QuickBooks Online 2021. Make loan payments using an amortization table. Let’s get into it with Intuit QuickBooks Online 2021. Here we are in our great guitars a practice file, we’re now going to make loan payments with the help and use of our amortization table, which we set up in a prior presentation. To do so let’s open up some of our reports, we’re going to duplicate the tabs up top, right click on the tab up top, duplicate it, we’re going to right click on the tab up top again, duplicate again opening up then our balance sheet and P and L Profit and Loss report going on down then to the reports on the left hand side, opening up the balance sheet report.
Posts with the interest tag
Make Loan Amortization Table 8.05
QuickBooks Online 2021. Make a loan amortization table, which we will then use to record loan payments within QuickBooks Online, making the loan amortization table with the help and use of Excel. Let’s get into it with Intuit QuickBooks Online 2021. Here we are, in our great guitars a practice problem, we’re going to be thinking about making payments on loans and breaking those payments out between interest and principal. As we do so, we’re going to be needing an amortization table. To help with that.
Financial Leverage 520
Corporate Finance PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will discuss financial leverage, get ready, it’s time to take your chance with corporate finance, financial leverage. Now remember, when you hear the term leverage, you’re typically thinking of two different categories, that being financial leverage. And then the operating leverage the financial leverage, usually the one that most people think of when they think of leverage having to do with the leverage related to the debt, the operating leverage having to do with their leverage related to the cost structure between the variable cost and the fixed cost, the operating leverage having the leverage component when you have the in the fixed costs.
Intercompany Transactions
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to discuss intercompany transactions. So typically we have a situation where where we have a parent subsidiary relationship or thinking about a consolidation type of process within it. And then we have those intercompany transactions between the companies that need to be consolidated between parent and subsidiary, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting intercompany transactions, the intercompany transactions we’ll be focusing in on here and working some practice problems in on will include the intercompany receivables and payables need to be eliminated for consolidated financial statements.
Consolidation for Non Wholly Owned Subsidiary
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to talk about a consolidation for a non wholly owned subsidiary. So in other words, we have a parent subsidiary relationship, but the parent doesn’t own 100% of the outstanding common stock of the subsidiary but something other than 100%. In other words, over 51% controlling interest less than 100% get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. Non controlling interest often will be represented NCI non controlling interest. So notice if we have a parent subsidiary relationship we’re talking about there is some controlling interest, the controlling interest is the interest that’s going to be over 51%. However, if we don’t have 100% ownership, then we have the amount that’s not in control and that of course is going to be the non controlling interest. So non controlling interest. NCI controlling interest is needed for consolidation. Obviously, if we’re going to consolidate this thing, that means typically that A parent has some controlling interest over 51% a 100% is not needed. So 100% of ownership, in other words, by one parent to the other is not necessary for a consolidation to take place control is necessary, which is typically over 51% less than 100% ownership will result in a non controlling shareholder, those other than the parent.
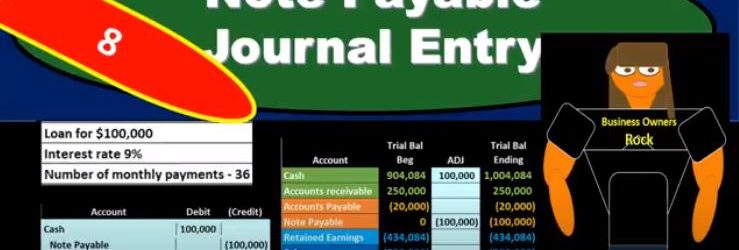
Note Payable Journal Entry
In this presentation, we will record the journal entry related to a note payable related to taking out a new loan from the bank. Here’s going to be our terms. We’re going to record that here in our general journal and then we’ll post that to our worksheet. The trial balances in order assets, liabilities, equity, income and expenses, we have the debits being non bracketed or positive and the credits being bracketed or negative debits minus the credits equaling zero net income currently at 700,000 income, not a loss, revenue minus expenses. The difficult thing in terms of a book problem, when we record the loan is typically that we have too much information and this is the difficult thing in practice as well. So once we have the terms of the loan, and we have the information, we’ve already taken the loan out, then it’s the question of well, how are we going to record this thing? How are we going to put it on the books and if we have this information here, if we have a loan for 100,000, the interest is 9%. And then the next number of payments that we’re going to have, we’re going to pay back our 36. Then how do we record this on the books? Well, first, we know that we can ask our question is cash affected? We’re going to say, Yeah, because we got a loan for 100,000. That’s why we got the loan.
