Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will discuss foreign currency transactions get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, foreign currency transactions. So remember when we’re thinking about foreign currency transactions, we’re thinking about them from the perspective of the US company in US dollar. So we’re have our currency that we’re making our financial statements in, we’re measuring all the stuff on our financial statements with the measuring tool that we need to be using, that’s going to be the US dollar, that’s going to be our standardization. And then anytime we have foreign currency transactions with something other than US dollars, then we want to see them from that perspective, right? Because when we put them on our financial statements, just like anything else, just like inventory, if we were to value units of inventory, or to value stocks and whatnot, we need to value them in terms of our measure into a which of course is the US dollar.
Posts with the foreign currency tag
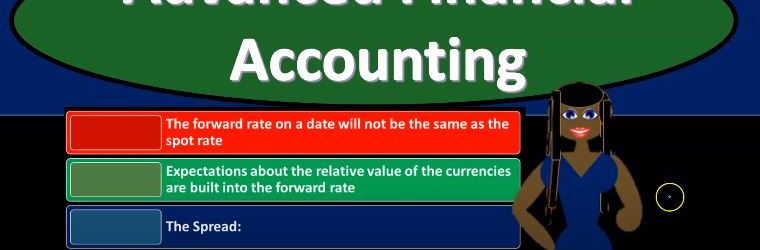
Foreign Currency Exchange Rates
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we’re going to discuss foreign currency exchange rates get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, foreign currency exchange rates, let’s first define foreign currency transactions. So what are from foreign currency transactions? When are we going to need to account for foreign currency transactions. So from our perspective, we’re going to be looking at this from the perspective of a US company US company that is having their books then accounted for or measured in dollars. And when you think about the foreign currency transaction, it’s just like anything else, but it can be a little bit more confusing. So you want to remember, of course, that the dollar is basically the measuring tool.
Other Foreign Operations Issues
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss other foreign operations issues, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, other foreign operations issues. So we’re going to start off with an issue related to the parent company having a foreign subsidiary. Typically when that is the case, they’re going to have to consolidate. In other words, you’re going to have to get the foreign subsidiary books in some way to the US dollar and then do the consolidation process. However, you might have a situation where that wouldn’t take place under certain conditions. So, parent generally consolidates a foreign subsidiary except when certain conditions are so severe that the US company owning the foreign company may not be able to exercise the necessary level of economic control. So notice when we think about the consolidation process, we’ll typically think about, we need to consolidate the entities if there’s control right over the 51% is that going to be a general rule but the overarching concept is that there is control. Now if there are certain conditions even though it’s the ownership is over the 51%, we would think there would be control, but there are certain conditions in the foreign subsidiary that are restricting that economic control, then then they might not meet you know that condition and therefore in that situation you might not have the consolidation process. So in that situation then you might have a parent company that has basically a controlling interest you would think in terms of the stock, the stock but you’re not having a consolidation due to the due to one of these factors limiting the actual economic control. So, those include restrictions on foreign exchange in foreign country. So severe strict restrictions, there could be one of the items that would stop the basically consolidation process possibly restrictions on transfers of property in foreign country.
Remeasure Financial Statement of Foreign Subsidiary
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss the remeasurement process for financial statements of a foreign subsidiary. Get ready to account with advanced financial accounting remeasurement financial statement of foreign subsidiary remeasurement overview so we’re going to go through the process of the remeasurement. As you think of the measurement process, you want to be comparing and contrasting it to the translation process. So you’re envisioning basically you got a parent company. The parent company has a subsidiary the subsidiary is a foreign subsidiary. The subsidiary then conducts their books. Typically we’re thinking in a foreign currency right, that subsidiary is conducting their books in a foreign currency. If we need to consolidate the subsidiary into the parents financial statements, the parent uses dollars to measure their books subsidiary uses a foreign currency on the bookkeeping side, how do we get them over $2 so we can do the consolidation process. two methods generally we can use a translation method or a remeasurement method, and we have to determine which method we’re going to use by determining what the functional currency is. And once we know what the functional currency is, then we can determine whether we need to use the translation method or the remeasurement method. And they’re going to be slightly different. Now note, there’s also a third kind of option where we might have to use translation and remeasurement if there was a situation where the foreign currency has the financial statements, and something other than the US dollars and then the functional currency was not the currency that their bookkeeping was in, and it’s not the US dollar.
