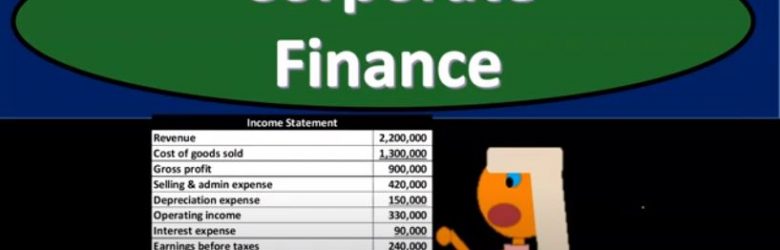
Corporate Finance PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we’re going to continue on discussing the income statement. Get ready, it’s time to take your chance with corporate finance income statement continued. Remember that as we think about the financial statements, we can break them out into basically two objectives that an investor might have the investor would want to know two general things one, where does the company stand at a point in time with their approximate value as of a point in time? And two? What is the likelihood of their performance in the future? What how well, will they do in the future? How can we predict how well they will do, we’re going to base it on past performance. So the point in time statement is going to be the balance sheet. So remember, if you’re looking at financial statements, for the year ended, say, December 31, the balance sheet will be as of a point in time and therefore as of December 31, it will not be a range. Whereas if you’re looking at a time frame, meaning the beginning to the end of the period, so if you’re looking for financial statements for the period ended, or the year ended, December 31, then the income statement, the primary timing statement, will be represented, it’ll say January through December or for the year ended December 31.
Posts with the typically tag
Income Statement Overview 220
Hello in this presentation we will discuss the income statement objectives. At the end of this presentation, we will be able to describe what an income statement is list the parts of the income statement and explain the reasons for an income statement. First, we’ll start off with a question we’ll which will explain the timing of the income statement or introduce us to an explanation of the timing of the income statement? And that is the question of asking somebody, how much do you make when we work through if we were to ask somebody how much they make? They would mentally make some type of assumption in order to answer that question, or they would ask you the question if they chose to answer at all. The question, What do you mean? Do you mean per month? Do you mean per year? Do you mean per week? And this is going to be something that needs to be answered in order to answer the question.
Balance Sheet Continued 215
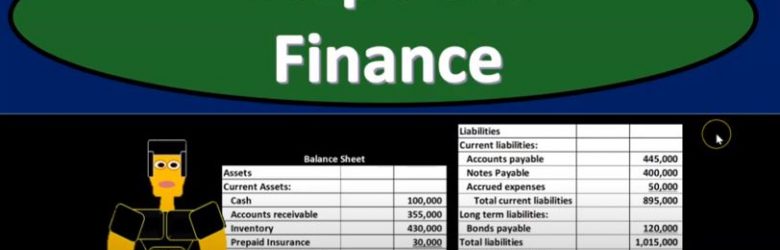
Corporate Finance PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will go into more detail about the balance sheet. Get ready, it’s time to take your chance with corporate finance, balance sheet continued. Remember when we’re thinking about the financial statements, we can break them out to two separate objectives. If we’re considering this from an investor standpoint, that is, where does the company stand at a point in time, and what’s the likelihood or their earnings potential in the future, which we will typically based on past performance, therefore, you’re going to have the timing statement and the point in time type of statement. So when we think about the balance sheet, that’s going to be the point in time type of statements. So if you’re looking at the financial statements for the year ended December 31, the balance sheet will be as of the end of the period, in this case, December 31, as opposed to the timing statements, which are going to be the income statement being the primary statement that should come to mind measuring performance, which will be as of January through December 31 measure and how well we did for that range of time. So our focus over here is going to be on the balance sheet.
Financial Markets 130
Corporate Finance PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will discuss financial markets Get ready, it’s time to take your chance with corporate finance, financial markets, financial markets help to provide indicators for maximizing shareholder value. So when we’re thinking about financial markets, we’re thinking about markets. In general, we’re thinking about purchasing and selling things, a place where people purchase and sell items, that means there’s competition, there’s different people competing within a market, that will typically lead to better information about the value of the items being sold.
Types of Business Organizations 120
Corporate Finance PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will discuss types of business organizations, including the corporation, partnership, and sole proprietorship Get ready, it’s time to take your chance with corporate finance types of business organizations. Now, as we go through here, note that we’re focusing in on corporate finance, and therefore on the corporate type of business organization, but many of the concepts that we will learn will be applicable to all types of business organizations. Therefore, we want to have a general idea of the different main kind of components or main types of business organizations. So those will include a sole proprietorship, partnership, and a corporation.
Finance, Accounting, & Economics 110
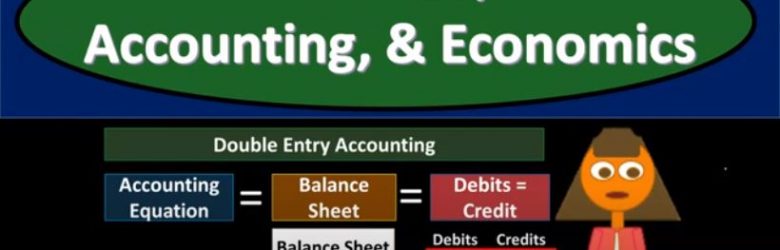
Corporate Finance PowerPoint presentation. And this presentation we will discuss the differences between finance, accounting and economics, the differences between the fields of finance, accounting and economics Get ready, it’s time to take your chance with corporate finance, there’s a lot of overlap and differences between the fields of finance, accounting and economics, what we want to do is think about those differences. And where that overlap is, as we do so we will do so from the perspective of corporate finance, because that’s the objective of our viewpoint here for this particular course.
