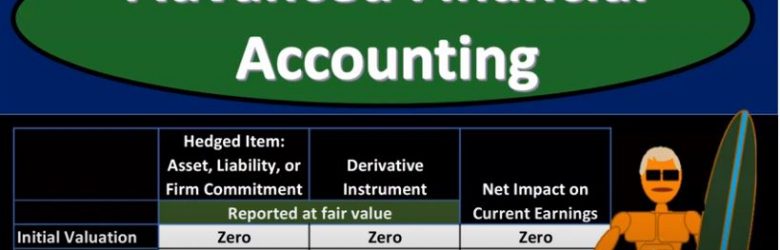
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss forward exchange of financial instruments get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, forward exchange financial instruments let’s start off with some definitions starting off with financial instrument itself will be either cash evidence of ownership or a contract that imposes on one entity on contractual obligation to deliver cash or another instrument and conveys to the second entity, the contractual right to receive cash or another financial instrument. That of course, being the most complex component here. So let’s read that one more time. The financial instrument a contract that imposes on one entity a contractual obligation to deliver either cash or another instrument and conveys to the second party the second party in this item, the second entity, the contractual right to of course, receive the cash or another financial instrument derivative. So a derivative, financial instrument or other contract whose value is derived from some other item that has a value that varies over time. So let’s think about that one more time again, derivative financial instruments or other contracts whose value is derived from, they’re going to get the value from some other item that has a value. That is that varies over time, meaning of course, that it will be changing over time. So let’s think about the derivative characteristics. And then we’ll apply these to the component of what we’re considering here. foreign currency and foreign currency transactions in terms of typically foreign currency type hedge transactions.
Posts in the Accounting Instruction category:
Requirements for Management Reporting Laws
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss requirements for management reporting laws. We’ll discuss major laws and the reporting requirements related to them get ready to account with advanced financial accounting requirements for management reporting laws, we’re going to be starting off with the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977. The fcpa Congress passed it as a major amendment to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, which we’ve discussed in prior presentations. It has two primary sections first section Part One prohibits bribing foreign governmental or political officials for the purpose of securing a contract or otherwise increasing the company’s business and part two requires publicly held companies to maintain accurate records. It also requires an adequate system of internal control. So internal controls again, taking more of a central point focus a lot of times with the regulations related to large companies, we have then the Sarbanes Oxley act of 2002, also known as s o x Sox signed to law July 30 2002. So July 30 2002, Sarbanes Oxley gained traction after the accounting and financial mismanagement of Enron, WorldCom and other large companies. So there’s there’s big large scandals that were happening. And it was feared that and I think rightly so to a large extent that there was going to be faith lost in the financial reporting system. And once again, that’s the foundation really, that’s a huge component to why people invest in US companies because they have some more measure of trust than many other areas where they can put their money in. So if the financial statements are going to lose, lose that trust, that’s going to be a very big problems. So Sarbanes Oxley was a reaction to some of these large scandals which were reflecting missed. statements in the financial statements that looked like deceptive misstatements in the financial statements in an attempt to regain security to people who are investing and users of the financial statements to have faith in the contents of them, they’ll help the law has many implications for accountants. So there’s going to be a lot of changes. accounting firms have many implications related to it. We’ll go through it in some detail here. Not a whole lot of detail, but some detail we’ll go through some of the major parts of it. It was intended to minimize corporate governance, accounting and financial reporting abuses, resulting in restoration of investor confidence in the financial reporting of publicly traded companies.
Enterprisewide Disclosures
Advanced financial accounting a PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss enterprise wide disclosure, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. enterprise wide disclosures established by ASC 280 standards provide users more information about the company’s risks generally made in a footnote to the financial statements. First category of required information to include under ASC 280 is information about products and services so information about products and services disclosure related to them. Companies are generally required to report revenues from external customers for each major product and service or each group of similar products and services. Unless doing so is not practical. primary reason for this is that the company could have organized its operating segments on a different basis from the organization of the entities product lines. So we’ve got then again, companies are generally required to report revenues and external customers for each major product and service. You might be saying, hey, well, they already have the segment’s reporting. But it’s possible that those two things don’t exactly line up in the way they put the segment reporting together and therefore, you know, you have this requirement. second category of required information to include under ASC 280 is going to be related to geographic areas information. The following needs to be reported unless it would be impractical to do so. revenues from external customers attributed to the company’s home country of domiciled revenue from external customers attributed to all foreign countries in which the enterprise generates revenues.
