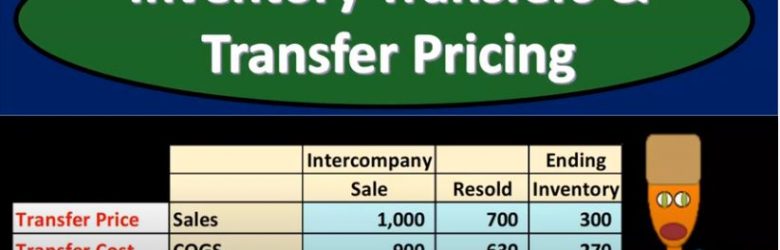
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we will discuss inventory transfers and transfer pricing. Our objective will be to get an idea of what inventory transfers are what will be the effect of inventory transfers and how to account for inventory transfers when considering a consolidation process, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, inventory transfers and transfer pricing. So in essence, we’re talking about the inventory going from one organization to another, we can think about this in terms of parent subsidiary type of relationships.
Posts with the happening tag
Internal Expansion Accounting
In this presentation, we will expand on the logistics of internal expansion, get ready to act, because it’s time to account with advanced financial accounting. We’re going to take a look now at the steps of the internal expansion. So note we have the two categories of expansion, the internal expansion and the external expansion, internal expansion with a company growing, we’re imagining the company growing, they can either grow internally make it another sub subsidiary, possibly, that would be owned by the parent company creating a parent subsidiary relationship internally, or has some kind of external expansion where we have two separate entities that are going to be together in some way, shape or form. So here, we’re talking about the internal expansion. So we have one company that is then thinking about expanding how are they going to put that expansion together? We’re thinking about the setting up then in this case of another legal entity such as a subsidiary, what steps for that? Well, first, you’re going to have a sub sub subsidiary B. created. So you get the parent company is going to be creating the subsidiary, then we have assets and liabilities are transferred to the new entity. So we’re imagining we have one company that wants to expand possibly have another division or another location that they will be expanding into. They make this subsidiary so they another legal entity created, we typically will think of another corporation that is owned by the prior Corporation, parent subsidiary relationship, the assets and liabilities that are going to be controlled or be part of that new segment are going to be transferred from the parent company now to the subsidiary company. And the key point here is that it’s going to be transferred at book value. And you might be thinking after looking at the external expansion, where you have two separate entities that are coming together and the need for us to then use the basically the acquisition method treat it basically like a sale happening.
Business Combinations Methods
In this presentation, we will take a look at business combination accounting methods, both historic methods and the current methods get ready to act, because it’s time to account with advanced financial accounting. We’re going to start off with business combinations from the past, these are not the current method that we’re going to be using. However, it’s good to have some historical context so that if you hear these methods, you know what you’re talking about. We also want to think about these concepts in terms of just a logistical standpoint. If you were to make these laws, then how would you do it? What are some of the challenges that have happened? And by looking through the historical process, you can kind of think about, okay, these are what were put in place, I see why those were put in place here that changes that are happening, we could see why the changes are happening, therefore have a better understanding of what we are doing, and how the current process is being put in place and why the decisions were made to put it in place. So in the past, we had combinations methods that included the purchase method and the pooling of interest. method. So they then what happened is the pooling of interest method was taken away by faz B. So faz B said, Hey, we’re not going to allow anymore, the pooling of interest method, and then the purchase method has been replaced with the acquisition method. So if you hear the purchase method, that in essence is what we’re currently doing. However, we changed the name from the purchase method to the acquisition method.
Post Closing Trial Balance & financial statements
Hello in this presentation we will discuss the post closing trial balance and financial statements. When considering the financial statement relationship to the trial balance, we typically think of the adjusted trial balance that being used to create the financial statement. It’s important to note, however, that any trial balance that we use can be generated into financial statements. It’s just that the adjusted trial balance is the one that we have totally completed and prepared and ready. In order to create the financial statements to be as correct as possible as of the date we want them, which is usually the end of the month or the end of the year. Note that the names of the unadjusted trial balance the adjusted trial balance and the post closing trial balance are really a convention they’re all basically trial balances.
