In this presentation, we will take a look at business combination accounting methods, both historic methods and the current methods get ready to act, because it’s time to account with advanced financial accounting. We’re going to start off with business combinations from the past, these are not the current method that we’re going to be using. However, it’s good to have some historical context so that if you hear these methods, you know what you’re talking about. We also want to think about these concepts in terms of just a logistical standpoint. If you were to make these laws, then how would you do it? What are some of the challenges that have happened? And by looking through the historical process, you can kind of think about, okay, these are what were put in place, I see why those were put in place here that changes that are happening, we could see why the changes are happening, therefore have a better understanding of what we are doing, and how the current process is being put in place and why the decisions were made to put it in place. So in the past, we had combinations methods that included the purchase method and the pooling of interest. method. So they then what happened is the pooling of interest method was taken away by faz B. So faz B said, Hey, we’re not going to allow anymore, the pooling of interest method, and then the purchase method has been replaced with the acquisition method. So if you hear the purchase method, that in essence is what we’re currently doing. However, we changed the name from the purchase method to the acquisition method.
Posts with the paid tag
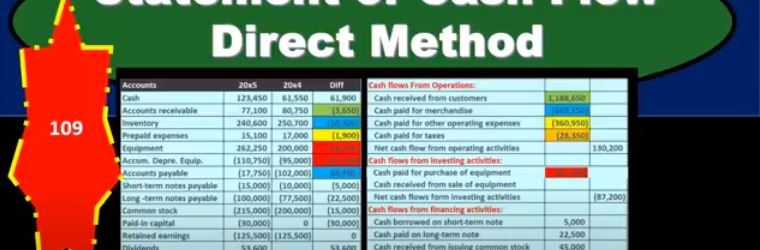
Statement of Cash Flow Direct Method
In this presentation, we will take a look at the statement of cash flows using the direct method. Here’s going to be our information we got the comparative balance sheet, the income statement and some additional information. And we will use this information to put together our worksheet which will be the primary source used to create the statement of cash flows using the direct method. This is going to be our worksheet. Now most of this worksheet will be similar to what we have done for the indirect method, in that we took the difference in the balance sheet accounts. So we’re taking the current year and the prior year, the current period, the prior period, all the balance sheet accounts, we’ve got cashed down to the retained earnings for the balance sheet accounts. But we’re also in this case going to give us the income statement accounts for the current period. So in other words, we’re going to break out the retained earnings the amount to its component parts, meaning we’ve got net income being broken out on the income statement. We’ve got sales cost of goods sold, the income statement accounts. So it’s going to be our same kind of worksheet here, we’re going to be in balance, we’ve converted it from a plus and minus format, we’ve removed all of the subtitles as we did under the indirect method.
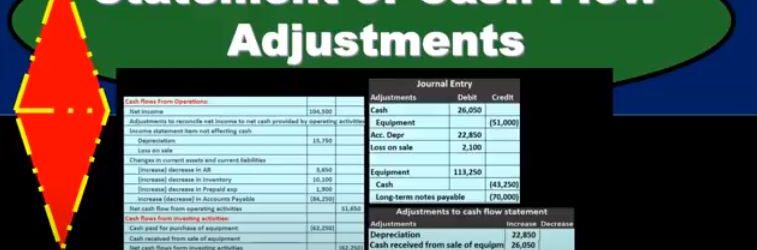
Statement of Cash Flow Adjustments
This presentation we will continue on with our statement of cash flows, we’re not going to enter the final adjustments that we will need to finalize the statement of cash flows to bring those last few numbers to the correct balances. In order to do that, we’re going to use this information we’ve got our comparative balance sheet, our income statement and additional information. We put together most of our information so far with the comparative balance sheet, which we made into a worksheet. Now we’re going to use some of these other resources, the income statement, the additional resources to make those final adjustments, those fine tunings that are needed to get those few numbers that we have left and noted into balance. And this is going to be part of the normal practice where once we get this information set up, we can then make some comparisons such as net income does it tie out, such as depreciation does it tie out on the cash flow statement to what we see here on the income statement, then we can have this other information which will be given in both problems in practice, of course, we’ll just go to the gym. General Ledger. And we’ll get this information in a book problem, we don’t want to give all the detail of a general ledger or just when we’re going over an example.
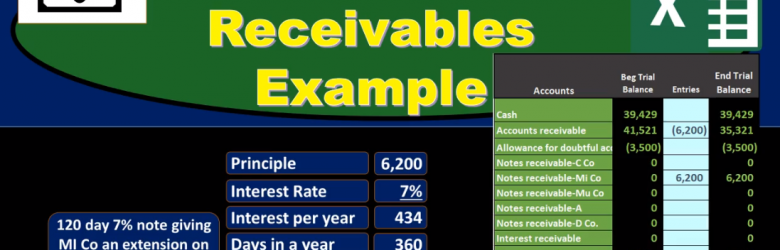
Note Receivable Example
In this presentation we will discuss notes receivable, giving some examples of journal entries related to notes receivable and a trial balance so we can see the effect and impact on the accounts as well as the effect on net income of these transactions. first transaction, we’re gonna have 120 day 7% note giving the company EMI and extension on past due AR or accounts receivable of 6200. When considering book problems and real life problems, one of our challenges is to interpret what is actually happening what is going on, which party are we in this transaction in? Therefore, how are we going to record this transaction when we’re looking at notes receivable? A common problem with notes receivable is the conversion of an accounts receivable to a notes receivable. So in this case, that’s what we have. We have an accounts receivable here that includes an amount of Due to us by this particular company in AI so these are our books, we have a receivable people owing us money for prior transactions goods or services provided in the past and they owe us in total, all customers owe us 41,521 this customer in particular owes us 6200 of this amount in the receivable that could be found not in the general ledger which would give backup of transactions by date.
