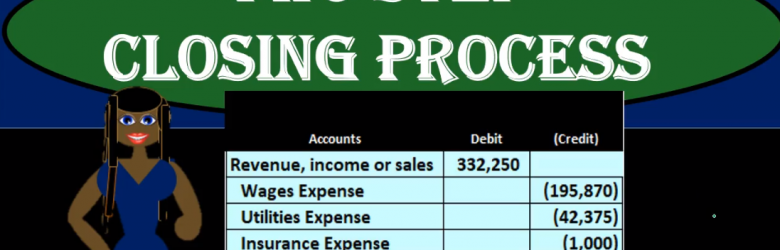
Hello in this presentation we will take a look at a two step closing process. In other words, we will perform the closing process using two journal entries. There’s a couple different ways we can see the closing process, each of them having a pros and cons. The two step process is nice because it allows us to see net income broken out and being closed out directly to the capital account, followed by draws, which is similar to what we see when we actually do the statement of equity, meaning that when we do the statement of owner’s equity, we start with beginning balance and then we increase it by net income and decrease it by drawers or dividends. Because this process is similar to that process, it’s often easy to remember it’s the easiest for me to remember in any case, so we will take a look at the two step closing process.
Posts in the QuickBooks category:
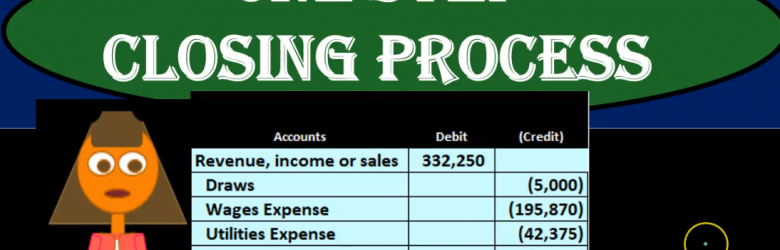
One Step Closing Process
Hello in this presentation, we will be looking at a one step closing process. In other words, we will be closing out temporary accounts using one journal entry. There’s a few different ways that we can perform the closing process. And there’s benefits and cons to each way of doing it. The one step closing process is the simplest way to do it. And it’s also a way that we can imagine what is happening within the closing process as easily as possible a skill useful when considering what’s happening from time period to time period, and how the financial statements are working. So here we’re going to look at a one step closing process. Remember what the closing process is, it’s going to be a process at the end of the time period that we will be performing.
Post Closing Trial Balance
Hello in this section we will define the post closing trial balance. When seeing the post closing trial balance, it’s easiest to look at it in comparison to the adjusted trial balance and consider where we are at in the accounting cycle in the accounting process. When we see these terms such as the adjusted trial balance and post closing trial balance, as well as an unadjusted trial balance, we’re really talking about the same type of thing. We’re talking about a trial balance, meaning we’re going to have the accounts with balances in them. And we’re going to have the amounts related to them. And of course, the debits and the credits will always remain in balance. If it is a trial balance, no matter the name, whether it be just a trial balance on an adjusted trial balance and adjusted trial balance or a post closing trial balance.
Closing Process Explained
Hello in this lecture we’re going to talk about the objectives of the closing process the closing process will happen after the financial statements have been created. So we will have done the journal entries where we will have compiled those journal entries into a trial balance, and then we will have made the financial statements. And then as of the end of the period in this case, we’re going to say as of December, when we move into the next time period, January, what we need to do is close out some of the temporary accounts those accounts including the income statement and the draws account so that we can start the new period from start in a similar way as if we were trying to see how many miles we could drive say in a month. If we wanted to Vince in December, and then see how many miles we’re going to drive in January of next year.
Accounting Building Blocks
Hello in this lecture we will discuss the accounting building blocks and the double entry accounting system. At the end of this we will be able to define and describe the double entry accounting system, write down the accounting equation and define each individual part of it, define and describe debits and credits, define a balance sheet and list its parts define an income statement list its parts and explain the relationship between the balance sheet and the income statement. Okay, so starting off every business and accounting software uses the double entry accounting system. So the double entry accounting system, it’s kind of like the math behind the calculator, every software is going to use it. In order to understand what the system is doing, we need to understand the double entry accounting system.
Accounting Cycle Steps in the Accounting Process
Hello, in this presentation, we’re going to be talking about the accounting cycle or the accounting process, that process that the accounting department will go through on a systematic basis over and over and over again, typically thought of as a monthly process. Although it could be thought of as a yearly process or some other process in terms of the amount of time that will pass. But these are going to be the steps that we’ll be going through in terms of the accounting process, always keeping in mind that in goal of financial accounting, which are the financial statements, some texts will have more steps than five as we have here. Some texts will have less than five steps. But the goal here is to really have a broad picture big picture, so that when we think about the accounting process, we can break down that that big picture view, five is a pretty good number for us to be able to memorize and keep in our mind if we have more than that, it can start to kind of muddy the picture.
