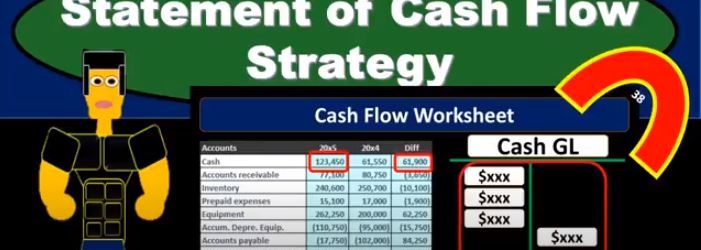
In this presentation, we will take a look at strategies for thinking about the statement of cash flows and how we will approach the statement of cash flows. When considering the statement of cash flows, we typically look at a worksheet or put together a worksheet such as this for my comparative balance sheet, that given the balance sheet accounts for the current year and the prior year or the current period, and the prior period, and then giving us the difference between those accounts. So we have the cash, we’ve got the accounts receivable inventory, we’re representing this in debits and credits. So this is in essence going to be a post closing trial balance one with just the balance sheet accounts, the debits represented with positive and the credits represented with negative numbers in this worksheet, so the debits minus the credits equals zero for the current year, the prior year. And then if we take the difference between all the accounts, and we were to add them up, then that’s going to equal zero as well. This will be the worksheet that we’re thinking about. Now. When can In the statement of cash flows, we can think about the statement of cash flows in a few different ways. We know that this, of course, is the change in cash, this is the time period in the current time period, the prior year, in this case, the prior period, the difference between those two is the difference in cash.
Posts with the typically tag
Statement of Cash Flow Tools For Completion
This presentation we will take a look at the tools needed in order to complete a statement of cash flows. to complete a statement of cash flows, we are typically going to need a comparative balance sheet that’s going to include a balance sheet from the prior period, whether that be the prior month or the prior year and a balance sheet from the current period, then we’re going to have to have an income statement. And then we’ll need some additional information in a book problem, it’ll typically give us some additional additional information often having to do with things like worth an equipment purchases, whether equipment purchases or equipment sales, were their investments in the company where their sales of stocks, what were the dividends within the company. In practice, of course, we would have to just know and recognize those types of areas where we might need more detail. And we would get that additional information with General Ledger we’d go into the general ledger, look at that added information. Now once we have this information, our major component we’re going to use is going to be the comparative balance sheet. That’s where we will start. So that comparative balance sheet is going to be used to make a worksheet such as this.
Cash Flow Category Thought Process
In this presentation, we will think about the thought process to know which category a cash flow should be entered into whether it should be operating, investing or financing activity. When putting together the statement of cash flows, we’re usually going to have a worksheet, which will typically have a comparison of balance sheet accounts. And we also might just have test questions that will ask us, where should this cash flow go? And that’s going to be a common kind of question that we’re going to have whether we build the entire cash flow statement from scratch, or whether we’re just asking test test questions and trying to know what types of Cash Flows we’re talking about. It’s also important for practice as well so that we can understand when we’re thinking about cash flows, where do they belong? What are these cash flows mean? What are they doing for us? What are they doing for the company? Are they part of the operations? Are they part of investing? Are they part of financing? If we look at a worksheet like this to build the statement of cash flow, typically we’re going to look at a balance sheet for two periods. So here our balance sheet for these two periods. And we’ll have the difference between the two periods in terms of the balance for these balance sheet accounts. So we’ve got cash, accounts receivable, inventory, prepaid expenses.
01:13
Now what we’re going to do is we’re going to take the change in cash, that’s going to be the end result on our statement of cash flows. And we’re going to kind of back in to that end result by looking at the change in the other balance sheet accounts and tried to figure out what’s causing this change. So we’re going to go through all the other balance sheet accounts, look through these changes. And we know that if we look if we add them all up, they add up to zero. Why? Because the debits and credits for one year, add up to zero the debits and credits for the other year add up to zero. In other words, the debits minus the credits equals zero. And therefore the difference between the two years debits and credits the change will add up to zero. So we know that’s the case and we know that if we add up then everything except cash Then the result will be the difference in cash. So that’s how we’re going to kind of work and put together our statement of cash flows. So what we need to do then is we’re going to take a look at these changes in receivables, changes in inventory changes in prepaid expenses, and then try to determine where does that change belong? Before we get into any other question is, is the change of inventory and operating, investing or financing activity? And is the change in long term notes payable? Is that going to be an operating investing or financing activity? Our goal here is to go through a thought process to see if we can think through more clearly which category these these should be belong to. So what’s the most common journal entry in this account? It’s going to be our first question.