Notes Receivable
In this presentation, we will take a look at notes receivable. We’re first going to consider the components of the notes receivable. And then we’ll take a look at the calculation of maturity and some interest calculations. When we look at the notes receivable, it’s important to remember that there are two components two people, two parties, at least to the note, that seems obvious. And in practice, it’s pretty clear who the two people are and what the note is and what the two people involved in the note our doing. However, when we’re writing the notes, or just looking at the notes as a third party that’s considering the note that has been documented. Or if we’re taking a look at a book problem, it’s a little bit more confusing to know which of the two parties are we talking about who’s making the note who is going to be paid at the end of the note time period? We’re considering a note receivable here, meaning we’re considering ourselves to be the business who is going to be receiving money. into the time period, meaning the customer is making a promise, the customer is in essence, we’re thinking of making a note in order to generate that promise, that will then be a promise to pay us in the future.
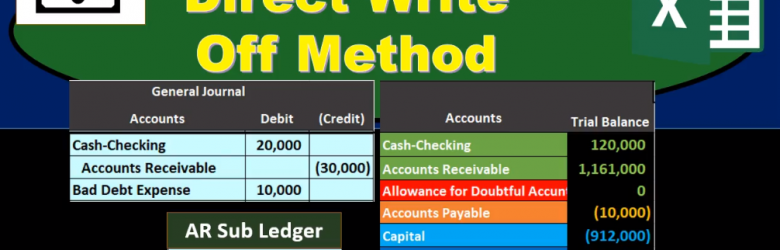
Direct Write Off Method
This presentation we will be discussing the direct write off method. The direct write off method as it relates to accounts receivable, quick summary of accounts receivable accounts receivable is a current asset, it’s an asset with a debit balance, we are going to be writing off certain amounts for accounts receivable that will become not due or not collectible at some point in the future. There are two ways to do this one is called the allowance method. The other is the direct write off method, we will be using the direct write off method here the non generally accepted accounting principles method being this direct write off method. However, a method that is typically much easier to use. Therefore, when considering whether or not to use an allowance method or direct write off method, we want to consider one do we have to use an allowance method due to the fact that we need to make our financial statements in accordance with generally accepted Accounting Principles, or are we able to choose between having an allowance method or direct write off method? If we choose to have a direct write off method, it’s probably because we’re thinking that the receivables that will be written off are not significant.
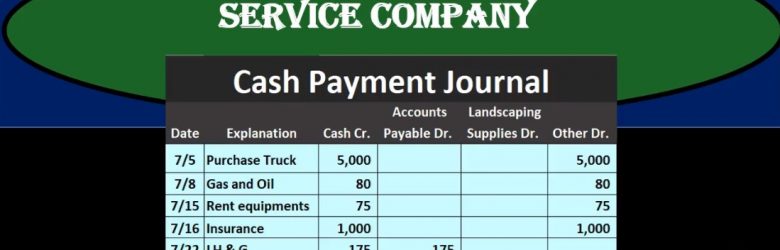
Cash Payments Journal Service Company 50
In this presentation, we will take a look at a cash payments journal for a service company, the cash payment journal we’ll be dealing with transactions where we have cash payments, that’s going to be the factor that will be the same for all transactions with cash payments meaning this column here cash payments will always be affected wish they kept cash payments journal cash payments journal will be used when using more of a manual system rather than an automated system. However, it’s good to know what the cash payments journal is, even if using an automated system because it’s possible that we or it’s very likely that we would need to run reports that will be similar in format to a cash payments journal. And it’s useful to see this format or how different types of accounting structures can be built.
Cash Receipts Journal 40
In this presentation we will talk about the cash receipts journal. The cash receipts journal will be used when we have cash receipts when using a more of a manual system or a data input system that we will be doing by hand as opposed to an automated system. It’s still useful to know the cash receipts journal if using an automated system for a few different reasons. One is that we might want to generate reports from an automated system, similar to what we would be creating in a manual system for a cash receipts journal. And to it’s just a good idea to have different types of systems in mind, so we can see what’s the same and what is different between different accounting systems. The cash receipts journal will be used for every time we have a cash receipts. So the thing that transaction triggering a cash receipt will be when cash is being used. And we’re going to have a little bit more complex complexity in a cash receipts journal than something like a sales journal because we may be receiving cash for multiple different things.
Special Journals Subsidiary Ledgers 2
In this presentation, we’re going to talk about special journals and subsidiary ledgers. First, we’re going to list out the special journals and talk about when we would use them, why we would use them and how they fit into the accounting system. The special journals are basically going to group types of transactions. So when we think about all the transactions that happened during the month, we typically see them in order of when they happen in the accounting system, we’re going to record transactions in other words, by date as they occur. But if we are able to group those transactions into special journals that can simplify the process.
Types of Adjusting Journal Entries Adjusting Journal Entry 2
Hello in this presentation we’re going to talk about types of adjusting journal entries. When considering adjusting journal entries we want to know where we are at within the accounting process within the accounting cycle. all the entries the normal adjusting entries have been done the bills have been paid the invoices have been entered for the month we have reconciled the bank accounts. Now we are considering the adjusting process. Those adjusting journal entries are needed in order to make the adjusted trial balance so that we can create the financial statements from them. The adjusting journal entries being used to be as close to an accrual basis as possible. those categories of adjusting journal entries, which will then have more types of adjusting entries within each category will include prepaid expense, unearned revenue, accrued expenses and accrued revenue. Let’s consider each of these we have the types of adjusting entries first type prepaid account expenses. prepaid expenses are items paid in advance.