Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss the process of registering securities with the SEC, the Securities and Exchange Commission get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, issuing securities. If a company wants to sell debt or stock securities in interstate offerings to the general public, they are usually required by the Securities Act of 1933 to register those securities with the SEC. So one more time, we’re talking about the issuing of securities if a company wants to sell debt or stocks securities in interstate offerings to the general public, so now we got the interstate offerings going to the general public, in order to have that benefit. They are usually required by the Securities Act of 1933 to register those securities with the SEC. And you can see we saw a little bit of history in the prior presentation on how this could develop. Obviously, it’s going to be a benefit to the businesses in order to To generate capital typically to be able to offer the stock to the general public in interstate offerings. But in order to do so then you would think you’d want to have some transparency that will be involved in it so that both sides of the negotiation will be involved. That’s where the SEC came into play here. So we talked a bit about the SEC and its role in a prior presentation we’ll get more into the process of the registration here. General financial statement required for this process will typically include two years of balance sheets three years of statements of income, three years of statements of cash flows, three year of statement of stockholders equity, prior years statements are generally presented on a comparative basis with the current years it will typically have a comparative basis. For the for the comparative years prior and current year.
Posts with the information tag
SEC Structure & Regulatory Authority
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss sec structure and Regulatory Authority get ready to account with advanced financial accounting in sec structure and regulatory authority, Securities and Exchange Commission the SEC What is it? It’s an independent federal agency It was created in 1934. It’s going to regulate and it does regulate the securities markets, the SEC helps maintain an effective marketplace for companies issuing securities and for investors seeking capital investments. Now we’ll take a look at a brief history of leading up to the creation of the SEC and a little bit about the SEC itself. So if we have an understanding of the history, then it gives us a little bit better of an understanding of why the SEC does what it does today and how it how it was created or came to be. So in 1792, was when the New York Stock Exchange was created to function as a clearing house. For the securities trades between its invit its investors. So now we have the New York Stock Exchange that will function as the clearing house. But then in 1911, states started to pass, quote, blue sky laws in quotes to help regulate the offerings of securities by companies without a solid financial base. So in other words, they saw a need for regulation, now that you have the securities that are on the New York Stock Exchange and can then be offered basically, to more to the public, more people will have access to purchasing them and putting capital into the market, then there’s a lack of transparency, the people that are putting money in maybe doing it solely on speculation, and we don’t have the information to really support the claims possibly that could be made by the stocks that are that are being traded and therefore, you could have situations and did have situations where you had stocks that had no supporting you know, value or very little supporting value to them.
Enterprisewide Disclosures
Advanced financial accounting a PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss enterprise wide disclosure, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. enterprise wide disclosures established by ASC 280 standards provide users more information about the company’s risks generally made in a footnote to the financial statements. First category of required information to include under ASC 280 is information about products and services so information about products and services disclosure related to them. Companies are generally required to report revenues from external customers for each major product and service or each group of similar products and services. Unless doing so is not practical. primary reason for this is that the company could have organized its operating segments on a different basis from the organization of the entities product lines. So we’ve got then again, companies are generally required to report revenues and external customers for each major product and service. You might be saying, hey, well, they already have the segment’s reporting. But it’s possible that those two things don’t exactly line up in the way they put the segment reporting together and therefore, you know, you have this requirement. second category of required information to include under ASC 280 is going to be related to geographic areas information. The following needs to be reported unless it would be impractical to do so. revenues from external customers attributed to the company’s home country of domiciled revenue from external customers attributed to all foreign countries in which the enterprise generates revenues.
Threshold Tests for Segment Reporting
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss threshold tests for segments reporting, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting threshold tests for segment reporting separate supplemental disclosures that need to be made for separately reportable operating segments. So we’ve got these separately reportable operating segments, we have to then determine what type of reporting needs to be taking place for them. determining if a segment needs separately reported information. There are 310 percent quantitative rules FA SB specifies separate disclosure is needed for any segment that meets at least one of the three tests that follow. So we have the segment we got to think about Okay, do we need separate disclosure for this segment, and in order to determine that we’re going to use these 310 percent tests, they only need to meet one of these tests in order for the separate disclosure to be necessary that being 10% revenue test 10% profit or loss test and 10% assets tests. We’re going to go into more detail on each of these tests. Now some we’re going next slides we’ll be focusing in on these three items. So we’re going to start of course with the 10% revenue test. If an operating segments revenue, including both external sales and intersegment sales or transfers is 10% or more of total revenues from external sales plus intersegment. transactions of all operating segments, then segment is separately reported and supplemental disclosures must be provided for it in the annual report so that we have the 10% of revenue basically top line of course on the income statement to determine if the segment is separately reportable. Then we have the 10% of profit and loss. So now the next test now looking at the bottom line, of the income statement, as opposed to The top line if the absolute value of the segments profit or loss or absolute value, so, if we have a income or loss is 10% or more of the higher in absolute value of a the total profit of all operating segments that did not report a loss or be total loss of all operating segments that did report a loss, then the segment is separately reportable and supplementary disclosures must be provided for it in the annual report. So, you can think about these tests you got the 10% of the top line of the income statement, the revenue, basically 10% of the bottom line, profit or loss on the income statement. Now, we’re looking at the balance sheet 10% of assets tests. If these segments assets are 10% or more of the total assets of all operating segments, then the segment is separately reportable and supplementary disclosures must be provided for it in the annual report.
