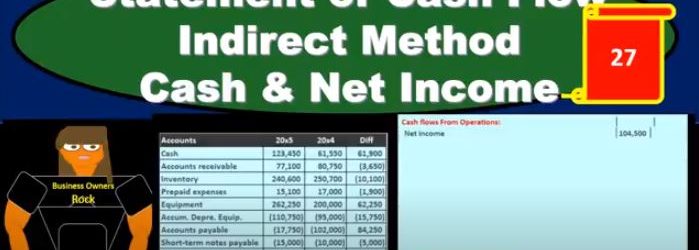
This presentation, we will start to construct the statement of cash flows using the indirect method focusing in on cash and net income. This is going to be the resources we will have, we’ll have that comparative balance sheet, the income statement, and we’re gonna have some added information. In order to construct the statement of cash flows, we’re mainly going to be working with a worksheet that we’ve put together from a comparative balance sheet. That’s where we will start. So we’re going to find a home, this is going to be our worksheet. We have the two periods. So we have the current year, we’ve got the prior year, and we’ve got the difference between those activities. Now our goal here is to basically just find a home for every component on this difference section. So that’s going to be our home. Why? Well, we can first start thinking about cash. What are we going to do with cash? That’s the main thing. This is a statement of cash flows here. So where are we going to put cash? that’s actually going to start at the bottom, we’re going to say that’s going to be our in numbers. In number we know it’s going to be cached. Now, we’re going to recalculate it. But it’s useful for us to just know and we might just want to put there, hey, that’s where we’re going to end up. That’s where we are looking to get. And now what we really want is the change.
Posts with the Balance sheet tag
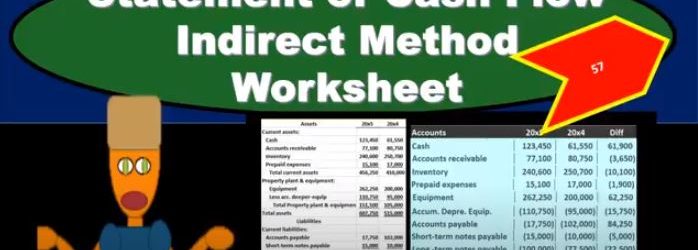
Statement of Cash Flow Indirect Method Worksheet
In this presentation, we will put together a worksheet that will then be used to create the statement of cash flows using the indirect method. To do this, we’re going to use our resources which will include a comparative balance sheet, and income statement and added information. Remember that in practice, we’re typically going to have a comparative balance sheet RS here being for the current year 2005 and 2000. x for the prior year. So we need a comparative to time periods in order to create our worksheet. This will be the primary components that we’ll use to create our worksheet. We will need the income statement when I’m creating the statement of cash flows mainly to check up on some of the differences that we will have in our worksheet. And then in a book problem will typically be told some other things related to for example, purchases of or sales of equipment, borrowings, if we had any cash dividends or any dividends at all, this is added information we would Need. In practice, of course, we would just be checking on these things by looking at the difference and going back to the GL. And just taking a look at those differences in order to determine if we have any added information that needs to be adjusted on our statement of cash flows.
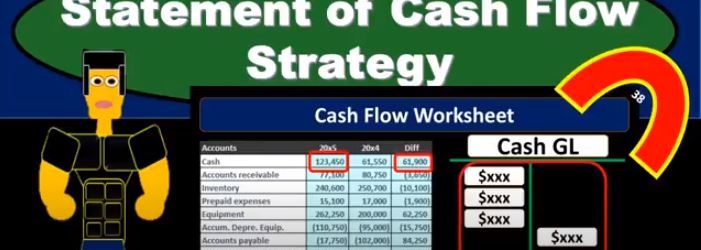
Statement of Cash Flow Strategy
In this presentation, we will take a look at strategies for thinking about the statement of cash flows and how we will approach the statement of cash flows. When considering the statement of cash flows, we typically look at a worksheet or put together a worksheet such as this for my comparative balance sheet, that given the balance sheet accounts for the current year and the prior year or the current period, and the prior period, and then giving us the difference between those accounts. So we have the cash, we’ve got the accounts receivable inventory, we’re representing this in debits and credits. So this is in essence going to be a post closing trial balance one with just the balance sheet accounts, the debits represented with positive and the credits represented with negative numbers in this worksheet, so the debits minus the credits equals zero for the current year, the prior year. And then if we take the difference between all the accounts, and we were to add them up, then that’s going to equal zero as well. This will be the worksheet that we’re thinking about. Now. When can In the statement of cash flows, we can think about the statement of cash flows in a few different ways. We know that this, of course, is the change in cash, this is the time period in the current time period, the prior year, in this case, the prior period, the difference between those two is the difference in cash.