Threshold Tests for Segment Reporting
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss threshold tests for segments reporting, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting threshold tests for segment reporting separate supplemental disclosures that need to be made for separately reportable operating segments. So we’ve got these separately reportable operating segments, we have to then determine what type of reporting needs to be taking place for them. determining if a segment needs separately reported information. There are 310 percent quantitative rules FA SB specifies separate disclosure is needed for any segment that meets at least one of the three tests that follow. So we have the segment we got to think about Okay, do we need separate disclosure for this segment, and in order to determine that we’re going to use these 310 percent tests, they only need to meet one of these tests in order for the separate disclosure to be necessary that being 10% revenue test 10% profit or loss test and 10% assets tests. We’re going to go into more detail on each of these tests. Now some we’re going next slides we’ll be focusing in on these three items. So we’re going to start of course with the 10% revenue test. If an operating segments revenue, including both external sales and intersegment sales or transfers is 10% or more of total revenues from external sales plus intersegment. transactions of all operating segments, then segment is separately reported and supplemental disclosures must be provided for it in the annual report so that we have the 10% of revenue basically top line of course on the income statement to determine if the segment is separately reportable. Then we have the 10% of profit and loss. So now the next test now looking at the bottom line, of the income statement, as opposed to The top line if the absolute value of the segments profit or loss or absolute value, so, if we have a income or loss is 10% or more of the higher in absolute value of a the total profit of all operating segments that did not report a loss or be total loss of all operating segments that did report a loss, then the segment is separately reportable and supplementary disclosures must be provided for it in the annual report. So, you can think about these tests you got the 10% of the top line of the income statement, the revenue, basically 10% of the bottom line, profit or loss on the income statement. Now, we’re looking at the balance sheet 10% of assets tests. If these segments assets are 10% or more of the total assets of all operating segments, then the segment is separately reportable and supplementary disclosures must be provided for it in the annual report.
Other Foreign Operations Issues
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss other foreign operations issues, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, other foreign operations issues. So we’re going to start off with an issue related to the parent company having a foreign subsidiary. Typically when that is the case, they’re going to have to consolidate. In other words, you’re going to have to get the foreign subsidiary books in some way to the US dollar and then do the consolidation process. However, you might have a situation where that wouldn’t take place under certain conditions. So, parent generally consolidates a foreign subsidiary except when certain conditions are so severe that the US company owning the foreign company may not be able to exercise the necessary level of economic control. So notice when we think about the consolidation process, we’ll typically think about, we need to consolidate the entities if there’s control right over the 51% is that going to be a general rule but the overarching concept is that there is control. Now if there are certain conditions even though it’s the ownership is over the 51%, we would think there would be control, but there are certain conditions in the foreign subsidiary that are restricting that economic control, then then they might not meet you know that condition and therefore in that situation you might not have the consolidation process. So in that situation then you might have a parent company that has basically a controlling interest you would think in terms of the stock, the stock but you’re not having a consolidation due to the due to one of these factors limiting the actual economic control. So, those include restrictions on foreign exchange in foreign country. So severe strict restrictions, there could be one of the items that would stop the basically consolidation process possibly restrictions on transfers of property in foreign country.
Disclosure Requirements
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss disclosure requirements get ready to account with advanced financial accounting disclosure requirements. We have the management discussion and analysis that’s often referred to as the M D and A discusses a company’s financial condition and results from operations. The MD and a are part of the basic information package required in major filing with the SEC, the Securities and Exchange Commission. Items currently required in the MD and a the management discussion and analysis include liquidity, capital resources, results of operations, off balance sheet arrangements, tabular disclosure of contractual obligations, disclosure requirements, pro forma disclosures, pro forma disclosures, financial presentations generally taking the form of summarized financial statements. demonstrate the effect of major transactions that happen after the end of the fiscal period or that happened during the year, but are not fully reflected in the company’s historical cost financial statements.
