Corporate finance a PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will discuss finance topics and activities going over some of the historical emphasis in the field of finance to get some context of where we’re coming from and where the current emphasis is. And we’ll be in corporate finance, get ready, it’s time to take your chance with corporate finance, finance topics and activities, we’re going to go over some of the emphasis in corporate finance in the past up into the present day to get some focus in on in context of what we will be talking about within corporate finance. So in the 1930s, what’s the emphasis in corporate finance in the 1930s, we have capital preservation.
Posts with the capital tag
Consolidation Parent Sale of Subsidiary Shares
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss a situation where we have a consolidation process and in the period of consolidation the parent sells subsidiary shares to a non affiliated entity. In other words, we have a consolidation process we have a parent subsidiary relationship parent owning a controlling interest over 51% of subsidiary. The parent then in that period sells some of the shares that they own in the subsidiary to a party that’s not affiliated in the consolidation, what will be the effect in the consolidation process of that get ready to account with advanced financial accounting?
Consolidation & Subsidiary Stock Dividends
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss the consolidation process and a situation where the subsidiary issues stock dividends we have stock default dividends issued by the subsidiary what will be the effect on the consolidation process get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. We’re talking about a consolidation process where the subsidiary then issued stock dividends. So we have stock dividends are issued to all common stockholders proportionally, therefore, the relative interest of the controlling and non controlling stockholders is not changed. So that relative interest isn’t changed, so we don’t have to worry about that which is nice. The carrying amount on the parents books is also not changed. So we’re not going to have to change anything on the books of the parent with basically an adjustment to the investment account using you know, typically the equity method, which is nice stockholders equity accounts for the subsidiary do change. So we do have a change to the stock There’s equity on the subsidiary, but total stockholders equity does not. So in other words, if we take stockholders equity as a whole, there’s no change there, even though there’s changes within the stockholders equity of the subsidiary. So we’re here we’re going to say this stock dividends represent a permanent capitalization of retained earnings. That’s basically what is happening, permanent capitalization of the retained earnings.
Subsidiary Purchases Shares from Parent
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss a consolidation process where we have a subsidiary that purchases shares from the parent. So what’s going to be the effect on the consolidation process? When we have a subsidiary that purchases shares from a parent get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. We are talking about a situation here where this subsidiary is purchasing shares from the parent what’s the effect on the consolidation process? In the past, the parent has often recognized a gain or loss on the difference between the selling price and the change in the carrying amount of its investment. So in the past, it’s often been recorded as a gain or loss on parent companies that difference as a gain or loss on the parent company’s income statement.
SEC Structure & Regulatory Authority
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss sec structure and Regulatory Authority get ready to account with advanced financial accounting in sec structure and regulatory authority, Securities and Exchange Commission the SEC What is it? It’s an independent federal agency It was created in 1934. It’s going to regulate and it does regulate the securities markets, the SEC helps maintain an effective marketplace for companies issuing securities and for investors seeking capital investments. Now we’ll take a look at a brief history of leading up to the creation of the SEC and a little bit about the SEC itself. So if we have an understanding of the history, then it gives us a little bit better of an understanding of why the SEC does what it does today and how it how it was created or came to be. So in 1792, was when the New York Stock Exchange was created to function as a clearing house. For the securities trades between its invit its investors. So now we have the New York Stock Exchange that will function as the clearing house. But then in 1911, states started to pass, quote, blue sky laws in quotes to help regulate the offerings of securities by companies without a solid financial base. So in other words, they saw a need for regulation, now that you have the securities that are on the New York Stock Exchange and can then be offered basically, to more to the public, more people will have access to purchasing them and putting capital into the market, then there’s a lack of transparency, the people that are putting money in maybe doing it solely on speculation, and we don’t have the information to really support the claims possibly that could be made by the stocks that are that are being traded and therefore, you could have situations and did have situations where you had stocks that had no supporting you know, value or very little supporting value to them.
