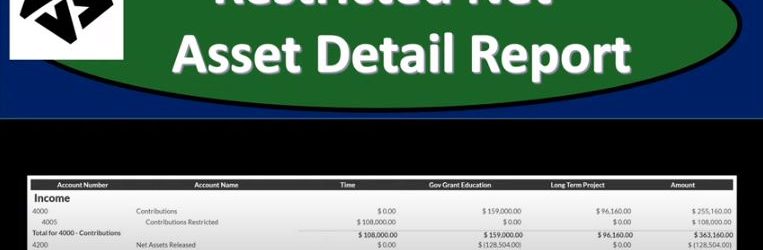
This presentation we will generate, analyze, print and export to an Excel a restricted net asset detailed report and get ready because here we go with aplos. Here we are in our not for profit organization dashboard, let’s head on over to Excel to see what our objective will be. We’re currently in the 10th, tab, tab number 10. And last time and a few prior presentations, we’ve been creating the statement of activities, including three columns, two columns, for width restrictions, without restrictions, we then broke out the width restriction column out into the expenses by both function and by their nature.
Posts with the net assets tag
Closing Entries 175
https://youtu.be/OdjLcvkWPfY?list=PL60SIT917rv6ERsGZxM9V_IZLVybpgfNU
This presentation, we’re going to discuss the closing process for our accounting system. Get ready, because here we go with aplos. Here we are in our not for profit organization dashboard, let’s head on over to our Excel file to see what our objective will be, you’ll recall, we’re going to be in tab 10. By the way, we’re over here in tab 10. You’ll recall that we’ve been looking at each transaction with the accounts that will be affected, posting those over to our Excel worksheet to see the effect on the trial balance on the accounts. Now, we did this in terms of posting to our first trial balance up top and so row one. And then we said, okay, what if we break this information out, and I want to break this information out by not just the expenses by their nature, but by their function. Now, in aplos, we have a nice system to do that we’re going to use the phones and the classes, or the funds and the tax to do that here.
Net Assets Released From Restriction 172
This presentation we will record a transaction related to net assets being released from restrictions. In other words, we have net assets that had some restrictions put on them, we’re going to be spending money in such a way that it will be releasing the net assets from restriction will record the journal entry to move those net assets from a restricted area to unrestricted so that they can be used and reflected on our statement of activities and statement of net position. Get ready, because here we go with aplos. Here we are in our not for profit organization dashboard. Let’s head on over to our Excel worksheet to see what our objective will be. We’re over here in tab 10. So tab number 10. On the Excel worksheet, you’ll recall in previous presentations, what we have done thus far is we’ve been thinking about recording transactions in terms of journal entries, the accounts that are affected, and then putting them into our trial balance.
Set up Funds & Tags 120
In this presentation, we’re gonna set up and customize our funds and tax features within our accounting software. Get ready, because here we go with aplos. Here we are in our not for profit organization dashboard, we’re gonna go into our chart of accounts over here. Now, we’re going to go into the fund accounting tabs and the fund accounting tab up top, then you’ll see another bar here with our drop downs, we want to go to the accounting drop down on the far left hand side, we’re going to first go to that first item, which is going to be the accounting tab, we’re going to be going into the accounting tab. And then right up top, we have our funds features.
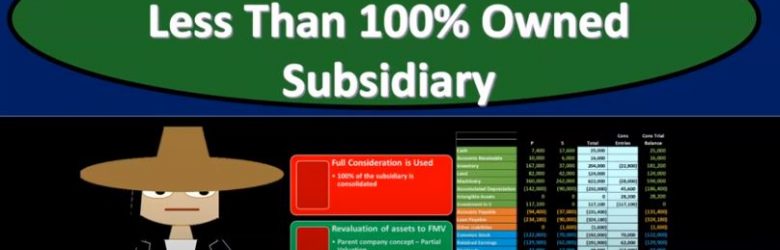
Consolidations Less Than 100% Owned Subsidiary
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to discuss the consolidation process for less than 100% owned subsidiary. In other words at the end of this, we’ll be able to understand some of the major differences in the consolidation process from a company that was 100% owned. In other words, the parent owns 100% of the subsidiary and one in which the parent owns some other percent some stock share and percent other than 100%. Get ready to account with advanced financial accounting when there is a controlling interest but less than 100% owned interest in a subsidiary. In other words, the parent company owns something other than 100% of the common stock something over 51% still having a controlling interest still makes sense to do consolidated financial statements, because it’s useful to see the assets minus the liabilities, the net assets that the parent has control over, even if they don’t have claim over them. The performance based on you know, the net assets that they have control over.
Push Down Accounting
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we will discuss push down accounting as it relates to parent subsidiary relationships controlling interest interest over 51%, where we have consolidation accounting taking place, we’re going to be applying pushdown accounting to it, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. So the concept of pushdown accounting will take place when we have the parent subsidiary type of relationship and we have a situation where the purchase price when the parent purchased the subsidiary, the purchase price was more than the book value of the subsidiary, which could complicate of course the consolidation process as we’ve talked about in prior presentations. So we have a couple different options that we could do.
