retiring it as well. And then the cash is going to be here, cash is going to go down. So there’s going to be our transaction. We have the bond payable and discount going away which has to be the case if we’re retiring the bonds. The cash is going down for the early retirement. And we resulted in a loss in order for us to be able to retire the bonds early.
Premium Amortization & Interest
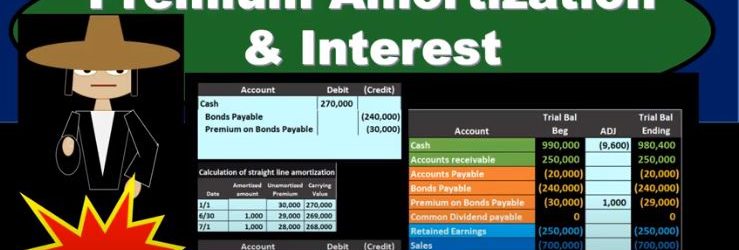
In this presentation, we will discuss the amortization of a bond premium and the recording of interest expense on bonds. This is going to be our starting point. This is the initial transaction in order to get the bonds on the books. Here’s our data down here we’ve got the number of years we’ve got the face amount of the bonds, we’ve got the issue price 270, we see that the interest on the market rate is different than the contract rate. The result then is that cash is going to be increased by the 217. The bonds payable went on the books for the face amount of the bond, the amount that’s on the bonds of the 240, which is a liability. And then we have the premium being the difference increasing the premium here by the 30. The 240 plus 230 is going to be equal to the 270,000 carrying amount book value of the bonds. Now we’re going to go through the process of recording the interest we can see that this is going to have 15 years bonds, we’re going to pay the bonds semi annually. So we’re going to have to record the interest on them. And we’re gonna have to reduce this premium in some way as well. Remember, at the end of the bonds, we’re not going to pay back the 270. We’re only going to pay back 240. So how are we going to get rid of that the premium on the bond and why are we going to do it in the way we will. We’ll start off by amortize in the premium using a straight line the method. Note that the effective method is the preferred method for amortize in a premium for generally accepted accounting principles, but the straight line method will be appropriate in some cases, if the difference is going to be a non material. And the straight line method is a simplified method and it’s easy for us to see what is going on. So we’ll start off with the straight line method.
Bond Issued at Premium
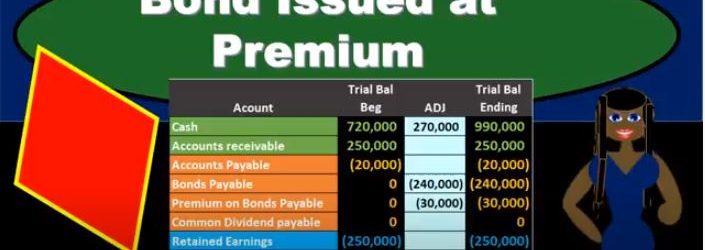
In this presentation, we will take a look at the journal entries related to issuing a bond at a premium. When considering the journal entry for a bond, remember what can change and what is the same for a bond. When we think about a bond, it’s already been printed, we know the amount of the bond, the interest on the bond, the maturity date of the bond, these are already set. So if we’re making a negotiation with the bond after it had already been printed, then we can’t change the face amount. We can’t change the interest due dates. What can we change in order to negotiate and make a sales price on the bond, we can change the amount that we issue it for. So keep that in mind. Whenever you think about these bond problems. That’s the thing that’s going to differ from a bond to a note. The thing that changes when we want to loan is the interest rate. The thing that changes when we want to issue a bond that’s already been made is going to be the amount we receive For the bond being different than the face amount of the bond if there’s a difference in the market rate and the contract rate. So in this example, we’re saying that we issued a bond. Now note that when we think about the issuance of the bond, just like a note, we often have more information than we really need. And that can be a little bit confusing for us.