Statement of Cash Flow Tools For Completion
This presentation we will take a look at the tools needed in order to complete a statement of cash flows. to complete a statement of cash flows, we are typically going to need a comparative balance sheet that’s going to include a balance sheet from the prior period, whether that be the prior month or the prior year and a balance sheet from the current period, then we’re going to have to have an income statement. And then we’ll need some additional information in a book problem, it’ll typically give us some additional additional information often having to do with things like worth an equipment purchases, whether equipment purchases or equipment sales, were their investments in the company where their sales of stocks, what were the dividends within the company. In practice, of course, we would have to just know and recognize those types of areas where we might need more detail. And we would get that additional information with General Ledger we’d go into the general ledger, look at that added information. Now once we have this information, our major component we’re going to use is going to be the comparative balance sheet. That’s where we will start. So that comparative balance sheet is going to be used to make a worksheet such as this.
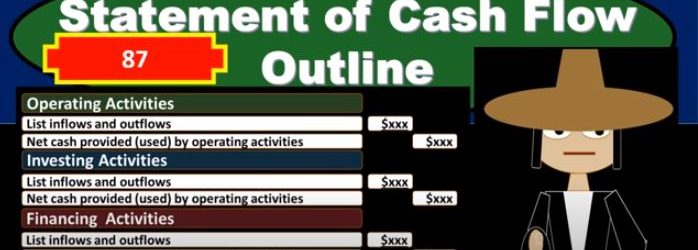
Statement of Cash Flow Outline
In this presentation, we will take a look at a basic outline for a statement of cash flows. In order to do this, we first want to give an idea of how the statement of cash flows will be generated. So we can think about these components of the statement of cash flows and where they come from. Typically, we will have a worksheet such as this that we will use in order to generate the statement of cash flows. That statement of cash flows, having three major components, operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. Our goal here is going to be to fill out these three components and typically we will use a worksheet such as this on the left. The worksheet is just basically a comparative balance sheet that we have here that we’ve reformatted from a balance sheet to just a trial balance type format, a debit and credit type format. So you can see that we have our balance sheet accounts, and we are imbalanced by having the debits the positive and the credits be negative or debits. Minus the credits equaling zero, given it’s an indication that this period, the current period that we are working on, is in balance, the prior period, same thing. So we have two points in time for to balance sheet points the prior year, or period the prior year in this case and the current year. And then we just took the difference between these two columns. And if we have something that’s in balance, here, the debits minus the credits equals zero, something that’s in balance here, the debits minus the credits equals zero. And then we take the difference of each line item in these columns. And some of those differences, it too must add up to zero. So in essence, what we’re going to do in order to create the statement of cash flows is find a home for all these differences. And that’ll give us a cash flow, a concept of the cash flow statement. We’ll get into more detail on how to do that when we create the cash flow statement. But as we look at the outline, keep that in mind. So here’s going to be the basic outline for the state. cash flows, we’re going to have the operating activities. That’s going to include a list of inflows and outflows from the operating activities. And then we’re going to have the net cash provided by the operating activities. Now, this list of inflows and outflows for the operating activity will be the most extensive list because the operating activities are in relation to you can think of it as similar to the income statement.