02:48
Whatever account they’re given us here, we’re going to say it let’s think about the most common journal entry that’s related to this account, there’s typically going to be one or two journal entries that are going to be very common and we want just right down first, once we know the most common journal entry, then we’re going to ask is an income statement account involved? So when we think about whatever account we’re dealing with, we’d write down the journal entry and say, Okay, is there an income statement account involved? Is there a revenue account or an expense account involved? If the answer is yes, then it’s probably the change that we’re dealing with is probably something that should be in the operating activities. Because remember, the operating activities is kind of like the income statement on a cash basis. So if we’re dealing with something that’s this change has something to do with the income statement, then it’s going to be something on the operating activities. Typically, if the journal entry has nothing to do with the income statement, there’s no revenue or expense accounts involved in the normal journal entries related to these accounts, then we’re going to ask the question, are we purchasing or selling an asset? Because it’s so if it’s not operating, this means that it’s not operating therefore, We’re trying to see if it’s going to be investing activity. And that typically means we’re purchasing or selling an asset. If it has to do with, for example, property, plant and equipment, or some other type of investment, then it’s going to be an investing activity. And then if it’s not, then it’s going to be financing. And of course, financing is going to be dealing with notes, something that we’re dealing with that doesn’t deal with operating activities in terms of the income statement, no revenue and expenses, and typically doesn’t have assets involved either, because what we’re doing is funding the company. So that’s typically going to be something that deals with cash and subtype of liability or the equity section. So this is going to be our thought process if we go through each of those line items, and think about each account on the balance sheet.
04:46
And then try to go through this thought process and think okay, which category are we going to be putting this change to? Now, this looks a little less intuitive than we might think at first glance here because no one We’re doing we’re looking at the balance sheet accounts. And we’re trying to see what category these things are going to fit into. And remember that the operating activities I’m keep on comparing that to the income statement. And you might be thinking, well, these are all balance sheet accounts. Why do you keep mentioning the income statement. And note, what we’re doing here is we’re really kind of backing into the activity is happening by looking at the change in two points in time. So we’re kind of still looking at the income statement activity type of accounts, we’re looking at change, we’re looking at activity, even though we’re doing that by looking at the change in two points in time to balance sheet accounts, which are points in time. So when we look at the change in accounts receivable for example, if we go through our thought process, we’re going to say okay, accounts receivable was at 80,007 50. In the prior year, end of the current year, it’s at 77,100.
05:51
That means it went down by 3650. So our goal here is just to determine which category That change belongs to it’s an operating, investing or financing. And if we think about that, then we could think Well, what’s the normal journal entry related to accounts receivable? We’re going to have a debit to accounts receivable and a credit to sales. That’s going to be our normal journal entry that we’ll have related to accounts receivable. And we can see there that sales is an income statement account. So we know that it is an income statement account involved, we’re going to say yes, therefore, it’s an operating activity. So note what we’re doing here, we’re looking at the change in a balance sheet account. We’re looking at the change in the balance sheet account, then ask yourself, what’s the normal journal entry related to this account? And if we think about the normal journal entry related to accounts receivable, that’s a sale of something on account. So accounts receivable goes up when we make a sale on account, and we credit revenue and revenue is clearly an income statement account. So this Change, then that’s what we’re going to think through, we’re going to say that change looks like it belongs somewhere in the operating activities. Because we’re dealing, we’re really kind of backing into sales. That’s what we’re really looking at. And we’re going to do that by writing down the journal entry. Let’s look at another account. We’re going to pick equipment now. So we’re just going to go through all these changes. And we just got to find a home for all these changes.
07:21
When we when we make the statement of cash flows. We got to find a home for them in either operating, investing or financing. And we’ll end up with the change in cash, which is kind of like the bottom line. The bottom line will be cashed at the end of the day. So we’re going to find a home for the equipment. Where’s that going to go that change? Well, if we think about the journal entry for equipment, then if we buy equipment, we’re going to debit equipment, and credit cash and possibly credit like a note payable, some type of financing. But if we pay cash for it, this would be the most simplified journal entry. Even if we had a note there’d be no Part of it that would be on the income statement, one asset went up, the other asset is going down. So therefore, is the is an income statement account involved? No. So we’re purchasing or weren’t, so it’s not going to be an operating activity. And then the next question is, are we purchasing or selling an asset? In this case, yeah, we’re purchasing an asset. And that means that it’s going to be an investing activity. So and this was the confusing thing for me when I first started learning this thing, because investing activities, I had a different conception of what investing is to invest in something like any asset any anything we purchase in the business that we’re not consuming now is an investment to the future. In terms of the cash flow statement, we’re trying to spend our cash in order to put our money somewhere that’s going to help us make money in the future. That’s going to be some type of investment. So in this case, it’s going to be an investing activity.
