Hello in this presentation we’re going to take a look at financial statement relationships. In other words, how do these financial statements fit together? How do these financial statements represent the double entry accounting system in the format of the accounting equation that have assets equal liabilities plus equity? First, we’ll take a look at the balance sheet. Note that most textbooks will talk about this relationship and constructing the financial statements by first saying to construct the income statement, then the statement of equity and then the balance sheet. If you’re constructing things by hand with a paper and pencil, that does reduce the number of calculations that you would need to do, however, if you’re using something like Excel, then it’s a lot easier to sum up columns of numbers and it might be useful to take a look at the balance sheet. In any case, the relationships will be the same when we consider the relationships between the financial statements.
00:53
We can consider them in the similar fashion. It’s nice to consider the relationships by first starting at the bank. sheet because the balance sheet is really the big picture. It’s really the double entry accounting system being expressed in the format of the accounting equation. So if we start there, we can see that we have assets, we have liabilities and we have the equity. That is the accounting equation, meaning total assets equal liabilities plus equity, that is going to be the accounting equation. That’s our starting point. That’s the double entry accounting system being expressed. Once we consider that then we have to consider how do the other statements fit into this accounting equation. And this is something that takes some time to figure out and understand fully, because the other statements if you take a look at the income statement, it has revenue and expenses. It doesn’t have assets, liabilities and equity in it, necessarily or directly.
01:46
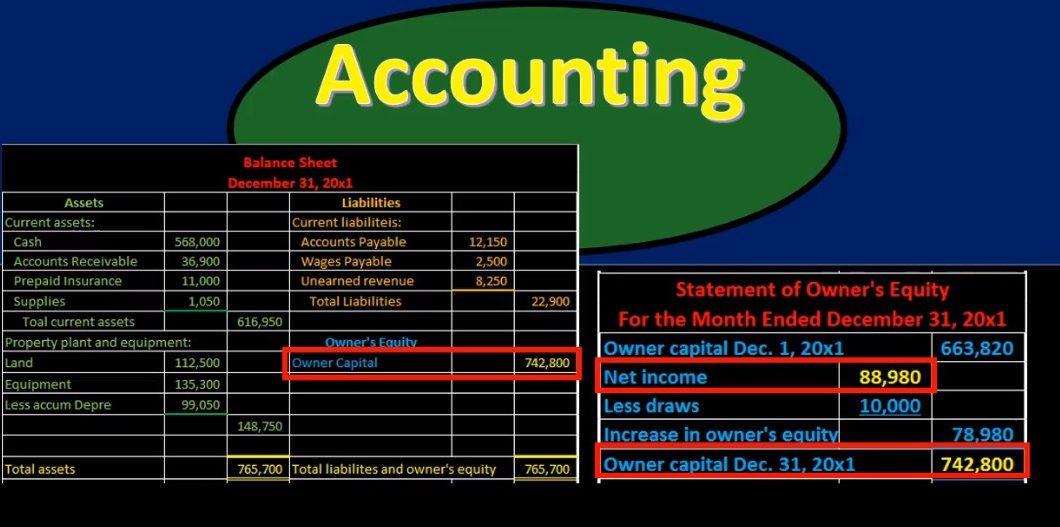
So then the question is, how do these fit into the double entry accounting system? How do they fit into the financial statements representing the double entry accounting system primarily through the balance sheet showing the balancing of the accounting equation assets equal liabilities plus equity, we’re going to start here with the equity section in order to see that relationship. And note that we can express the accounting equation in another format, we could say that assets minus liabilities, equal equity. So that’s another format we can use in order to show the financial to the accounting equation. And that gives us this equity as basically the book value the value of the company, if we were to sell the company, then we would, we would, on a book value basis, not get this amount of money in terms of revenue, meaning, if we sold the assets for the exact value that was here, paid off all the liabilities, then we wouldn’t be able to walk away with this amount of money.
02:39
Now, of course, that’s only on a book basis. And we don’t know that we would be able to sell all our assets for exactly this amount of money. But from a theoretical basis, this is in essence, the value of the company. What we’re going to do in the next statements is really break this out into timing. Notice that this account shows us a point in time. It shows us where we start And it doesn’t show us performance, it doesn’t show us how we have done. So what we’ll do is we’ll measure performance getting to this end number here. But by showing how we’ve done in the last time period, the last year, the last month using, of course, the income statement and statement of equity, the the final number and the owner’s equity will be represented in the statement of owner’s equity, the statement of owner’s equity is going to show the beginning balance in the equity section.
03:28
And then it’s going to increase it by net income, decrease it by draws, and that’ll give us the net change to give us that ending balance. So this number is influenced in part by the statement of owner’s equity, which will reflect this same number. Now, the statement of owner’s equity really is only giving us a little bit more detail than the main statement that’s going to show us the timing difference here, that being the income statement. Note that we have the net income shown here, and that’s that’s going to be grouped together. It’s just one grouping of numbers that will be represented in more detail on the income statement. So the statement of owner’s equity is where we’ll get to this final number. But most of the detail in the statement of owner’s equity is within this net income, which we will further break out into the timing statement of the income statement. So here’s our income statement. It’s part of the statement of owner’s equity is part of this net income, the big portion, the main piece to the statement of owner’s equity, the statement of owner’s equity showing us where we stood at the beginning of the time period.
04:29
And then the activity that happened including net income draws and investments if there are any, and that gives us the ending balance on the balance sheet. So the net income then on the income statement is going to be what is included on the statement of owner’s equity. So when we think about this, how is the income statement related to the double entry accounting system, including the accounting equation of assets, liabilities and equity, when the income statement doesn’t have any assets, liability and equity only has revenue and expenses and the answer that is d Timing accounts, these are timing accounts meaning they’re really part of the equity section, they’re gonna close out to the equity section. These are giving detail in a timing format of the permanent accounts of equity, in this case, the capital account. So if we take a look at our financial statements, we got the balance sheet, the income statement, statement of equity, we want to check these numbers every time we’re going to say well do total assets equal liabilities plus equity, if they do not, then our account then we’re not in balance, so that would be a problem. If they are, then we are in balance.
05:32
That’s our main portion. That’s our accounting equation. That’s our double entry accounting system. That’s the assets equal liabilities plus equity, then we want to see that the capital account here ties out to the capital account on the statement of owner’s equity. Then we want to see that the net income on the statement of owner’s equity ties out to the net income on the income statement. Always want to check these numbers. They should always tie out if they do then we’re feeling In a pretty good situation you want to consider this pretty well to get the idea of how the income statement and the statement of equity fit into tie together with the balance sheet and what that means in terms of the double entry accounting system, what that means in terms of the accounting equation.