QuickBooks Online 2021. pay sales tax. Let’s get into it with Intuit QuickBooks Online 2021. Here we are in our get great guitars practice file, we’re going to be opening up a new tab to open up the trial balance, I’m going to go up top, right click on the tab up top, duplicate that tab to open up, then the trial balance, which is going to be found then on the left hand side in the reports, going to type up top to find the trusty TB trial balance typing into the find score, trial balance, trial balance.
Posts with the amount tag
Make Loan Amortization Table 8.05
QuickBooks Online 2021. Make a loan amortization table, which we will then use to record loan payments within QuickBooks Online, making the loan amortization table with the help and use of Excel. Let’s get into it with Intuit QuickBooks Online 2021. Here we are, in our great guitars a practice problem, we’re going to be thinking about making payments on loans and breaking those payments out between interest and principal. As we do so, we’re going to be needing an amortization table. To help with that.
Customer Prepayment Unearned Revenue Two Methods 8.45
QuickBooks Online 2021 customer prepayment or unearned revenue, we’re going to take a look at two different methods to record the unearned revenue. Let’s get into it with Intuit QuickBooks Online 2021. Here we are in our get great guitars practice problem, we’re going to take a look at the trial balance.
00:18
First, let’s first duplicate a tab up top, we’re going to right click on the tab up top and duplicate it, then we’re going to go down to the reports down below, we’re going to be opening up then a trial balance typing into the find area trial balance and open that up range, change it up top Indian ads, we’re going to say 1230 121. And then we’re going to go ahead and run that report. Let’s close up the hamburger for this tab, hold down Control scroll up just a bit.
Allocate Expenses to Categories Par 1 170
https://youtu.be/F4FtVtXckPo?list=PL60SIT917rv6ERsGZxM9V_IZLVybpgfNU
This presentation and we’re going to start breaking out our expenses by nature. In other words of what the expenses are used for with the use of the tags, the categories being the education, the community service, the administrative and the fundraising for that 4020 2020. Being the allocation percentages, we will be using, get ready, because here we go with abalos. Here we are in our not for profit organization dashboard, we’re going to be heading on over to Excel to see what our objective will be.
Office Space Donated 125
This presentation, we’re going to record a transaction related to the contribution or donation of office days to our not for profit organization. Get ready because here we go with aplos. Here we are in our not for profit organization dashboard, we’re going to jump on over to Excel to see what our objective will be, we’re going to be on tab one. So I’m on tap one here, and number one says it’s going to be office space donated. So it’s going to be a bit of a tricky transaction for the first transaction here we got a contribution, but that contribution isn’t cash and which would be the normal type of contribution what was contributed instead, the use of the facilities the use of office space.
Financial Leverage 520
Corporate Finance PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will discuss financial leverage, get ready, it’s time to take your chance with corporate finance, financial leverage. Now remember, when you hear the term leverage, you’re typically thinking of two different categories, that being financial leverage. And then the operating leverage the financial leverage, usually the one that most people think of when they think of leverage having to do with the leverage related to the debt, the operating leverage having to do with their leverage related to the cost structure between the variable cost and the fixed cost, the operating leverage having the leverage component when you have the in the fixed costs.
Consolidation When there is Complex Ownership Structure
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we’re going to discuss a consolidation that when there is a complex ownership structure, so more complex ownership structure comparing the direct ownership, which is what we’ve normally been dealing with, with structures such as multi level ownership and reciprocal ownership, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. Normally, when we think about our consolidation structure, we’re dealing with a direct ownership situation which looks like this direct ownership type of situation, it gets more complex. Of course, if we have more complex type of ownership structures, such as a multiple multi level ownership structure where we have a parent owning a subsidiary, that basically we have an indirect ownership, let’s say in another subsidiaries, that’s going to be more complex for us to deal with or if we have a situation where we have reciprocal ownership, where the parent has ownership a controlling interest in s, but as also has some ownership in p, right. We’ve been dealing with basically P parent company owning portion of S. So if we talk about direct ownership we’re talking about the parent has, as has controlling interest in every subsidiary. So that’s going to be of course, this situation.
