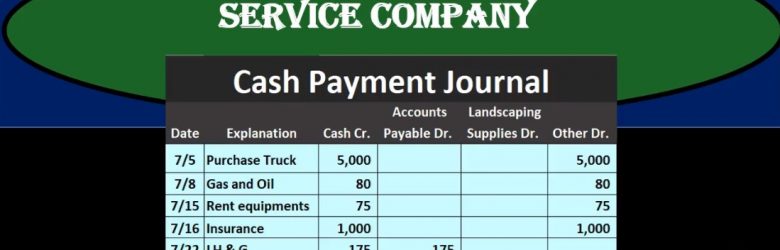
In this presentation, we will take a look at a cash payments journal for a service company, the cash payment journal we’ll be dealing with transactions where we have cash payments, that’s going to be the factor that will be the same for all transactions with cash payments meaning this column here cash payments will always be affected wish they kept cash payments journal cash payments journal will be used when using more of a manual system rather than an automated system. However, it’s good to know what the cash payments journal is, even if using an automated system because it’s possible that we or it’s very likely that we would need to run reports that will be similar in format to a cash payments journal. And it’s useful to see this format or how different types of accounting structures can be built.
Cash Receipts Journal 40
In this presentation we will talk about the cash receipts journal. The cash receipts journal will be used when we have cash receipts when using a more of a manual system or a data input system that we will be doing by hand as opposed to an automated system. It’s still useful to know the cash receipts journal if using an automated system for a few different reasons. One is that we might want to generate reports from an automated system, similar to what we would be creating in a manual system for a cash receipts journal. And to it’s just a good idea to have different types of systems in mind, so we can see what’s the same and what is different between different accounting systems. The cash receipts journal will be used for every time we have a cash receipts. So the thing that transaction triggering a cash receipt will be when cash is being used. And we’re going to have a little bit more complex complexity in a cash receipts journal than something like a sales journal because we may be receiving cash for multiple different things.
Purchase Journal Merchandising Co.
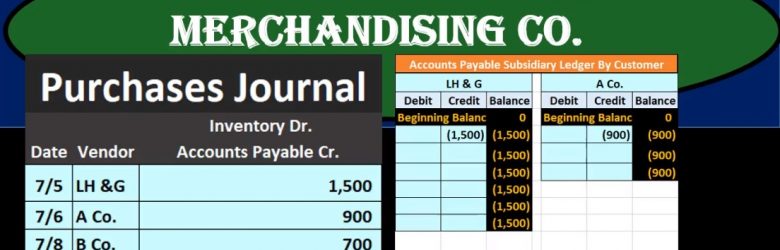
In this presentation we will take a look at the purchases journal for a merchandising company. Purchases journal will be used when we make purchases for a type of system that will typically more be more of a manual system as opposed to an automated system. However, it is useful to know this in order to have an automated system because the automated system will generate reports that will be similar to a purchase journal and because it’s good to know how different system works to know what are similar what’s different, so that we better understand whatever system we are using. The purchases journal may better be described as the purchase journal on account. So that’s going to be the major point meaning if we make purchases for something that in cash if we spent cash to make the purchase then it will not go in the purchases journal even though we made a purchase because it will go into cash payments journal. So this is really kind of a short name. The accounts payable journal might be a better name for it or the purchases journal on account, but purchases journal is typically the term that will be used.
Sales Journal Merchandising Co.
In this presentation, we will take a look at a sales journal for a merchandising company. When recording transactions related to a sales journal, we will be recording transactions for sales into the sales journal those been journal entries that are typically used when we have a system done by hand rather than an automated system. So a sales journal will be used. Typically when we’re having more of a manual system. It is good to know this for a automated system as well. Because the automated system one might want to run reports that are similar to the sales journal and to it’s good to know different types of formats for the accounting process to know what’s the same and what is different. So that that will better help us to understand any type of system we are using.
Sales Journal Service Company 10
In this presentation, we will take a look at the sales journal for a service company. We’ll use the sales journal in a manual system or a system we do by hand. When we make sales. However, it’s a little bit more complicated than that because if sales journal really means sales that we make on account, meaning we’re not receiving cash at the point in time we make the sale. If we do receive cash at the point in time we make sale even though we have sales being recorded or revenue accounts being recorded. It should be going into the cash receipts journal, because that’s the journal we use whenever we get cash. So the better term for this journal may be something like accounts receivable, or more specifically, sales made on accounts or sales and accounts receivable, but it’s typically called the sales journal. So don’t let that confuse you.
