Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss a situation where we have a consolidation process and in the period of consolidation the parent sells subsidiary shares to a non affiliated entity. In other words, we have a consolidation process we have a parent subsidiary relationship parent owning a controlling interest over 51% of subsidiary. The parent then in that period sells some of the shares that they own in the subsidiary to a party that’s not affiliated in the consolidation, what will be the effect in the consolidation process of that get ready to account with advanced financial accounting?
Posts with the adjustment tag
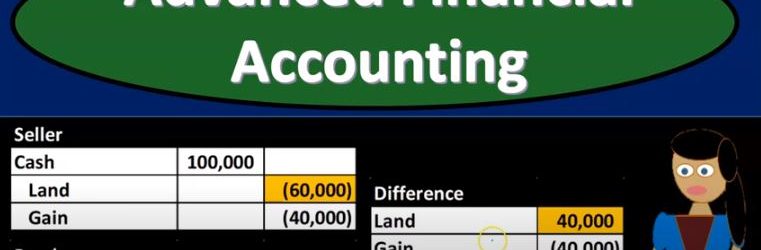
Equity Method and Land Transfer
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we’ll take a look at the equity method and land transfer get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, land transfer intercompany. Within the context of our consolidation, then we’re talking about situations where land is transferred from subsidiary to parent like a sale from subsidiary to parent or from parent to subsidiary. That resulting in basically an intercompany type of transaction we’re going to have to deal with with the consolidation process and possibly with the recording of the equity method by the parent as they reflect their investment in the subsidiary. We talked a little bit last time about the land transfer being similar to the inventory transfer because typically you’ll have like a gain that will be involved in it and your physical inventory that is changing hands. It does not have the added complexity as the property plant and equipment type of transfer. That would be depreciable assets with regards to accumulated appreciation and appreciation.
Consolidation & Subsidiary Stock Dividends
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss the consolidation process and a situation where the subsidiary issues stock dividends we have stock default dividends issued by the subsidiary what will be the effect on the consolidation process get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. We’re talking about a consolidation process where the subsidiary then issued stock dividends. So we have stock dividends are issued to all common stockholders proportionally, therefore, the relative interest of the controlling and non controlling stockholders is not changed. So that relative interest isn’t changed, so we don’t have to worry about that which is nice. The carrying amount on the parents books is also not changed. So we’re not going to have to change anything on the books of the parent with basically an adjustment to the investment account using you know, typically the equity method, which is nice stockholders equity accounts for the subsidiary do change. So we do have a change to the stock There’s equity on the subsidiary, but total stockholders equity does not. So in other words, if we take stockholders equity as a whole, there’s no change there, even though there’s changes within the stockholders equity of the subsidiary. So we’re here we’re going to say this stock dividends represent a permanent capitalization of retained earnings. That’s basically what is happening, permanent capitalization of the retained earnings.
Subsidiary Sells Additional Shares to Parent
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation in this presentation will discuss a consolidation process where we have a parent subsidiary relationship and the subsidiary sells additional shares to the parent. So we have a situation where we have the subsidiary selling additional shares to the parent, what’s going to be the effect on the Consolidated Financial Statements get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. We’re talking about a situation here where the subsidiary is going to sell additional shares to the parent and the price is going to be equal to the book value of the existing shares. In that case, it’s going to increase the parents ownership percent, because the parent now has more stocks and no one else got more stocks. Therefore, their percent ownership is increasing. The increase in the parents investment accounts will equal the increase in the stockholders equity of the subsidiary the book value of the non controlling interest is not changed and the normal consolidation entries will be made based on the parents and new ownership percent. So obviously when we do The consolidation entries, we’re going to be basing them on the new ownership percent, that’s going to be the more simple kind of situation where we have the price equal to the book value. What if there’s a sale of additional shares to the parent at an amount of different than the book value, so we still have shares going from the subsidiary to the parent, but now the amount is different than the book value. This increases the carrying amount of the parents investment by the fair value of the consideration. So in other words, the carrying amount of the parents investment in the subsidiary is going to go up by that what was paid for it that consideration given whether that be cash at the fair value of something other than cash. At consolidation, the amount of a non controlling interest needs to be adjusted to reflect the change in its interest in the subsidiary.
Other Foreign Operations Issues
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss other foreign operations issues, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, other foreign operations issues. So we’re going to start off with an issue related to the parent company having a foreign subsidiary. Typically when that is the case, they’re going to have to consolidate. In other words, you’re going to have to get the foreign subsidiary books in some way to the US dollar and then do the consolidation process. However, you might have a situation where that wouldn’t take place under certain conditions. So, parent generally consolidates a foreign subsidiary except when certain conditions are so severe that the US company owning the foreign company may not be able to exercise the necessary level of economic control. So notice when we think about the consolidation process, we’ll typically think about, we need to consolidate the entities if there’s control right over the 51% is that going to be a general rule but the overarching concept is that there is control. Now if there are certain conditions even though it’s the ownership is over the 51%, we would think there would be control, but there are certain conditions in the foreign subsidiary that are restricting that economic control, then then they might not meet you know that condition and therefore in that situation you might not have the consolidation process. So in that situation then you might have a parent company that has basically a controlling interest you would think in terms of the stock, the stock but you’re not having a consolidation due to the due to one of these factors limiting the actual economic control. So, those include restrictions on foreign exchange in foreign country. So severe strict restrictions, there could be one of the items that would stop the basically consolidation process possibly restrictions on transfers of property in foreign country.