Consolidation When There is a Book & Fair Value Difference
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to take a look at a consolidation process when there is a book and fair value difference. In other words, we’ll have a consolidation. We have two companies, we have a parent subsidiary type of relationship, and the parent has a controlling interest of the subsidiary. Therefore consolidation is what we’re going to be doing. That means we’re going to take two separate sets of books combine them together as if they were one. And we had some complications with the fact that when the purchase took place, there was a difference between the book value and the fair value, what will be the effect of that difference on the consolidation process, elimination entry example. So when we consider this difference, we want to think about what’s going on with the parents books and the subsidiaries books and then what would be the process to consolidate them and what type of problems would be caused if there was a difference between the book and fair value of the net assets so the parents books investment accounts starts out containing the acquisition costs at the fair market value of net assets and goodwill, so we have, that’s basically what’s going to be on the parents books, right. And we’re thinking here typically have an equity method being used. So we have the parents books, we have the subsidiary books that we’re gonna have to consolidate together, and then do our elimination entries. And on the parents books, you’re accounting for the subsidiaries.
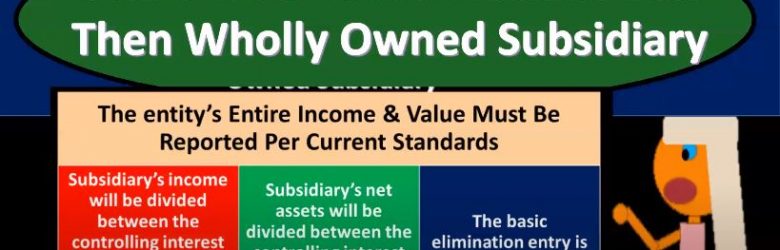
Consolidation Calculations Less Then Wholly Owned Subsidiary
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to talk about consolidation calculations for less than wholly owned subsidiaries. So we have a parent subsidiary relationship, we’re going to be looking at the consolidation process to put the financial statements of the parents and the subsidiaries as if they are one entity, but we don’t have a wholly owned subsidiary. In other words, the parent does not own 100% of the subsidiary. How do we do the consolidation? in bad case, consolidation calculations less than wholly owned subsidiaries, that entities entire income and value must be reported per the current standards? So in other words, once again, we might think, well, on the income statement, maybe we would just report the part of the subsidiary that belongs to or is controlled by the parent, but that’s not typically the case. That’s not the case under generally accepted accounting principles.
Consolidation for Non Wholly Owned Subsidiary
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to talk about a consolidation for a non wholly owned subsidiary. So in other words, we have a parent subsidiary relationship, but the parent doesn’t own 100% of the outstanding common stock of the subsidiary but something other than 100%. In other words, over 51% controlling interest less than 100% get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. Non controlling interest often will be represented NCI non controlling interest. So notice if we have a parent subsidiary relationship we’re talking about there is some controlling interest, the controlling interest is the interest that’s going to be over 51%. However, if we don’t have 100% ownership, then we have the amount that’s not in control and that of course is going to be the non controlling interest. So non controlling interest. NCI controlling interest is needed for consolidation. Obviously, if we’re going to consolidate this thing, that means typically that A parent has some controlling interest over 51% a 100% is not needed. So 100% of ownership, in other words, by one parent to the other is not necessary for a consolidation to take place control is necessary, which is typically over 51% less than 100% ownership will result in a non controlling shareholder, those other than the parent.
Subsidiary Sells Additional Shares to Parent
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation in this presentation will discuss a consolidation process where we have a parent subsidiary relationship and the subsidiary sells additional shares to the parent. So we have a situation where we have the subsidiary selling additional shares to the parent, what’s going to be the effect on the Consolidated Financial Statements get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. We’re talking about a situation here where the subsidiary is going to sell additional shares to the parent and the price is going to be equal to the book value of the existing shares. In that case, it’s going to increase the parents ownership percent, because the parent now has more stocks and no one else got more stocks. Therefore, their percent ownership is increasing. The increase in the parents investment accounts will equal the increase in the stockholders equity of the subsidiary the book value of the non controlling interest is not changed and the normal consolidation entries will be made based on the parents and new ownership percent. So obviously when we do The consolidation entries, we’re going to be basing them on the new ownership percent, that’s going to be the more simple kind of situation where we have the price equal to the book value. What if there’s a sale of additional shares to the parent at an amount of different than the book value, so we still have shares going from the subsidiary to the parent, but now the amount is different than the book value. This increases the carrying amount of the parents investment by the fair value of the consideration. So in other words, the carrying amount of the parents investment in the subsidiary is going to go up by that what was paid for it that consideration given whether that be cash at the fair value of something other than cash. At consolidation, the amount of a non controlling interest needs to be adjusted to reflect the change in its interest in the subsidiary.