In this presentation, we will take a look at the statement of cash flows non cash items. First question, why would we be looking at non cash items when considering a statement of cash flows? We’re gonna go through a list of non cash items first and see if you can recognize a trend in these and why we might be linking them to a statement of cash flows discussion, then we will explain more fully on the idea of looking at non cash items when considering a statement of cash flows. So, some examples of non cash items would be the purchase of long term assets by issuing a note the purchase of non cash assets by issuing equity or debt, the retirement of debt by issuing equity stock, lease of assets in a capital lease transaction and exchange non cash asset for other non cash asset. Consider these examples and note some of the common features including the deal with investing and financing activities. and think through why we might be linking them to a statement of cash flows. We’ll go more fully through this by giving an example of the purchase of long term assets by issuing a note, an example that we can then apply out to the rest of these items. So what are we going to do with these non cash items, we’re going to report them at the bottom of the statement of cash flows or report them in a note related to the statement of cash flows. So we’re going to have to say in some format, or other, hey, look, these are some non cash items that we’re linking to, for some reason, the statement of cash flows.
Posts with the Equity tag
Post Closing Trial Balance & financial statements
Hello in this presentation we will discuss the post closing trial balance and financial statements. When considering the financial statement relationship to the trial balance, we typically think of the adjusted trial balance that being used to create the financial statement. It’s important to note, however, that any trial balance that we use can be generated into financial statements. It’s just that the adjusted trial balance is the one that we have totally completed and prepared and ready. In order to create the financial statements to be as correct as possible as of the date we want them, which is usually the end of the month or the end of the year. Note that the names of the unadjusted trial balance the adjusted trial balance and the post closing trial balance are really a convention they’re all basically trial balances.
Closing Process Step 4 of 4 Closing Journal Entry Draws or Withdraws
Hello in this lecture we’re going to continue on with the closing process with step four, the final step of the process which will be to close out the draws. Remember that the objective is to have the adjusted trial balance be converted to the post closing trial balance. adjusted trial balance is what we use to create the financial statements. And the difference between the adjusted trial balance and the post closing trial balance will be that we want to have all temporary accounts including draws revenue and expense accounts to be converted to zero and have all that be in the owner capital account meaning the owner capital account will now be including all these accounts underneath it crunched into basically one number, we’re going to do that with a four step process.
Closing Entries Journal Entry 3 of 4 Step 3 Income summary
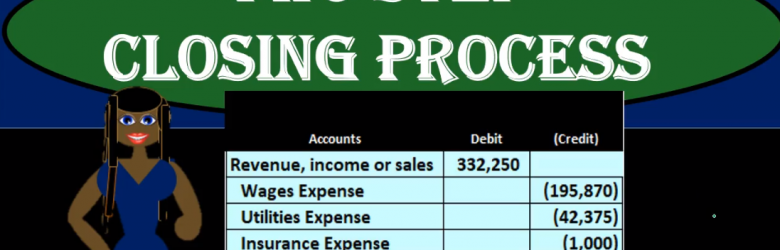
Hello in this lecture, we’re going to talk about the closing process step three of the four step closing process, which will include the close of the income summary to the capital account. Remember that our objective is to close out all the temporary accounts, which are all the accounts below capital, including drawers, and the income statement accounts of revenue and expenses. So we want the adjusted trial balance to be converted to the post, post closing trial balance, which means that everything from capital on down will be zero. The way we do that is the four steps and that includes step one we did in a prior video closeout income to the income summary. Step two was to close out expenses to the income summary. Step three is what we’re going to do now close out the income summary now having net income in it to the capital account, then we’re finally going to close out the draws to the capital account.
Two Step Closing Process
Hello in this presentation we will take a look at a two step closing process. In other words, we will perform the closing process using two journal entries. There’s a couple different ways we can see the closing process, each of them having a pros and cons. The two step process is nice because it allows us to see net income broken out and being closed out directly to the capital account, followed by draws, which is similar to what we see when we actually do the statement of equity, meaning that when we do the statement of owner’s equity, we start with beginning balance and then we increase it by net income and decrease it by drawers or dividends. Because this process is similar to that process, it’s often easy to remember it’s the easiest for me to remember in any case, so we will take a look at the two step closing process.