Requirements for Management Reporting Laws
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss requirements for management reporting laws. We’ll discuss major laws and the reporting requirements related to them get ready to account with advanced financial accounting requirements for management reporting laws, we’re going to be starting off with the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977. The fcpa Congress passed it as a major amendment to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, which we’ve discussed in prior presentations. It has two primary sections first section Part One prohibits bribing foreign governmental or political officials for the purpose of securing a contract or otherwise increasing the company’s business and part two requires publicly held companies to maintain accurate records. It also requires an adequate system of internal control. So internal controls again, taking more of a central point focus a lot of times with the regulations related to large companies, we have then the Sarbanes Oxley act of 2002, also known as s o x Sox signed to law July 30 2002. So July 30 2002, Sarbanes Oxley gained traction after the accounting and financial mismanagement of Enron, WorldCom and other large companies. So there’s there’s big large scandals that were happening. And it was feared that and I think rightly so to a large extent that there was going to be faith lost in the financial reporting system. And once again, that’s the foundation really, that’s a huge component to why people invest in US companies because they have some more measure of trust than many other areas where they can put their money in. So if the financial statements are going to lose, lose that trust, that’s going to be a very big problems. So Sarbanes Oxley was a reaction to some of these large scandals which were reflecting missed. statements in the financial statements that looked like deceptive misstatements in the financial statements in an attempt to regain security to people who are investing and users of the financial statements to have faith in the contents of them, they’ll help the law has many implications for accountants. So there’s going to be a lot of changes. accounting firms have many implications related to it. We’ll go through it in some detail here. Not a whole lot of detail, but some detail we’ll go through some of the major parts of it. It was intended to minimize corporate governance, accounting and financial reporting abuses, resulting in restoration of investor confidence in the financial reporting of publicly traded companies.
Periodic Reporting Requirements
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss periodic reporting requirements for publicly traded companies get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, periodic reporting requirements, companies that have more than 10 million in assets and whose securities are held by over 500. Persons must file annual and other periodic reports to provide updates on their economic activities. So remember the general rule here we’re talking about publicly traded companies that have a benefit of being able to be publicly traded to the public on the exchanges. And in exchange for that we want to see some more basically transparency, and therefore you’ve got the filing process that needed to take place. We see some regulation by the SEC that we talked about in prior presentations. And then going forward, we want to keep and maintain the transparency the information so that there’s both the investors and the companies have the information necessary in order to enter into a agreements. And therefore we’re going to need some continuing reporting, what are the what’s going to be the requirements in terms of the continuing reporting. So once again, companies that have more than 10 million in assets and whose securities are held by over 500 persons must file annual and other periodic reports to provide updates on their economic activities. And that’s going to increase that transparency so that investors know what is happening and they can invest with full information to do so. three basic periodic reporting forms used for this updating our form 10 k form 10 Q and form eight K. Let’s start with the form 10 k form 10 k is the annual filing to the SEC the Security and Exchange Commission.
Registering Securities with SEC Process
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss the process of registering securities with the SEC, the Securities and Exchange Commission get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, issuing securities. If a company wants to sell debt or stock securities in interstate offerings to the general public, they are usually required by the Securities Act of 1933 to register those securities with the SEC. So one more time, we’re talking about the issuing of securities if a company wants to sell debt or stocks securities in interstate offerings to the general public, so now we got the interstate offerings going to the general public, in order to have that benefit. They are usually required by the Securities Act of 1933 to register those securities with the SEC. And you can see we saw a little bit of history in the prior presentation on how this could develop. Obviously, it’s going to be a benefit to the businesses in order to To generate capital typically to be able to offer the stock to the general public in interstate offerings. But in order to do so then you would think you’d want to have some transparency that will be involved in it so that both sides of the negotiation will be involved. That’s where the SEC came into play here. So we talked a bit about the SEC and its role in a prior presentation we’ll get more into the process of the registration here. General financial statement required for this process will typically include two years of balance sheets three years of statements of income, three years of statements of cash flows, three year of statement of stockholders equity, prior years statements are generally presented on a comparative basis with the current years it will typically have a comparative basis. For the for the comparative years prior and current year.
SEC Structure & Regulatory Authority
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss sec structure and Regulatory Authority get ready to account with advanced financial accounting in sec structure and regulatory authority, Securities and Exchange Commission the SEC What is it? It’s an independent federal agency It was created in 1934. It’s going to regulate and it does regulate the securities markets, the SEC helps maintain an effective marketplace for companies issuing securities and for investors seeking capital investments. Now we’ll take a look at a brief history of leading up to the creation of the SEC and a little bit about the SEC itself. So if we have an understanding of the history, then it gives us a little bit better of an understanding of why the SEC does what it does today and how it how it was created or came to be. So in 1792, was when the New York Stock Exchange was created to function as a clearing house. For the securities trades between its invit its investors. So now we have the New York Stock Exchange that will function as the clearing house. But then in 1911, states started to pass, quote, blue sky laws in quotes to help regulate the offerings of securities by companies without a solid financial base. So in other words, they saw a need for regulation, now that you have the securities that are on the New York Stock Exchange and can then be offered basically, to more to the public, more people will have access to purchasing them and putting capital into the market, then there’s a lack of transparency, the people that are putting money in maybe doing it solely on speculation, and we don’t have the information to really support the claims possibly that could be made by the stocks that are that are being traded and therefore, you could have situations and did have situations where you had stocks that had no supporting you know, value or very little supporting value to them.