01:14
So cash is a debit balance, it’s going to go up with a debit, so we’ll increase the cash. And then the other side of it is going to be something we owe back in the future. And that’s going to be note payable. And that’s as easy as it is to record the initial loan. The problem with this the thing it’s difficult in practice, and in the book question is that we’re often given, of course, the other information, like the interest in the number of payments, and possibly more information that can cloudy up the what we’re doing, and the reason these are needed, so that we calculate interest in the future, but they’re not really We don’t even need that information to record the initial loan. All we need to know is that we got cash and we owe it back in the future. And you might be asking, Well, what about the interest we owe interest in the future as well? We do, but we don’t know it yet. And that that’s the confusing thing interest, although we we will pay interest and we know exactly how much interest we’re going to pay in the future. We don’t owe it yet. Why don’t we owe it yet? Because we’re going to pay back more than 100,000. Why don’t we Why don’t we record something greater than 100,000? You might say, because we know we’re going to pay more than 100,000. And that’s because the interest is something that it’s like rent. So we’re paying rent on the use of this 100,000. And just like if we if we had a building that we rented, that we’re using for office space, we’re not even though we know we’re going to pay rent in the future. We’re not going to record the rent now. Because we haven’t incurred it until we use the building.
02:41
So the same things happening here. We know we’re going to pay interest in the future we’re no we know we’re going to pay more than 100,000 but it hasn’t happened yet. We haven’t used up we haven’t gotten the use of this hundred thousand and therefore haven’t incurred the expense of it yet. So the interest and is something we need to negotiate when making To turn off the loan, but once the loan has been made, and we’re just trying to record it, it’s not going to be in the initial recording. It will be there when we calculate the payments need and the amortization table. So the initial recording is pretty straightforward. We’re just going to say okay, cash is going to go up by 100,000. And then the notes payable is going to go up from zero in the credit direction to 100,000. So what we have here is the cash increasing the liability increasing, although we got cash, there’s no effect on net income because we haven’t incurred any expenses. We’re going to use that cash most likely to pay for expenses possibly or pay for other assets or pay off liabilities in order to help us to generate revenue in the future. But as of now, we’ve gotten we increase an asset and we increase the liability
Notes Payable Introduction
In this presentation, we will introduce the concept of notes payable as a way to finance a business. Most people are more familiar with notes payable than bonds payable, the note payable basically just being a loan from the bank. Typically, the bond payable is a little more confusing just because we don’t see it as often, especially as a financing option. From the business perspective, we often see it more as an investing or type of investment. But from a loan perspective, it’s very similar in that we’re going to receive money to finance the business if we were to issue a bond, or if we’re taking a loan from the bank. And then of course, we’re going to pay back that money. The difference between the note and the bond is that one the note is something we typically take from the bank. Whereas a bond is something we can issue to individuals so a bond we could have more options in terms of issuing the bonds than we do for a loan. Typically when we have a loan, we typically are Gonna have less resources, we can take a loan from the bank. When we pay back the bond, we often think of the bond as two separate things. And we set it up as two separate things, meaning we have the principal of the bond that we’re going to pay back at the end. And then we have the interest payments, which are kind of like the rent on the money that we’re getting, we’re getting this money, we’re gonna have to pay rent on it, just like we would pay rent if we had got the use of any physical thing.