Translation vs Remeasurement
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss translation versus remeasurement. Get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, translation versus remeasurement methods to restate to foreign entities statements to US dollar. So the most straightforward methods can be translation of foreign entities functional currency statement to US dollars. So the translation is what we’ll use the most straightforward method when the entity statement is using the functional currency. So typically, if the if the entity is using the functional currency, and we need to translate it, then we’ll simply translate it from the functional currency to the US dollars. And then there’s remeasurement of foreign entities statement into its functional currency. So remeasurement means that the entity is running their bookkeeping in a currency that is not the functional currency. Right? So then we’re going to have to re measure we’re going to use this term re measure rather than translate the To the functional currency, so after we remeasure to the functional currency, after remeasurement statements need to be translated to the reporting currency if the functional currency is not the US dollar. So in other words, if we’re assuming, in this case, in the case of the remeasurement, or let’s say, we have an entity that we’re going to be consolidating a subsidiary entity in another country, and we’re in the US and we need to basically consolidate these data together in terms of US dollars at the end of the day, if the entity is using the functional currency as as their financial statements, their bookkeeping is in the functional currency, then we can simply use the term translate it to the US dollars, which will be the parent currency that we’re talking about here. If however, the foreign entity is having their books in some currency, that is not the functional currency, then what we’re going to have to do is re measure it. We want to use remeasurement To the functional currency, we want to make remeasure at first to the functional currency rather than straight to the US dollar. So we’re going to use remeasure to the functional currency. And after we re measure to the functional currency, if the functional currency is the US dollar, then then we should be able to stop there. That’s okay. If however, the functional currency is not the US dollar, then we would have to go from the functional currency and then translate to the US dollar. So we’ll talk a little bit more about that as we go. So let’s think about translation.
Functional Currency
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss functional currency get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, functional currency. When financial statements are restated from a foreign currency into US dollars, we must consider which exchange rate should be used to translate the foreign currency amounts to the domestic currency. So, when we translate the foreign currency to the domestic currency, we’ll have to determine what our exchange rate Are we going to be using in order to do so how will we account for translation gains and losses? So if there’s going to be a translation gain or loss, what are we going to do with that? In other words, should we put the translation gains and losses as part of the income statement reporting it on the income statement, the gains and losses that are due to the translation process exchange rates that may be used? So what kind of exchange rates might we use during this exchange process? Well, we could use the current rates probably the first thing that comes to mind you say, Hey, we got the financial status. As of the year ended of this time period, why don’t we just use the current rate. And that’s typically what we will do for the balance sheet amounts. And that typically makes sense for the balance sheet amounts, because remember, the financial statements, of course on the balance sheet represents where we are at a particular point in time. So simply converting them makes some sense on the balance sheet. But you also might think, Well, what about those things, you know, that we purchased, like fixed assets at a point in time, maybe we should use the point in time that we had the purchase took place. So you could argue on that on the balance sheet, but the current rate on the balance sheet and makes the most sense, but if you’re looking at the income statement, the current rate might not make as much sense because we’re measuring a timeframe that from a year will, let’s say, for a year’s timeframe from the beginning to the end, so maybe it doesn’t seem quite right to use simply the current rate, which would be the rate as of the end of the financial statements if we’re talking like December 31, rather than using some type of race. That would be representative of the period that would covered being January through December, we could use the historical rate, that’s gonna be the rate that exists at the time the initial transaction took place. And again, this one is often would make sense to us if we’re talking about a situation like if we bought equipment or something like that fixed assets, property, plant and equipment, large purchases that are on the books, we might say, well, maybe we should be putting those on the books at the rate that we should be using at the time, basically, the transaction took place. So maybe we would argue for the historical right there. And then we have the average rate for the period, generally a simple average for a period of time, usually the exchange rate used to measure revenues and expenses.