Notes Payable Introduction
In this presentation, we will introduce the concept of notes payable as a way to finance a business. Most people are more familiar with notes payable than bonds payable, the note payable basically just being a loan from the bank. Typically, the bond payable is a little more confusing just because we don’t see it as often, especially as a financing option. From the business perspective, we often see it more as an investing or type of investment. But from a loan perspective, it’s very similar in that we’re going to receive money to finance the business if we were to issue a bond, or if we’re taking a loan from the bank. And then of course, we’re going to pay back that money. The difference between the note and the bond is that one the note is something we typically take from the bank. Whereas a bond is something we can issue to individuals so a bond we could have more options in terms of issuing the bonds than we do for a loan. Typically when we have a loan, we typically are Gonna have less resources, we can take a loan from the bank. When we pay back the bond, we often think of the bond as two separate things. And we set it up as two separate things, meaning we have the principal of the bond that we’re going to pay back at the end. And then we have the interest payments, which are kind of like the rent on the money that we’re getting, we’re getting this money, we’re gonna have to pay rent on it, just like we would pay rent if we had got the use of any physical thing.
Interest Calculations
In this presentation, we will take a look at how to calculate simple interest a few different ways. As we look at this, you may ask yourself, why are we going over this a few different ways, why not just go over it one way, the best way. And let us learn that well and be able to apply it in each situation. While one way does work in most situations. In other words, we will probably learn one way have a favorite way to calculate the simple interest and apply that in every circumstance. It’s also the case that when we look at other people’s calculations or technical calculation, they may have some different form of the calculation. For example, I prefer away when I think about the calculation of simple interest to have some subtotals in the calculation and have more of a vertical type of calculation the way we would see if done in something like a calculator. If we see a type of equation in a book, then the idea there is that Have the most simple type of equation expressed in as short a way as possible. And that typically is going to be some type of formula. And that formula will often not be showing the subtotal.
Receivables Introduction
In this presentation we will take a look at receivables. The major two types of receivables and the ones we will be concentrating on here are accounts receivable and notes receivable. There are other types of receivables we may see on the financial statements or trial balance or Chart of Accounts, including receivables, such as rent receivable, and interest receivable. Anything that has a receivable, it basically means that someone owes us something in the future. We’re going to start off talking about accounts receivable that’s going to be the most common most familiar most used type of receivable and that means something someone, some person some company, some customer typically owes us money for a transaction happening in the past, typically some type of sales transaction. So if we record the sales transaction, that would typically be the way accounts receivable would start within the financial statements, meaning If we made a sale, we would credit the revenue account, we’ll call it sales. If we sell inventory, it would be called sales. If we sold something else, it might be called fees earned, or just revenue or just income, increasing income with a credit, and then the debit not going to cash. But going to accounts receivable.
Statement of Equity From Trial Balance 17
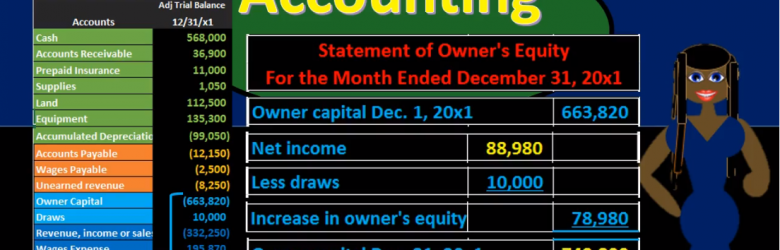
More in this presentation we will take a look at the statement of owner’s equity and see how to construct the statement of owner’s equity from the trial balance. When looking at the trial balance, we can see the accounts will be in order with the assets and then the liabilities, then the equity and then the revenue and expenses. The equity accounts being broken out here of owner capital and draws. But it’s a little deceiving to break out this equity section. Because the trial balance really is showing both a point in time the balance sheet account permanent accounts up top and timing accounts which are going to be the revenue accounts down below. When we think about the point in time for total equity as a whole. We’re really considering the entire blue area here. This is one of the most confusing concepts to really know when you’re looking at these financial statements.