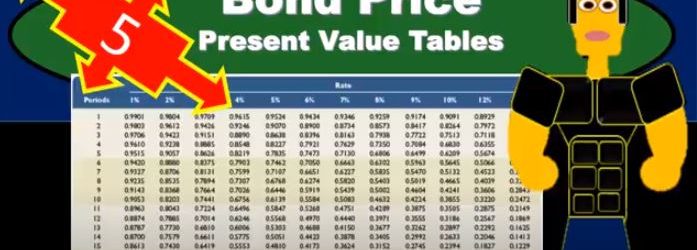
Bond Price Present Value Tables
In this presentation, we will calculate the bond price using present value tables. Remember that the bonds is going to be a great tool for understanding the time value of money. Because of those two cash flow streams we have when with relation to bonds, meaning we’re going to pay the bond back the face amount of the bond, and we’re going to have the income stream. And those are going to be perfect for us to think about time value of money, how to calculate time value of money, our goal being to get a present value of those two streams. So we’re going to think of those two streams separately generally, and present value each of them to find out what the present value of the bond will be. We can do that at least three or four different ways. We can do that with a formula actually doing the math on it. We can do it now, which is probably more popular. Now. Do it with a calculator or with tables in Excel, I would prefer Excel or we can use just tables pre formatted tables. The goal here the point is to really understand what we’re doing in terms of what what is happening, what can it tell it? What can it tell us, and then understand that these different methods are all doing the same thing.
Bonds Present Value Formulas
In this presentation, we will take a look at present value formulas related to bonds. One of the reasons bonds is so important to accounting and finance is because they’re a good example of the term of present value of money. We’re trying to look for an equal measure of money, when we think of bonds and bonds is going to have this relationship between market rates and the stated rate, which helps us to kind of look through and figure out these types of concepts. So even if we don’t work with bonds, in other words, if we’re not planning on issuing bonds, or buying bonds, or knowing anything about bonds not being important to us, the time value of money is a very important concept and bonds is going to be a major tool to help us with that. Why is bonds so useful for learning time value of money, because there’s two types of cash flows with bonds meaning at the end of the time period, we typically are going to get the face amount of the bond that 100,000 similar to a note and then we’ve got the interest payments that are going to happen on a periodic To basis, and therefore we have these two different types of cash flows, that we can use two different formulas for, to think about how to equalize.
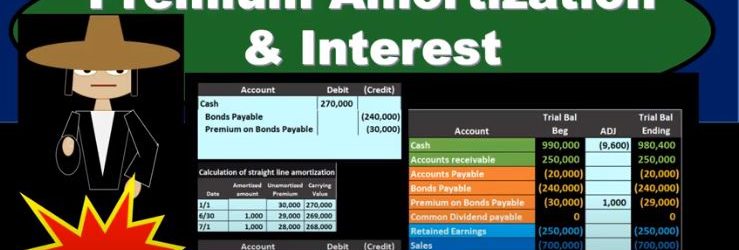
Premium Amortization & Interest
In this presentation, we will discuss the amortization of a bond premium and the recording of interest expense on bonds. This is going to be our starting point. This is the initial transaction in order to get the bonds on the books. Here’s our data down here we’ve got the number of years we’ve got the face amount of the bonds, we’ve got the issue price 270, we see that the interest on the market rate is different than the contract rate. The result then is that cash is going to be increased by the 217. The bonds payable went on the books for the face amount of the bond, the amount that’s on the bonds of the 240, which is a liability. And then we have the premium being the difference increasing the premium here by the 30. The 240 plus 230 is going to be equal to the 270,000 carrying amount book value of the bonds. Now we’re going to go through the process of recording the interest we can see that this is going to have 15 years bonds, we’re going to pay the bonds semi annually. So we’re going to have to record the interest on them. And we’re gonna have to reduce this premium in some way as well. Remember, at the end of the bonds, we’re not going to pay back the 270. We’re only going to pay back 240. So how are we going to get rid of that the premium on the bond and why are we going to do it in the way we will. We’ll start off by amortize in the premium using a straight line the method. Note that the effective method is the preferred method for amortize in a premium for generally accepted accounting principles, but the straight line method will be appropriate in some cases, if the difference is going to be a non material. And the straight line method is a simplified method and it’s easy for us to see what is going on. So we’ll start off with the straight line method.