Forward Exchange Contracts
Advanced financial accounting a PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will discuss forward exchange contracts get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, forward exchange contracts. Now we’re going to go over some of the components of the foreign exchange contracts here, we’ll go into them on a lot more detail as we work through practice problems related to the forward exchange contracts. But just to visualize the basic kind of layout of a foreign exchange contract as you think about these items, and there’ll be a lot more concrete once we look at practice problems, we’re basically have a setup where we’re going to be working with a bank or a dealer, typically a bank, and we’re going to be setting up a foreign exchange contract which is basically going to say, we have a receivable and payable on the books at this point in time and we’re either going to put the receivable or the payable that is going to be due to us or something that we will pay in foreign currency at the end of the time period. Whereas the other side the receivable or the payable, the other side that’s not in foreign currency will be in US dollars. In other words, we We will determine the amount that will that we’re talking about. And then we’ll use an exchange rate which we’ll talk a little bit more about the exchange rate that we will use to value it in today’s dollars will put either the receivable or the payable in US dollars and either the receivable or the payable and foreign dollars as of this point in time. And then as time changes, as the rate of the foreign currency changes, then that could result in the difference between, you know, what we thought the value would be, at the point in time we went into the forward contract between the US dollar and the foreign currency as that difference changes over time that could result in basically a gain or loss.
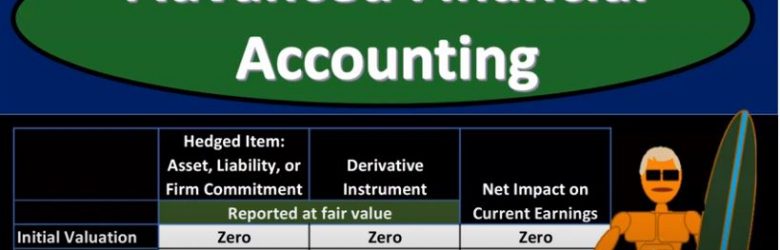
Forward Exchange Financial Instruments
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss forward exchange of financial instruments get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, forward exchange financial instruments let’s start off with some definitions starting off with financial instrument itself will be either cash evidence of ownership or a contract that imposes on one entity on contractual obligation to deliver cash or another instrument and conveys to the second entity, the contractual right to receive cash or another financial instrument. That of course, being the most complex component here. So let’s read that one more time. The financial instrument a contract that imposes on one entity a contractual obligation to deliver either cash or another instrument and conveys to the second party the second party in this item, the second entity, the contractual right to of course, receive the cash or another financial instrument derivative. So a derivative, financial instrument or other contract whose value is derived from some other item that has a value that varies over time. So let’s think about that one more time again, derivative financial instruments or other contracts whose value is derived from, they’re going to get the value from some other item that has a value. That is that varies over time, meaning of course, that it will be changing over time. So let’s think about the derivative characteristics. And then we’ll apply these to the component of what we’re considering here. foreign currency and foreign currency transactions in terms of typically foreign currency type hedge transactions.
Other Foreign Operations Issues
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss other foreign operations issues, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, other foreign operations issues. So we’re going to start off with an issue related to the parent company having a foreign subsidiary. Typically when that is the case, they’re going to have to consolidate. In other words, you’re going to have to get the foreign subsidiary books in some way to the US dollar and then do the consolidation process. However, you might have a situation where that wouldn’t take place under certain conditions. So, parent generally consolidates a foreign subsidiary except when certain conditions are so severe that the US company owning the foreign company may not be able to exercise the necessary level of economic control. So notice when we think about the consolidation process, we’ll typically think about, we need to consolidate the entities if there’s control right over the 51% is that going to be a general rule but the overarching concept is that there is control. Now if there are certain conditions even though it’s the ownership is over the 51%, we would think there would be control, but there are certain conditions in the foreign subsidiary that are restricting that economic control, then then they might not meet you know that condition and therefore in that situation you might not have the consolidation process. So in that situation then you might have a parent company that has basically a controlling interest you would think in terms of the stock, the stock but you’re not having a consolidation due to the due to one of these factors limiting the actual economic control. So, those include restrictions on foreign exchange in foreign country. So severe strict restrictions, there could be one of the items that would stop the basically consolidation process possibly restrictions on transfers of property in foreign country.