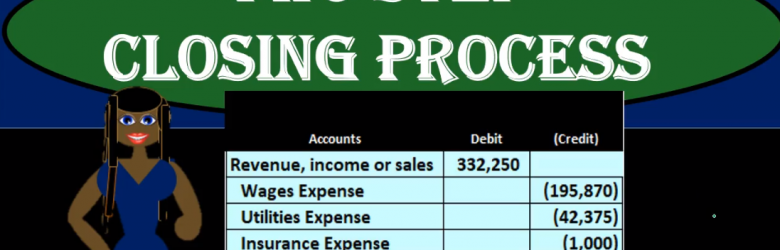
Closing Process Step 4 of 4 Closing Journal Entry Draws or Withdraws
Hello in this lecture we’re going to continue on with the closing process with step four, the final step of the process which will be to close out the draws. Remember that the objective is to have the adjusted trial balance be converted to the post closing trial balance. adjusted trial balance is what we use to create the financial statements. And the difference between the adjusted trial balance and the post closing trial balance will be that we want to have all temporary accounts including draws revenue and expense accounts to be converted to zero and have all that be in the owner capital account meaning the owner capital account will now be including all these accounts underneath it crunched into basically one number, we’re going to do that with a four step process.
Closing Entries Journal Entry 3 of 4 Step 3 Income summary
Hello in this lecture, we’re going to talk about the closing process step three of the four step closing process, which will include the close of the income summary to the capital account. Remember that our objective is to close out all the temporary accounts, which are all the accounts below capital, including drawers, and the income statement accounts of revenue and expenses. So we want the adjusted trial balance to be converted to the post, post closing trial balance, which means that everything from capital on down will be zero. The way we do that is the four steps and that includes step one we did in a prior video closeout income to the income summary. Step two was to close out expenses to the income summary. Step three is what we’re going to do now close out the income summary now having net income in it to the capital account, then we’re finally going to close out the draws to the capital account.
Closing Step 2 of 4 – Journal Entry 2 of 4
Hello in this lecture, we’re going to talk about the closing process. Step two of the four step process being closing the expense accounts to the income summary. Remember that the goal of the closing process is to close out the temporary accounts that would include the drawers as well as all the income statement accounts, including revenue and expenses to the capital account. So we want our adjusted trial balance to thing we used to make our financial statements to look like the post closing trial balance with all the zeros from the capital accounts down. How do we do that? Last time we did the first step step one, which was to close out income to the income summary. This time we’re going to close out expenses to the income summary. Next time we’re going to close out the income summary to the capital account. And finally closeout draws to the capital account.
Closing Process Step 1 of 4 – Journal Entry 1 of 4
Hello, in this lecture, we’re going to talk about the closing process step one of the step four process. Last time, we talked about the objectives of the closing process, which in essence was to close out the temporary accounts, all the accounts from the draws, and the revenue and expenses on down to zero. Putting that balance into the capital account, we talked about how we were going to do that, we’re going to do a four step process, including closeout, the income to the income summary, and then close out the expenses to the income summary. And then we’re going to close out the entire income summary to the capital account. And finally closeout draws to the capital account. We’re going to start off with step one of those four step processes. In order to do this. We are adding this new account you’ve probably been wondering, income summary account, what is that? Where did it come from? Why is it there? The income summary can be called a clearing account, meaning it’s going to start at zero and it’s going to end at zero right when we’re done with this four step process which we’re going to do basically at the same point. Time.
Two Step Closing Process
Hello in this presentation we will take a look at a two step closing process. In other words, we will perform the closing process using two journal entries. There’s a couple different ways we can see the closing process, each of them having a pros and cons. The two step process is nice because it allows us to see net income broken out and being closed out directly to the capital account, followed by draws, which is similar to what we see when we actually do the statement of equity, meaning that when we do the statement of owner’s equity, we start with beginning balance and then we increase it by net income and decrease it by drawers or dividends. Because this process is similar to that process, it’s often easy to remember it’s the easiest for me to remember in any case, so we will take a look at the two step closing process.