Segment Reporting Overview
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will give an overview of segment reporting, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, overview segment reporting. So when we think about segment reporting, we’re thinking about a company breaking that company into the segments. And when we think about the segments, two questions we want to consider are what is a segment? How does one qualify or how does a segment qualify as a segment and once qualifying for a segment, then what are going to be the financial reporting that needs to be done for the segment? So three characteristics of an operating segment, the component units, business activities, generate revenue and incur expenses. So the component unit that unit you can think about like a separate unit incurs revenue and has expenses including any revenue or expenses in transactions with other business units of the company? So we’re including the transactions if you’re thinking about it as a different segment, a different unit? You’re thinking okay, they have revenue and expenses with In the revenue worth, we’re also including any revenue or expenses, in transactions with other business units of the company. So you’re kind of thinking about a segment as being somewhat autonomous in and of itself here, and therefore having its own basically revenue and expenses, although it can be connected to other segments, the component units, operating results are regularly reviewed by the entities Chief Operating mark, operating decision maker.
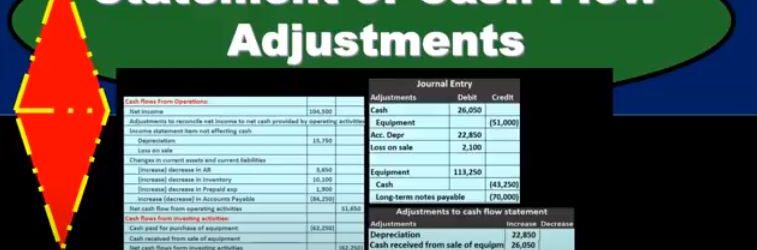
Statement of Cash Flow Adjustments
This presentation we will continue on with our statement of cash flows, we’re not going to enter the final adjustments that we will need to finalize the statement of cash flows to bring those last few numbers to the correct balances. In order to do that, we’re going to use this information we’ve got our comparative balance sheet, our income statement and additional information. We put together most of our information so far with the comparative balance sheet, which we made into a worksheet. Now we’re going to use some of these other resources, the income statement, the additional resources to make those final adjustments, those fine tunings that are needed to get those few numbers that we have left and noted into balance. And this is going to be part of the normal practice where once we get this information set up, we can then make some comparisons such as net income does it tie out, such as depreciation does it tie out on the cash flow statement to what we see here on the income statement, then we can have this other information which will be given in both problems in practice, of course, we’ll just go to the gym. General Ledger. And we’ll get this information in a book problem, we don’t want to give all the detail of a general ledger or just when we’re going over an example.
Accounting Cycle Steps in the Accounting Process
Hello, in this presentation, we’re going to be talking about the accounting cycle or the accounting process, that process that the accounting department will go through on a systematic basis over and over and over again, typically thought of as a monthly process. Although it could be thought of as a yearly process or some other process in terms of the amount of time that will pass. But these are going to be the steps that we’ll be going through in terms of the accounting process, always keeping in mind that in goal of financial accounting, which are the financial statements, some texts will have more steps than five as we have here. Some texts will have less than five steps. But the goal here is to really have a broad picture big picture, so that when we think about the accounting process, we can break down that that big picture view, five is a pretty good number for us to be able to memorize and keep in our mind if we have more than that, it can start to kind of muddy the picture.
Statement of Cash Flows Introduction
In this presentation, we will introduce the financial statement of statement of cash flows. When thinking about the statement of cash flows, we want to compare and contrast the reasons for it to what the other financial statements are providing us what information in other words, are we going to get from the statement of cash flows that’s not on the other financial statements, those being the balance sheet, the income statement, the statement of equity, we’re mainly comparing against the income statement, because the statement of cash flows going to give us some similar information. It’s going to give us information over time, what’s happening over time, unlike the balance sheet, which is going to have a point in time. So we’re still looking at at timing what is what is going on over time. That’s typically our income statement, which measures performance. The major goal of the income statement is to measure performance, how have we done how much work have we done, revenue minus expenses, revenue being recognized when we earn the work when we’ve done the job expenses when we We’ve incurred something in order to help generate in the same time period. And that’s going to be the net income. What that doesn’t do, however, is measure cash flow. And when we first learn about the income statement, that’s going to be a real big distinction we want to look at, we want to say, okay, the income statements on an accrual basis.
Accounts Receivable AR Subsidiary Ledger Explained
Hello, in this lecture we’re going to talk about the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger, the subsidiary ledger being the ledger that will be backing up the account of accounts receivable showing on the trial balance with 27,000. In it, in this case, accounts receivable being that accounts that represents what is owed to us. If we were the owner of the company, we might ask our accounting department, how much money do people owe us? In this case, it would be 27,000 would be the reply. Next follow up question would most likely be who owes us that money? And have we called them when are we going to get paid that money? In order to answer that question, we cannot look at the normal backup balance for all accounts that being the general ledger accounts. If we look at the GL we do get some detail in terms of the activity that has happened. However, that activity is not going to be in terms of who owes us the money. It’s in terms of date.
Cash Disbursements Internal Controls
In this presentation, we’re going to talk about Cash Disbursements, internal controls. Now we’re going to talk about a voucher system for the payment process. But before we get too into the voucher system, note that the systems will change depending on the type of organization and what industry we’re in and how large the organization is. So if we just have a small organization, then we probably just want to have some internal controls for the owner of the company, the owner, being a key component of the internal control system and having a lot more oversight over many of the things that happened. For example, for the payments that happen, we may have someone that requests something on an employee that wants to request a payment may even you know, enter the payment into this system. However, we want to make sure that the owner still has some control over such as the cheque signing.