Statement of Cash Flows Introduction
In this presentation, we will introduce the financial statement of statement of cash flows. When thinking about the statement of cash flows, we want to compare and contrast the reasons for it to what the other financial statements are providing us what information in other words, are we going to get from the statement of cash flows that’s not on the other financial statements, those being the balance sheet, the income statement, the statement of equity, we’re mainly comparing against the income statement, because the statement of cash flows going to give us some similar information. It’s going to give us information over time, what’s happening over time, unlike the balance sheet, which is going to have a point in time. So we’re still looking at at timing what is what is going on over time. That’s typically our income statement, which measures performance. The major goal of the income statement is to measure performance, how have we done how much work have we done, revenue minus expenses, revenue being recognized when we earn the work when we’ve done the job expenses when we We’ve incurred something in order to help generate in the same time period. And that’s going to be the net income. What that doesn’t do, however, is measure cash flow. And when we first learn about the income statement, that’s going to be a real big distinction we want to look at, we want to say, okay, the income statements on an accrual basis.
Allowance Method % Accounts Receivable vs % Sales Method
In this presentation, we will be taking a look at the allowance method for accounts receivable focusing in on the calculation of the allowance for doubtful accounts. There are two methods that can be used in order to calculate the allowance for doubtful accounts accounts. One being the percentage of accounts receivable, the other is the percentage of sales, we will take a look at them both and look at the pros and cons of them. First, we’re going to look at the accounts receivable method. We’re going to start off with the percentage of accounts receivable method for a few different reasons. One, it’s the one that’s most often tested. And two is the one that may be most often used in practice often making the most sense to people that are looking at the two methods. It’s also a bit more complicated. So when we’re looking at test questions, they typically would focus on this method in order to have a bit more complicated process to do the calculation.
Inventory Methods Explained and compared FIFO LIFO 15 600
Hello in this lecture we’re going to talk about estimating inventory methods methods such as first in first out last in first out and the average method. Last time we talked about specific identification when we were selling the inventory of forklifts. We use specific identification meaning we had an ID number for each particular forklift and knew exactly which forklift we sold and the cost of that particular forklift. reason that makes sense for forklifts is because they’re relatively large, they could be distinct in nature, and they have a fairly large dollar amount in comparison to other types of inventory. If we’re selling something else, like coffee mugs over here, we may have a large amount of coffee mug they may be all completely the same.
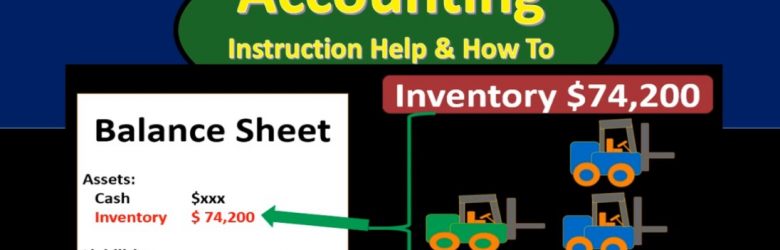
Inventory Tracking Explained – Introduction-Specific 10 600
Hello. In this lecture we’re going to talk about the idea of tracking inventory and recording inventory, both in terms of the balance sheet as well as the income statement in the format of cost of goods sold. In our example, we’re going to be purchasing and selling forklifts, meaning we’re going to purchase forklifts from the factory and then we’re going to sell those forklifts. That means that forklifts to us will be inventory their inventory because we are purchasing the forklifts in order to resell them for the generation of revenue. That’s really going to be the definition of inventory the purchasing of something for the resale of it as opposed to if we were someone else purchasing the forklift in order to help us generate revenue in another way through the use of the forklift, in which case it would then be property plant and equipment.
Accounts Payable AP Subsidiary Ledger 6
Hello. In this lecture we’re going to talk about the accounts payable subsidiary ledger accounts payable subsidiary ledger will be backing up the accounts payable account on the trial balance or the balance sheet. As we can see in the example here we have a balance of 1640 in accounts payable. If an owner asks the question of how much money do we owe to vendors? The answer would then be 1006 40, which we can see on the balance sheet or the trial balance. But the next question that will follow will be who do we owe that money to? And how do is it which of these vendors should we be paying? First? In order to answer that question, we may try to go to the detailed account, which is the general ledger. Typically every account is backed up by the general ledger, we can see that we have the same balance here and we can see that we have activity however, the activity is in order by date. And that’s not really helpful for us to determine who exactly we still owe at this point in time. In order to determine who we owe, we need to organize this information.