Consolidations Less Than 100% Owned Subsidiary
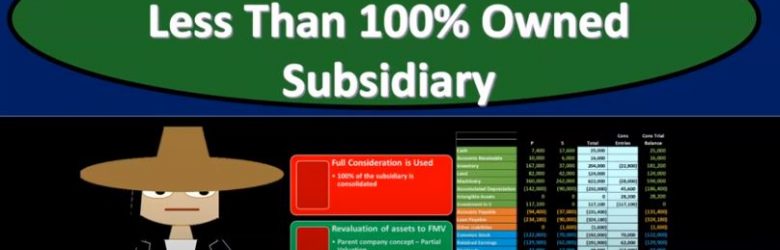
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to discuss the consolidation process for less than 100% owned subsidiary. In other words at the end of this, we’ll be able to understand some of the major differences in the consolidation process from a company that was 100% owned. In other words, the parent owns 100% of the subsidiary and one in which the parent owns some other percent some stock share and percent other than 100%. Get ready to account with advanced financial accounting when there is a controlling interest but less than 100% owned interest in a subsidiary. In other words, the parent company owns something other than 100% of the common stock something over 51% still having a controlling interest still makes sense to do consolidated financial statements, because it’s useful to see the assets minus the liabilities, the net assets that the parent has control over, even if they don’t have claim over them. The performance based on you know, the net assets that they have control over.
Consolidation With Difference Simple Example
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to talk about the consolidation process with a differential we’re going to look at the component parts with a simple example a simple calculation, you’re ready to account with advanced financial accounting, consolidation with differential example. So here’s going to be the basic scenario for many of the practice problems we will be looking with. We have P and S, there’s going to be a parent subsidiary relationship in which we will be making consolidated financial statements. How did this situation take place what constituted this situation, we’re going to say that in this example, P is purchasing the stocks of S. So notice they’re purchasing the stocks of s and therefore negotiating the stock price, which we’re going to say is $1,000 here. Now to simplify this example, you first want to think about this as p purchasing 100% of the stock of s for $1,000. And then once they have control, anything over 51% would then be controlled.
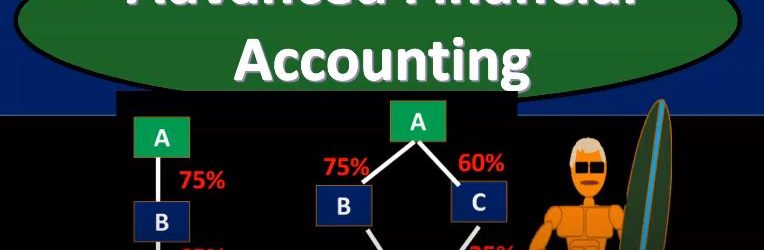
Direct & Indirect Control
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to talk about the concepts of direct and indirect control. If you’re ready to account with advanced financial accounting, we want to consider these concepts within the context of financial statements and consolidation. So you’ll recall that when we have consolidated financial statements, the idea is to put two financial statements together when one company has basically control over another company that being defined typically by having more than 51% interest because if you have more than 51%, then you have basically a voting share for you to vote on anything, then of course, you would win the vote at that point in time. So let’s consider then direct control and indirect control direct control when one company has a majority of another company’s stock common stock. So that would be a situation where you got a and b, one company has a majority interest over 51% control is pretty easy to see at that point. When you start to get into indirect control. This can get more complicated things can get more confusing here. So indirect control, one company’s common stock is owned by one or more other companies that are under common control. So this can get a lot more detailed structure in terms of what is going to constitute control. So for example, if we have direct control, then you have just simply a parent subsidiary type of relationship. And, you know, the parent has more than 51% of the subsidiary, interest common stock. So and that could happen if we have to, we could still have a little bit more complexity here, where we have two subsidiaries, right. But they’re both going to be consolidated in this case, because there’s 75% over 51% direct control is parent over as one direct control over as to here because it’s over the 51%. So both of these cases would be direct control.
Consolidation for Non Wholly Owned Subsidiary
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to talk about a consolidation for a non wholly owned subsidiary. So in other words, we have a parent subsidiary relationship, but the parent doesn’t own 100% of the outstanding common stock of the subsidiary but something other than 100%. In other words, over 51% controlling interest less than 100% get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. Non controlling interest often will be represented NCI non controlling interest. So notice if we have a parent subsidiary relationship we’re talking about there is some controlling interest, the controlling interest is the interest that’s going to be over 51%. However, if we don’t have 100% ownership, then we have the amount that’s not in control and that of course is going to be the non controlling interest. So non controlling interest. NCI controlling interest is needed for consolidation. Obviously, if we’re going to consolidate this thing, that means typically that A parent has some controlling interest over 51% a 100% is not needed. So 100% of ownership, in other words, by one parent to the other is not necessary for a consolidation to take place control is necessary, which is typically over 51% less than 100% ownership will result in a non controlling shareholder, those other than the parent.