Subsidiary Sells Additional Shares to Parent
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation in this presentation will discuss a consolidation process where we have a parent subsidiary relationship and the subsidiary sells additional shares to the parent. So we have a situation where we have the subsidiary selling additional shares to the parent, what’s going to be the effect on the Consolidated Financial Statements get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. We’re talking about a situation here where the subsidiary is going to sell additional shares to the parent and the price is going to be equal to the book value of the existing shares. In that case, it’s going to increase the parents ownership percent, because the parent now has more stocks and no one else got more stocks. Therefore, their percent ownership is increasing. The increase in the parents investment accounts will equal the increase in the stockholders equity of the subsidiary the book value of the non controlling interest is not changed and the normal consolidation entries will be made based on the parents and new ownership percent. So obviously when we do The consolidation entries, we’re going to be basing them on the new ownership percent, that’s going to be the more simple kind of situation where we have the price equal to the book value. What if there’s a sale of additional shares to the parent at an amount of different than the book value, so we still have shares going from the subsidiary to the parent, but now the amount is different than the book value. This increases the carrying amount of the parents investment by the fair value of the consideration. So in other words, the carrying amount of the parents investment in the subsidiary is going to go up by that what was paid for it that consideration given whether that be cash at the fair value of something other than cash. At consolidation, the amount of a non controlling interest needs to be adjusted to reflect the change in its interest in the subsidiary.
Subsidiary Sells Additional Shares to Nonaffiliate
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss a consolidation process where we have a parent subsidiary relationship and the subsidiary sells additional shares to a non affiliate. So we have the subsidiary selling shares not to the parent, but to a non affiliate what will be the effect on the consolidation process? Get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. We are talking about a situation here where the subsidiary is selling more stock or additional stock to someone outside of the organization, someone who is not affiliated not to the parent or some other subsidiary, what will be the effect in the consolidation process? It’s going to increase the total stockholders equity of the consolidated entity by the amount received by the subsidiary in the sale. That of course would make sense because if you imagine the transaction taking place, then if they got cash for it, for example, cash would be going up the other side going to the equity so it’s going to be increasing the total stockholders equity will increase total shares outstanding for the subsidiary reducing the percent ownership of the parent company. So if the subsidiary then issues more shares and they didn’t go to the parent, then that means there’s going to be more shares outstanding. That means the shares that the parent owns will go down, therefore, their percentage ownership will typically go down. In that case, we’ll increase the amount assigned to the non controlling interest.
Bond Retirement
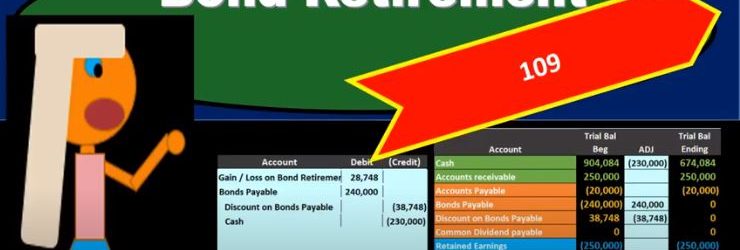
In this presentation, we will discuss the journal entries related to the retirement of bonds. the retirement of bonds just means that we’re going to pay off the bonds in some form or another at some time or another, meaning the bonds are going to go away. Typically, that’ll happen at the maturity date at the end of the bond. So for example, if we have a bond on these terms, with the face amount of 240, the issue price of 198 for 80, for 15 year bonds, they’re going to be semi annual. What would happen is when we put this on the books, we would put it on the books as cash we got for the 198, the bond payable on the books for 240, and then a discount. And then of course, over the life of the bond, we would be paying interest for that 15 year time period two times that’s 30 payments. And then at the end of this we would also be be amortizing out the discount to get rid of it, to make it go away to the interest and then By the end of this time period, the discount would be zero. And we would only be left with a bond on the books. In other words, at the maturity date, we would have something like this on our trial balance, the discount is now zero. And the bond is on the books at 240, which is the face amount of the bond, if it were a premium, it would be it would be the same in that we would be left with just the bond amount and the premium would be gone to zero. And now it’s just like anything else that we don’t have to deal with interest at this point or anything else, we just need to close out the bond. And so it’s just like any other liability, we’re just going to pay at the maturity date. That’s how we’re going to retire it. So this is a 240 credit, we’re going to make it go down by doing the opposite thing to it a debit, and we’re going to pay cash, cash is a debit balance, we need to make it go down. So we’re going to credit cash. So this is going to be our journal entry. We’ll debit the bond make go away, and then we’ll pay off the cash. When we post this then the bond payable will be here. Here, it’s going to go it’s a credit, we’re going to debit it, making it go away to zero, and then the cash has a debit balance, we’re going to credit it making the cash go down. So it’s a pretty straightforward journal entry.