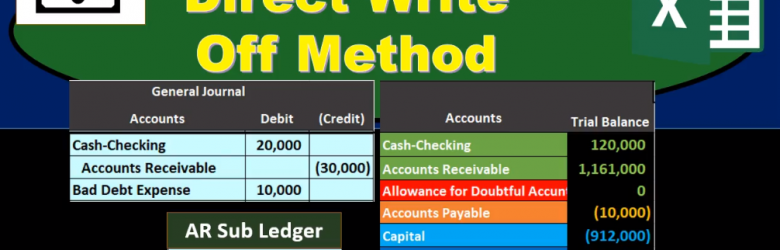
Allowance Method VS Direct Write Off Method
In this presentation, we will take a look at a comparison between the allowance method and the direct write off method. When considering both the allowance method and the direct write off method, we are considering the accounts receivable account. Remember that the accounts receivable account represents some money that is owed to the company, typically from sales made in the past, on account haven’t yet received the funds for sales made in the past and therefore, the company is owed money. We see this amount on the trial balance in this case 1,000,001 91. We then want to know information about that, including who owes us that money. We can’t find that typically in the GL as we have a GL for every account the GL only giving us the information by date. Typically, we want to see that information also broken out in the subsidiary ledger saying who owes us this money.
Allowance Method Accounts Receivable-financial accounting
Hello in this presentation we’re going to take a look at the allowance method which is of course related to the accounts receivable account, we will be able to define the allowance method record transactions related to recording bad debt recording the receivable account that has been determined to be uncollectible recording every single account that has been collected after being determined that it was uncollectible. So we’re going to take a look at some different transactions, the most common transactions when dealing with the allowance method and see what those look like and why we use the allowance method. We’re going to work through a problem. So what we’re going to have here is we’ve got our accounting equation, of course we have our trial balance, I do suggest working problems to take a look at a trial balance because it can give you the context in which to work problems. So here’s what we have. We’ve got the assets in green, the liabilities are going to be orange, the light blue is the capital account and the equity section.
Direct Write Off Method
This presentation we will be discussing the direct write off method. The direct write off method as it relates to accounts receivable, quick summary of accounts receivable accounts receivable is a current asset, it’s an asset with a debit balance, we are going to be writing off certain amounts for accounts receivable that will become not due or not collectible at some point in the future. There are two ways to do this one is called the allowance method. The other is the direct write off method, we will be using the direct write off method here the non generally accepted accounting principles method being this direct write off method. However, a method that is typically much easier to use. Therefore, when considering whether or not to use an allowance method or direct write off method, we want to consider one do we have to use an allowance method due to the fact that we need to make our financial statements in accordance with generally accepted Accounting Principles, or are we able to choose between having an allowance method or direct write off method? If we choose to have a direct write off method, it’s probably because we’re thinking that the receivables that will be written off are not significant.
Accounts Receivable AR Subsidiary Ledger Explained
Hello, in this lecture we’re going to talk about the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger, the subsidiary ledger being the ledger that will be backing up the account of accounts receivable showing on the trial balance with 27,000. In it, in this case, accounts receivable being that accounts that represents what is owed to us. If we were the owner of the company, we might ask our accounting department, how much money do people owe us? In this case, it would be 27,000 would be the reply. Next follow up question would most likely be who owes us that money? And have we called them when are we going to get paid that money? In order to answer that question, we cannot look at the normal backup balance for all accounts that being the general ledger accounts. If we look at the GL we do get some detail in terms of the activity that has happened. However, that activity is not going to be in terms of who owes us the money. It’s in terms of date.
Receivables Introduction
In this presentation we will take a look at receivables. The major two types of receivables and the ones we will be concentrating on here are accounts receivable and notes receivable. There are other types of receivables we may see on the financial statements or trial balance or Chart of Accounts, including receivables, such as rent receivable, and interest receivable. Anything that has a receivable, it basically means that someone owes us something in the future. We’re going to start off talking about accounts receivable that’s going to be the most common most familiar most used type of receivable and that means something someone, some person some company, some customer typically owes us money for a transaction happening in the past, typically some type of sales transaction. So if we record the sales transaction, that would typically be the way accounts receivable would start within the financial statements, meaning If we made a sale, we would credit the revenue account, we’ll call it sales. If we sell inventory, it would be called sales. If we sold something else, it might be called fees earned, or just revenue or just income, increasing income with a credit, and then the debit not going to cash. But going to accounts receivable.