Accounts Payable AP Subsidiary Ledger 6
Hello. In this lecture we’re going to talk about the accounts payable subsidiary ledger accounts payable subsidiary ledger will be backing up the accounts payable account on the trial balance or the balance sheet. As we can see in the example here we have a balance of 1640 in accounts payable. If an owner asks the question of how much money do we owe to vendors? The answer would then be 1006 40, which we can see on the balance sheet or the trial balance. But the next question that will follow will be who do we owe that money to? And how do is it which of these vendors should we be paying? First? In order to answer that question, we may try to go to the detailed account, which is the general ledger. Typically every account is backed up by the general ledger, we can see that we have the same balance here and we can see that we have activity however, the activity is in order by date. And that’s not really helpful for us to determine who exactly we still owe at this point in time. In order to determine who we owe, we need to organize this information.
Accounts Receivable AR Subsidiary Ledger Explained 5
Hello, in this lecture we’re going to talk about the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger, the subsidiary ledger being the ledger that will be backing up the account of accounts receivable showing on the trial balance with 27,000. In it, in this case, accounts receivable being that accounts that represents what is owed to us. If we were the owner of the company, we might ask our accounting department, how much money do people owe us? In this case, it would be 27,000 would be the reply. Next follow up question would most likely be who owes us that money? And have we called them when are we going to get paid that money? In order to answer that question, we cannot look at the normal backup balance for all accounts that being the general ledger accounts. If we look at the GL we do get some detail in terms of the activity that has happened. However, that activity is not going to be in terms of who owes us the money. It’s in terms of date.
Special Journals Subsidiary Ledgers 2
In this presentation, we’re going to talk about special journals and subsidiary ledgers. First, we’re going to list out the special journals and talk about when we would use them, why we would use them and how they fit into the accounting system. The special journals are basically going to group types of transactions. So when we think about all the transactions that happened during the month, we typically see them in order of when they happen in the accounting system, we’re going to record transactions in other words, by date as they occur. But if we are able to group those transactions into special journals that can simplify the process.
Financial Statement Relationships 18
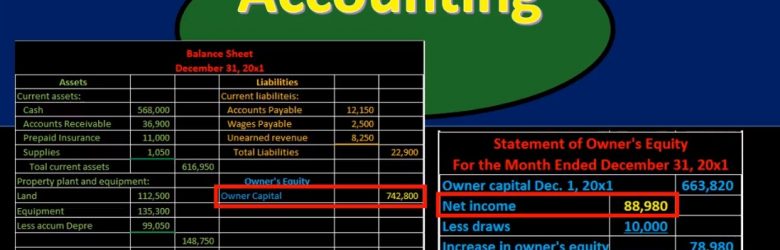
Hello in this presentation we’re going to take a look at financial statement relationships. In other words, how do these financial statements fit together? How do these financial statements represent the double entry accounting system in the format of the accounting equation that have assets equal liabilities plus equity? First, we’ll take a look at the balance sheet. Note that most textbooks will talk about this relationship and constructing the financial statements by first saying to construct the income statement, then the statement of equity and then the balance sheet. If you’re constructing things by hand with a paper and pencil, that does reduce the number of calculations that you would need to do, however, if you’re using something like Excel, then it’s a lot easier to sum up columns of numbers and it might be useful to take a look at the balance sheet. In any case, the relationships will be the same when we consider the relationships between the financial statements.
Statement of Equity From Trial Balance 17
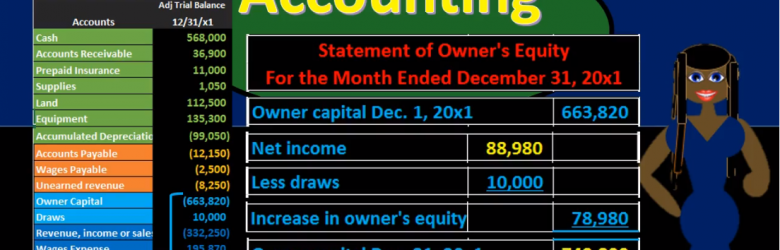
More in this presentation we will take a look at the statement of owner’s equity and see how to construct the statement of owner’s equity from the trial balance. When looking at the trial balance, we can see the accounts will be in order with the assets and then the liabilities, then the equity and then the revenue and expenses. The equity accounts being broken out here of owner capital and draws. But it’s a little deceiving to break out this equity section. Because the trial balance really is showing both a point in time the balance sheet account permanent accounts up top and timing accounts which are going to be the revenue accounts down below. When we think about the point in time for total equity as a whole. We’re really considering the entire blue area here. This is one of the most confusing concepts to really know when you’re looking at these financial statements.