Translation vs Remeasurement
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss translation versus remeasurement. Get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, translation versus remeasurement methods to restate to foreign entities statements to US dollar. So the most straightforward methods can be translation of foreign entities functional currency statement to US dollars. So the translation is what we’ll use the most straightforward method when the entity statement is using the functional currency. So typically, if the if the entity is using the functional currency, and we need to translate it, then we’ll simply translate it from the functional currency to the US dollars. And then there’s remeasurement of foreign entities statement into its functional currency. So remeasurement means that the entity is running their bookkeeping in a currency that is not the functional currency. Right? So then we’re going to have to re measure we’re going to use this term re measure rather than translate the To the functional currency, so after we remeasure to the functional currency, after remeasurement statements need to be translated to the reporting currency if the functional currency is not the US dollar. So in other words, if we’re assuming, in this case, in the case of the remeasurement, or let’s say, we have an entity that we’re going to be consolidating a subsidiary entity in another country, and we’re in the US and we need to basically consolidate these data together in terms of US dollars at the end of the day, if the entity is using the functional currency as as their financial statements, their bookkeeping is in the functional currency, then we can simply use the term translate it to the US dollars, which will be the parent currency that we’re talking about here. If however, the foreign entity is having their books in some currency, that is not the functional currency, then what we’re going to have to do is re measure it. We want to use remeasurement To the functional currency, we want to make remeasure at first to the functional currency rather than straight to the US dollar. So we’re going to use remeasure to the functional currency. And after we re measure to the functional currency, if the functional currency is the US dollar, then then we should be able to stop there. That’s okay. If however, the functional currency is not the US dollar, then we would have to go from the functional currency and then translate to the US dollar. So we’ll talk a little bit more about that as we go. So let’s think about translation.
Other Foreign Operations Issues
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss other foreign operations issues, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, other foreign operations issues. So we’re going to start off with an issue related to the parent company having a foreign subsidiary. Typically when that is the case, they’re going to have to consolidate. In other words, you’re going to have to get the foreign subsidiary books in some way to the US dollar and then do the consolidation process. However, you might have a situation where that wouldn’t take place under certain conditions. So, parent generally consolidates a foreign subsidiary except when certain conditions are so severe that the US company owning the foreign company may not be able to exercise the necessary level of economic control. So notice when we think about the consolidation process, we’ll typically think about, we need to consolidate the entities if there’s control right over the 51% is that going to be a general rule but the overarching concept is that there is control. Now if there are certain conditions even though it’s the ownership is over the 51%, we would think there would be control, but there are certain conditions in the foreign subsidiary that are restricting that economic control, then then they might not meet you know that condition and therefore in that situation you might not have the consolidation process. So in that situation then you might have a parent company that has basically a controlling interest you would think in terms of the stock, the stock but you’re not having a consolidation due to the due to one of these factors limiting the actual economic control. So, those include restrictions on foreign exchange in foreign country. So severe strict restrictions, there could be one of the items that would stop the basically consolidation process possibly restrictions on transfers of property in foreign country.
Investments Using the Equity Method
This presentation we’re going to focus in on investments using the equity method. In other words, we’re going to have a situation where we have one company that’s investing in another company, this time they have significant influence. And therefore, we will be using the equity method to account for that investment, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. In prior presentations, we gave an overview about different accounting methods that could be used based on different levels of influence and control those general rules being that if there is 20, or zero to 20%, ownership, we use the carried value 20 to 50%, which is where we’re going to focus in on now, the equity method, idea of there being that there is now significant influence. So in other words, if we own zero to 20%, that would be kind of like you investing in a large company like apple or whatnot. We’re the assumption being, we don’t have significant influence, even though we do have a vote of what happens However, when our vote gets to be 20% Have the total, that’s kind of a shady line or not completely solid line. But that’s kind of an arbitrary line that’s been drawn, then you’re thinking, Okay, now there’s pretty much significant influence. And therefore, we’re going to use a different method equity method, then if we’re over 51%, which is a more solid line, if you have more than 51%, and you’re voting on things, and you have like more than 51%, then you pretty much win. And that would mean control for that situation typically. And then we may use a different method, such as a consolidation. So we’re going to be focusing in here on the middle method, where we have significant influence where we have that lower line that’s a little bit fuzzy that 20% arbitrarily drawn. And then if you’re over the 51%, then it’s more likely that then you do have control and may be using the consolidated method. In that case. So equity method we’re focusing in on investments using the equity method, the equity method will reflect the investors changing interest in the investi. So we’re going to try to basically reflect what’s going on on the investor side with the change investment in the investi, the company that we are investing in that company, we have a significant influence over investment is recorded at the starting purchase price.
Accounting Cycle Steps in the Accounting Process
Hello, in this presentation, we’re going to be talking about the accounting cycle or the accounting process, that process that the accounting department will go through on a systematic basis over and over and over again, typically thought of as a monthly process. Although it could be thought of as a yearly process or some other process in terms of the amount of time that will pass. But these are going to be the steps that we’ll be going through in terms of the accounting process, always keeping in mind that in goal of financial accounting, which are the financial statements, some texts will have more steps than five as we have here. Some texts will have less than five steps. But the goal here is to really have a broad picture big picture, so that when we think about the accounting process, we can break down that that big picture view, five is a pretty good number for us to be able to memorize and keep in our mind if we have more than that, it can start to kind of muddy the picture.