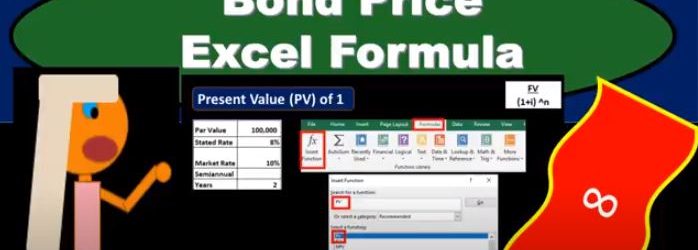
In this presentation, we will calculate the bond price explaining how this can be done using present value formulas within Excel. Remember that the bonds is going to be a great tool for both accounting and finance to describe the present value calculation. So that’s why it’s going to be used. Oftentimes It has two cash flows related to it, one’s going to be the face amount of the bond that’s going to be due at the end of the term of the bond. In our case, it’s going to be two years semiannual or four time periods. And the other is the flow of interest. So bonds are a great example because they have the two types of present value problems that we need in one area. So even if you’re not in an area where you’re dealing with bonds all the time, they’re still going to be used and useful to understand present value types of calculations. So here we’ve got the bond is going to have one cash flow of 100,000 at the end of four periods or two years, and we need to figure out what the present value is in order to price it back here at your at time period zero. And then we have these four payments in terms of the annuity 4000. And we need to take those and present value them, we could take each period and present value each payment and present value it. But the easier thing to do is to present value, an annuity when it’s applicable and present value, the one amount when it’s applicable. And therefore think of that about these as two basically separate cash flows that we’re going to have to present value separately. So we can do this multiple different ways. And it just depends on what you’re what tools you have. And where you are, in order to know how to do it. What you want to know is just that there’s different tools to do it. Anytime someone uses a different tool. What are they doing the same thing? And and when can you apply these tools and what’s actually happening here. So that’s what’s actually happening. We’re present valuing this information.
Posts with the period tag
Bonds Present Value Formulas
In this presentation, we will take a look at present value formulas related to bonds. One of the reasons bonds is so important to accounting and finance is because they’re a good example of the term of present value of money. We’re trying to look for an equal measure of money, when we think of bonds and bonds is going to have this relationship between market rates and the stated rate, which helps us to kind of look through and figure out these types of concepts. So even if we don’t work with bonds, in other words, if we’re not planning on issuing bonds, or buying bonds, or knowing anything about bonds not being important to us, the time value of money is a very important concept and bonds is going to be a major tool to help us with that. Why is bonds so useful for learning time value of money, because there’s two types of cash flows with bonds meaning at the end of the time period, we typically are going to get the face amount of the bond that 100,000 similar to a note and then we’ve got the interest payments that are going to happen on a periodic To basis, and therefore we have these two different types of cash flows, that we can use two different formulas for, to think about how to equalize.
Allowance Method % Accounts Receivable vs % Sales Method
In this presentation, we will be taking a look at the allowance method for accounts receivable focusing in on the calculation of the allowance for doubtful accounts. There are two methods that can be used in order to calculate the allowance for doubtful accounts accounts. One being the percentage of accounts receivable, the other is the percentage of sales, we will take a look at them both and look at the pros and cons of them. First, we’re going to look at the accounts receivable method. We’re going to start off with the percentage of accounts receivable method for a few different reasons. One, it’s the one that’s most often tested. And two is the one that may be most often used in practice often making the most sense to people that are looking at the two methods. It’s also a bit more complicated. So when we’re looking at test questions, they typically would focus on this method in order to have a bit more complicated process to do the calculation.
Allowance Method VS Direct Write Off Method
In this presentation, we will take a look at a comparison between the allowance method and the direct write off method. When considering both the allowance method and the direct write off method, we are considering the accounts receivable account. Remember that the accounts receivable account represents some money that is owed to the company, typically from sales made in the past, on account haven’t yet received the funds for sales made in the past and therefore, the company is owed money. We see this amount on the trial balance in this case 1,000,001 91. We then want to know information about that, including who owes us that money. We can’t find that typically in the GL as we have a GL for every account the GL only giving us the information by date. Typically, we want to see that information also broken out in the subsidiary ledger saying who owes us this money.
First In First Out (FIFO) Periodic System
In this presentation we will discuss first in first out or FIFO using a periodic system as compared to a perpetual system. As we go through this, we want to keep that in mind all the time that been that we are using first in first out as opposed to some other systems lastin first out, for example, or average cost, and we’re doing so using a periodic system rather than a perpetual system. Best way to demonstrate is with examples. So we’ll go through an example problem. We’re going to be using this worksheet for our example problem. It looks like an extended worksheet or large worksheet, but it really is the best worksheet to go through in order to figure out all the components of problems that deal with these cost flow assumptions, including a first in first out lastin first out, or an average method, and using a periodic or perpetual for any of them.
Consistency Concept
In this presentation we will discuss the consistency principle as it relates to inventory and inventory assumptions. First, we’re going to define the consistency principle and then apply it to an assumption such as the flow assumption such as do we use something like a first out last In First Out average inventory system, the definition of consistency principle according to fundamental accounting principles, while 22nd edition is a principle that prescribes use of the same accounting method methods over time so that financial statements are comparable across periods. So, here we’re considering the assumptions that we’re making with the flow of inventory those being either first in first out last in first out or the average method typically for the cost flow assumptions, because those are assumptions.