Statement of Cash Flow Indirect Method Change In Inventory
In this presentation, we will continue putting together our statement of cash flows using the indirect method. Now taking a look at the change in inventory, we’re going to be using our materials here with a comparative balance sheet, the income statement and some added information, working primarily at this time from a worksheet that was made from the comparative balance sheet. So here is our worksheet. Here’s what we have. So far, we basically have a comparative balance sheet in a trial balance type format, where we have the current year, the prior year, and then the difference. Our goal is to find a home for all of these differences are in number that we’re looking for, is basically the 61 900 change in cash. So we’ve gone through this, from top to bottom, we’re working through basically the operating cash flows from operating First, the indirect method. So we started off with the net income, then we made our adjustments. And then now we’re going through basically The accounts receivable to inventory. Now once we get into the current assets, we’re going to group those into this change in current assets under the cash flows from operations. Once we know the theme here on what’s going to happen with these current assets, it’s it’s always going to be the same.
Statement of Cash Flow Indirect Method Change In Accounts Receivable
In this presentation, we will continue putting together the statement of cash flows using the indirect method focusing here on the change in accounts receivable. The information will be a comparative balance sheet, the income statement and some added information we will be focusing in on a worksheet that was composed from the comparative balance sheet. So here is our worksheet. So our worksheet that we can pay that we made from the comparative balance sheet, current period, prior period change. So we have all of our balances here for the current period, the prior period and the change, we have put in this change. And this is really the column that we are focusing in on we’re trying to get to this change in cash by finding a home for all other changes. Once we find a home for all other changes. We will get to this change in cash the bottom line here 61,900. The major thing we’re looking for is right here. We’ve already taken a look at the change in the retained earnings. And the change in the accumulated depreciation. Now we’re going to look at the changes in current assets and current liabilities.
Statement of Cash Flow Indirect Method Adjustments to Reconcile Net Income to Net Cash Provided
In this presentation, we will continue putting together a statement of cash flows using the indirect method focusing in on adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities. So this is going to be the information we will be using, we have the comparative balance sheet, the income statement added information, we took this comparative balance sheet to create our worksheet. So here is our worksheet for two time periods. This is the difference we’re basically looking to find a home for all of these differences we have done so with cash, and we’ve done so with a difference in retained earnings. So here’s cash, here’s net income, the difference in retained earnings, we will have to adjust net income shortly or at the end of the problem. We’ll we’ll take a look at that we’ll make an adjustment for it. We’re going to now find the difference for all the rest of these. Also note that of course cash is going to be the change in cash will be our bottom line. Never we’re going to recalculate this But it’s nice to know where we are ending up at. So this is kind of like even though it’s at the top of our worksheet, that’s where we want to end up by finding a home for everything else. So now we’re going to take a look at the adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities. So these are going to be those types of things that we look at the income statement, and we’re going to say that these are non cash activities, meaning income is calculated as revenue minus expenses. And the cash flow.
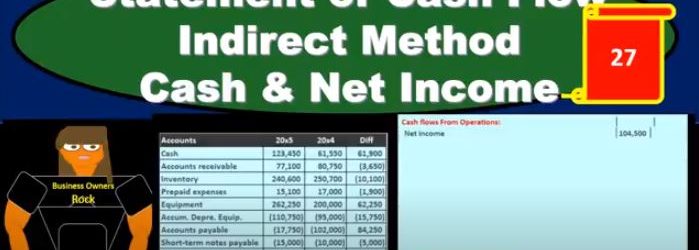
Statement of Cash Flow Indirect Method Cash & Net Income
This presentation, we will start to construct the statement of cash flows using the indirect method focusing in on cash and net income. This is going to be the resources we will have, we’ll have that comparative balance sheet, the income statement, and we’re gonna have some added information. In order to construct the statement of cash flows, we’re mainly going to be working with a worksheet that we’ve put together from a comparative balance sheet. That’s where we will start. So we’re going to find a home, this is going to be our worksheet. We have the two periods. So we have the current year, we’ve got the prior year, and we’ve got the difference between those activities. Now our goal here is to basically just find a home for every component on this difference section. So that’s going to be our home. Why? Well, we can first start thinking about cash. What are we going to do with cash? That’s the main thing. This is a statement of cash flows here. So where are we going to put cash? that’s actually going to start at the bottom, we’re going to say that’s going to be our in numbers. In number we know it’s going to be cached. Now, we’re going to recalculate it. But it’s useful for us to just know and we might just want to put there, hey, that’s where we’re going to end up. That’s where we are looking to get. And now what we really want is the change.