In this presentation, we will take a look at notes receivable. We’re first going to consider the components of the notes receivable. And then we’ll take a look at the calculation of maturity and some interest calculations. When we look at the notes receivable, it’s important to remember that there are two components two people, two parties, at least to the note, that seems obvious. And in practice, it’s pretty clear who the two people are and what the note is and what the two people involved in the note our doing. However, when we’re writing the notes, or just looking at the notes as a third party that’s considering the note that has been documented. Or if we’re taking a look at a book problem, it’s a little bit more confusing to know which of the two parties are we talking about who’s making the note who is going to be paid at the end of the note time period? We’re considering a note receivable here, meaning we’re considering ourselves to be the business who is going to be receiving money. into the time period, meaning the customer is making a promise, the customer is in essence, we’re thinking of making a note in order to generate that promise, that will then be a promise to pay us in the future.
Posts with the note tag
Allowance Method Accounts Receivable-financial accounting
Hello in this presentation we’re going to take a look at the allowance method which is of course related to the accounts receivable account, we will be able to define the allowance method record transactions related to recording bad debt recording the receivable account that has been determined to be uncollectible recording every single account that has been collected after being determined that it was uncollectible. So we’re going to take a look at some different transactions, the most common transactions when dealing with the allowance method and see what those look like and why we use the allowance method. We’re going to work through a problem. So what we’re going to have here is we’ve got our accounting equation, of course we have our trial balance, I do suggest working problems to take a look at a trial balance because it can give you the context in which to work problems. So here’s what we have. We’ve got the assets in green, the liabilities are going to be orange, the light blue is the capital account and the equity section.
Receivables Introduction
In this presentation we will take a look at receivables. The major two types of receivables and the ones we will be concentrating on here are accounts receivable and notes receivable. There are other types of receivables we may see on the financial statements or trial balance or Chart of Accounts, including receivables, such as rent receivable, and interest receivable. Anything that has a receivable, it basically means that someone owes us something in the future. We’re going to start off talking about accounts receivable that’s going to be the most common most familiar most used type of receivable and that means something someone, some person some company, some customer typically owes us money for a transaction happening in the past, typically some type of sales transaction. So if we record the sales transaction, that would typically be the way accounts receivable would start within the financial statements, meaning If we made a sale, we would credit the revenue account, we’ll call it sales. If we sell inventory, it would be called sales. If we sold something else, it might be called fees earned, or just revenue or just income, increasing income with a credit, and then the debit not going to cash. But going to accounts receivable.
Last In First Out LIFO Periodic
In this presentation we will discuss the lastin first out inventory system on a periodic basis rather than a perpetual basis. As we go through this process, we want to always be comparing those to one, the LIFO or lastin first out system to other systems such as first in first out and average, as well as comparing the perpetual system to the periodic system. We’re going to go through this by looking at a problem the problem going into a worksheet such as this, I do recommend learning this worksheet. This worksheet should look repetitive if you seen the first in first out presentation as well as presentations for the perpetual system.
First In First Out (FIFO) Periodic System
In this presentation we will discuss first in first out or FIFO using a periodic system as compared to a perpetual system. As we go through this, we want to keep that in mind all the time that been that we are using first in first out as opposed to some other systems lastin first out, for example, or average cost, and we’re doing so using a periodic system rather than a perpetual system. Best way to demonstrate is with examples. So we’ll go through an example problem. We’re going to be using this worksheet for our example problem. It looks like an extended worksheet or large worksheet, but it really is the best worksheet to go through in order to figure out all the components of problems that deal with these cost flow assumptions, including a first in first out lastin first out, or an average method, and using a periodic or perpetual for any of them.
Cash Receipts Journal 40
In this presentation we will talk about the cash receipts journal. The cash receipts journal will be used when we have cash receipts when using a more of a manual system or a data input system that we will be doing by hand as opposed to an automated system. It’s still useful to know the cash receipts journal if using an automated system for a few different reasons. One is that we might want to generate reports from an automated system, similar to what we would be creating in a manual system for a cash receipts journal. And to it’s just a good idea to have different types of systems in mind, so we can see what’s the same and what is different between different accounting systems. The cash receipts journal will be used for every time we have a cash receipts. So the thing that transaction triggering a cash receipt will be when cash is being used. And we’re going to have a little bit more complex complexity in a cash receipts journal than something like a sales journal because we may be receiving cash for multiple different things.