02:12
The only confusing thing about this journal entry is that it happens at the end of the bond term. So when we’re talking about book questions, we often don’t get asked it because usually we’re concentrating on how to calculate the interest how to calculate the face amount of the bond, how to record the bond, how to amortize the the bond, discount or premium. And we don’t really typically get all the way to the end of the bond, the retirement the maturity date, to record the end transaction oftentimes, and it’s a pretty easy transaction if we were to do so. And it’s a lot easier to if we can actually see the trial balance. When you see the trial balance, you say, oh, there’s a liability there. We’re going to pay it just like we would if it were note payable at this time. It needs to go down and then we’re going to pay it off with cash. Now it is possible for us To have a callable bond that we’re going to retire before the end of the bond date before the maturity date. So in other words, in this case, we have the bond on the books of 240,000. And we have the discount of 338 748. And therefore, if we were to calculate the carrying amount, we’d have 240,000 minus 238 748, or two a one 252. This 201 252 is the carrying amount of this bond payable. This is something that we owe in the future. If we can pay it off at this point in time for some cash that’s going to be less than this amount, then we’re going to have a gain resulting in a gain. And if we are paying it off early for something more than this, we’re going to have a loss. So let’s see what that’s going to look like.
03:52
The gain or loss can be confusing here. When we’re talking about a bond. It’s easier to get to that point by just doing the journaling So if we have all this information, especially if we have the trial balance, because then we can see what accounts are debited and credited on the trial balance or which accounts have a debit or credit balance, then it’s a lot easier for us to construct the journal entry. So the first is going to be given to us, we’re going to say that the cash that we’re paying is 230,000. That’s gonna have to just be given in the problem because that’s the callable price that’s how much we’re able to purchase these bonds for. So cash is going to go down because remember, we are buying them back basically, or we’re we’re paying them off early before the maturity date. So it’s going to be 230. Then we’re going to say that the bond payable has to go off the books. Now the bond payables on the books at 240,000, we can see it’s a liability, it has a credit balance. So to take it off the books, we do the opposite thing to it, a debit for whatever it needs to be to make it go to zero, the discount. Same thing we need to do whatever we need to do to make it go to zero because it’s Gotta go away. So when we construct the journal entry, we just know that we just got to do whatever we need to do to make it go to zero. If you have a trial balance in front of you, that’s easy to do, because we can see the discounts on the books at a debit. And we need to do the opposite to make it go down, which is a credit. If you’re looking at a book problem that doesn’t give you a trial balance, and just tells you that the bond is on the books at a discount, then you got to think through it. And one way to think through it might be to say, well, the bonds is a liability, it must be a credit, that discount means that we’re making the bond go down, because it must be decreasing, we’re having it less than the state, the face amount, the sticker price.
05:40
And since it’s a credit, the thing that makes a credit go down would be a debit. So that discount must be a debit because these two are really combined together. And a discount means that we we really the net of the two are below the face amount price, so this must be a debit. So if it were a premium, then this amount be increasing or greater than the face amount, and it would be a credit normal balance. Once we know that this is a, this is a debit normal balance for a discount, then we can do the opposite thing to it to credit it to make it go down. And then of course, we just need to figure out what the difference is we’ve got credits of 230,038 748 minus the 240. Debit means we need a 28 748 debit. And that of course, in this case, I’m going to say it’s a gain loss account here because it could have gone either way. But if it’s a debit here, then it’s on the income statement. That’s going to be a loss. And you just got to basically start to be able to recognize that why would that be a loss? Well, you can think through that. We paid 230 versus the carrying value, or you can also just think well, if it’s a debit on the income statement, It’s acting more like an expense, meaning expenses have debit balances, they go up in the debit direction, and they bring net income down.
07:08
Revenue has a credit balance, it brings net income up. This is acting like a, an expense because it’s a debit balance. If we debit the income statement, it’s going to make net income go down, that means it must be a loss rather than a gain, which we would think would make net income go up. So the other way we can think about this is to is remember, the carrying value is going to be the 240,000 minus the 38 748. So this is kind of a value that we owe on the bond. And it’s a liability, that’s kind of the value we owe and we paid more than the value that we owe. So that’s going to be a loss in this case. And that’s another way you can think through it being a loss. So if we post this out, then we’re going to say that the gain or loss 28 748 Here, making the income statement accounts go up, kind of like an expense bringing net income down. The bond payable will be posted here, it’s going to make the bond payable go to zero. That’s why we are retiring. It’s making it go away. And then we’ve got the discount, it’s going to make the discount go to zero because we’re retiring it as well. And then the cash is going to be here, cash is going to go down. So there’s going to be our transaction. We have the bond payable and discount going away which has to be the case if we’re retiring the bonds. The cash is going down for the early retirement. And we resulted in a loss in order for us to be able to retire the bonds early.