Closing Process Explained
Hello in this lecture we’re going to talk about the objectives of the closing process the closing process will happen after the financial statements have been created. So we will have done the journal entries where we will have compiled those journal entries into a trial balance, and then we will have made the financial statements. And then as of the end of the period in this case, we’re going to say as of December, when we move into the next time period, January, what we need to do is close out some of the temporary accounts those accounts including the income statement and the draws account so that we can start the new period from start in a similar way as if we were trying to see how many miles we could drive say in a month. If we wanted to Vince in December, and then see how many miles we’re going to drive in January of next year.
Accounting Building Blocks
Hello in this lecture we will discuss the accounting building blocks and the double entry accounting system. At the end of this we will be able to define and describe the double entry accounting system, write down the accounting equation and define each individual part of it, define and describe debits and credits, define a balance sheet and list its parts define an income statement list its parts and explain the relationship between the balance sheet and the income statement. Okay, so starting off every business and accounting software uses the double entry accounting system. So the double entry accounting system, it’s kind of like the math behind the calculator, every software is going to use it. In order to understand what the system is doing, we need to understand the double entry accounting system.
Accounts Receivable Journal Entries
Hello in this presentation we will be recording that journal entries for business transactions related to accounts receivable otherwise known as the revenue cycle. We will be recording these using debits and credits. At the end of this we will be able to list transactions involving accounts receivable record transactions involving accounts receivable using debits and credits and explain the effect of transactions on assets liabilities, equity, revenue, expenses and net income. We’re going to be recording these transactions up here on the left hand side constructing those journal entries in accordance with our thought process our list of questions to most efficiently construct the journal entries. We will then be posting them not to the general ledger but to this worksheet here so that we can see the quick calculation of the beginning balance and what is happening to the individual accounts as well. account types, in that we have the accounts categorized, as is the case for all trial balances. accounts have been in order that order been assets in this case in green, the liabilities in orange of the equity, light blue and the income statement accounts of Revenue and Expense Type accounts. first transaction perform work on account for $10,000.
Financial Statement Relationships 18
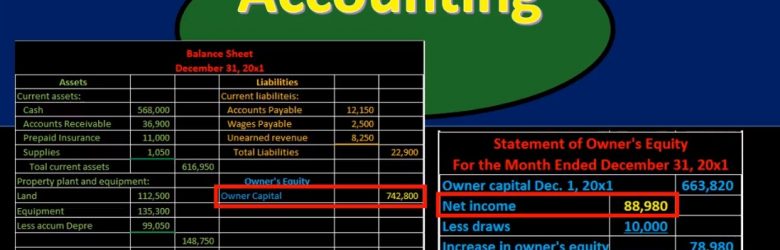
Hello in this presentation we’re going to take a look at financial statement relationships. In other words, how do these financial statements fit together? How do these financial statements represent the double entry accounting system in the format of the accounting equation that have assets equal liabilities plus equity? First, we’ll take a look at the balance sheet. Note that most textbooks will talk about this relationship and constructing the financial statements by first saying to construct the income statement, then the statement of equity and then the balance sheet. If you’re constructing things by hand with a paper and pencil, that does reduce the number of calculations that you would need to do, however, if you’re using something like Excel, then it’s a lot easier to sum up columns of numbers and it might be useful to take a look at the balance sheet. In any case, the relationships will be the same when we consider the relationships between the financial statements.
Income Statement from Trial Balance 16
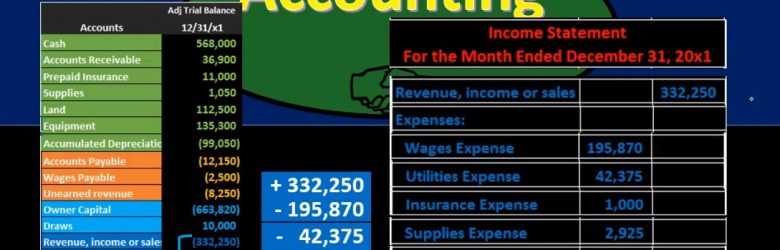
Hello in this presentation we’re going to take a look at the creation of the income statement from the trial balance. First, we want to take a look at the trial balance and consider where the income statement accounts will be. When looking at the trial balance, it will be in order we have the assets in green, the liabilities in orange, the equity in light blue, and then the income statement accounts including revenue and expenses. That’s what we are concentrating here we’re looking at those income statement accounts. And that is what will be used in order to create the financial statements to create the income statement. Note that all the blue accounts represents the equity section. So the income statement really is going to be part of total equity. If we consider that on the balance sheet, then we’re really looking at a component of this capital account.