Statement of Cash Flow Indirect Method Change In Accounts Receivable
In this presentation, we will continue putting together the statement of cash flows using the indirect method focusing here on the change in accounts receivable. The information will be a comparative balance sheet, the income statement and some added information we will be focusing in on a worksheet that was composed from the comparative balance sheet. So here is our worksheet. So our worksheet that we can pay that we made from the comparative balance sheet, current period, prior period change. So we have all of our balances here for the current period, the prior period and the change, we have put in this change. And this is really the column that we are focusing in on we’re trying to get to this change in cash by finding a home for all other changes. Once we find a home for all other changes. We will get to this change in cash the bottom line here 61,900. The major thing we’re looking for is right here. We’ve already taken a look at the change in the retained earnings. And the change in the accumulated depreciation. Now we’re going to look at the changes in current assets and current liabilities.
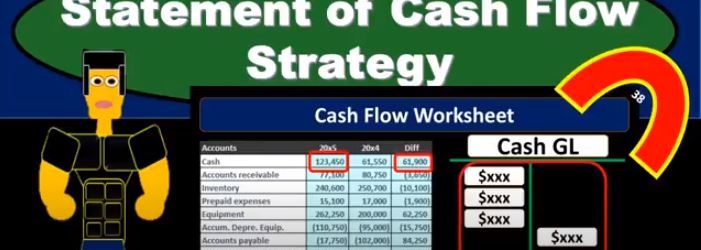
Statement of Cash Flow Strategy
In this presentation, we will take a look at strategies for thinking about the statement of cash flows and how we will approach the statement of cash flows. When considering the statement of cash flows, we typically look at a worksheet or put together a worksheet such as this for my comparative balance sheet, that given the balance sheet accounts for the current year and the prior year or the current period, and the prior period, and then giving us the difference between those accounts. So we have the cash, we’ve got the accounts receivable inventory, we’re representing this in debits and credits. So this is in essence going to be a post closing trial balance one with just the balance sheet accounts, the debits represented with positive and the credits represented with negative numbers in this worksheet, so the debits minus the credits equals zero for the current year, the prior year. And then if we take the difference between all the accounts, and we were to add them up, then that’s going to equal zero as well. This will be the worksheet that we’re thinking about. Now. When can In the statement of cash flows, we can think about the statement of cash flows in a few different ways. We know that this, of course, is the change in cash, this is the time period in the current time period, the prior year, in this case, the prior period, the difference between those two is the difference in cash.
Bonds Present Value Formulas
In this presentation, we will take a look at present value formulas related to bonds. One of the reasons bonds is so important to accounting and finance is because they’re a good example of the term of present value of money. We’re trying to look for an equal measure of money, when we think of bonds and bonds is going to have this relationship between market rates and the stated rate, which helps us to kind of look through and figure out these types of concepts. So even if we don’t work with bonds, in other words, if we’re not planning on issuing bonds, or buying bonds, or knowing anything about bonds not being important to us, the time value of money is a very important concept and bonds is going to be a major tool to help us with that. Why is bonds so useful for learning time value of money, because there’s two types of cash flows with bonds meaning at the end of the time period, we typically are going to get the face amount of the bond that 100,000 similar to a note and then we’ve got the interest payments that are going to happen on a periodic To basis, and therefore we have these two different types of cash flows, that we can use two different formulas for, to think about how to equalize.
Accounts Receivable Journal Entries
Hello in this presentation we will be recording that journal entries for business transactions related to accounts receivable otherwise known as the revenue cycle. We will be recording these using debits and credits. At the end of this we will be able to list transactions involving accounts receivable record transactions involving accounts receivable using debits and credits and explain the effect of transactions on assets liabilities, equity, revenue, expenses and net income. We’re going to be recording these transactions up here on the left hand side constructing those journal entries in accordance with our thought process our list of questions to most efficiently construct the journal entries. We will then be posting them not to the general ledger but to this worksheet here so that we can see the quick calculation of the beginning balance and what is happening to the individual accounts as well. account types, in that we have the accounts categorized, as is the case for all trial balances. accounts have been in order that order been assets in this case in green, the liabilities in orange of the equity, light blue and the income statement accounts of Revenue and Expense Type accounts. first transaction perform work on account for $10,000.