Sales Journal Service Company 10
In this presentation, we will take a look at the sales journal for a service company. We’ll use the sales journal in a manual system or a system we do by hand. When we make sales. However, it’s a little bit more complicated than that because if sales journal really means sales that we make on account, meaning we’re not receiving cash at the point in time we make the sale. If we do receive cash at the point in time we make sale even though we have sales being recorded or revenue accounts being recorded. It should be going into the cash receipts journal, because that’s the journal we use whenever we get cash. So the better term for this journal may be something like accounts receivable, or more specifically, sales made on accounts or sales and accounts receivable, but it’s typically called the sales journal. So don’t let that confuse you.
Income Statement from Trial Balance 16
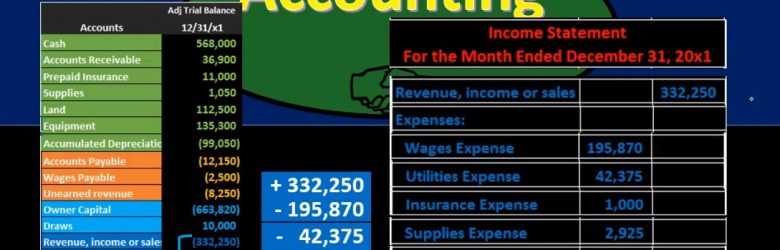
Hello in this presentation we’re going to take a look at the creation of the income statement from the trial balance. First, we want to take a look at the trial balance and consider where the income statement accounts will be. When looking at the trial balance, it will be in order we have the assets in green, the liabilities in orange, the equity in light blue, and then the income statement accounts including revenue and expenses. That’s what we are concentrating here we’re looking at those income statement accounts. And that is what will be used in order to create the financial statements to create the income statement. Note that all the blue accounts represents the equity section. So the income statement really is going to be part of total equity. If we consider that on the balance sheet, then we’re really looking at a component of this capital account.
Balance Sheet Liability Section Creation From Trial Balance 14
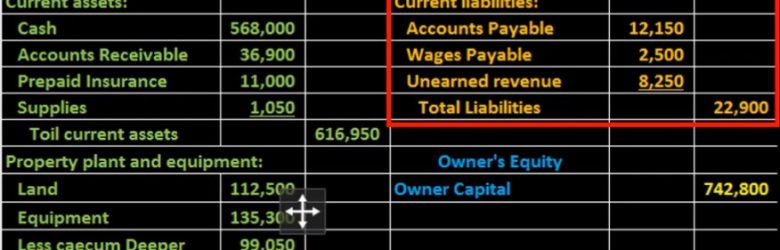
Hello in this lecture we’re going to create the liability section of the balance sheet. In prior lectures, we have taken a look at the assets in terms of first current assets and then property, plant and equipment and given us the total assets at that time, then we are now going to move on to liabilities, and that will be part of the second part of the balance sheet meaning it’ll then sum up to total liabilities and owner’s equity. We are going to be taking this information of course from the adjusted trial balance the adjusted trial balance in the format of debits and credits, we are now formatting it in the format of the accounting equation. Still the double entry accounting system just in two different formats, just reshuffling the puzzles so that different readers can understand the financial statements even though they don’t understand debits and credits.
Journal Entry Thought Process 215
Hello in this presentation that we will discuss a thought process for recording financial transactions using debits and credits. Objectives. At the end of this, we will be able to list a thought process for recording journal entries. explain the reasons for using a defined thought process and apply thought process to recording journal entries. When we think about a thought process, we’re going to start with cash as the first part of the thought process is cash affected. We’ve discussed the thought process when we have considered the double entry accounting system in the format of the accounting equation, the thought process will be much the same here we now applying that thought process to the function of debits and credits recording the journal entries with regard to debits and credits.