In this presentation, we will continue with the statement of cash flows indirect method looking at the change in prepaid expenses, we’re going to be using this information, we’ve got the comparative balance sheet, we’ve got the income statement and some additional information, we will be working primarily with the difference in the comparative balance sheet with the use of a worksheet taking this information to create this worksheet. So this is just basically a comparative balance sheet that has been condensed down to something that looks like a post closing trial balance. We are constructing our cash flows from operations from it, we have all of our differences. We’re basically just finding a home for these differences. We know if we do so that if we find a home for all of these differences, then it’ll add up to that difference, the difference in cash, which is basically the bottom line of our cash flow statement, or that’s what we want to get to in terms of adding up the cash flows. So we’ve gotten so far We’re working on the cash flows from operations. And we’ve done the cash flows in terms of the accounts receivable, inventory. Now we’re on prepaid expenses. We’re just going through these.
Posts with the receivable tag
Statement of Cash Flow Indirect Method Change In Inventory
In this presentation, we will continue putting together our statement of cash flows using the indirect method. Now taking a look at the change in inventory, we’re going to be using our materials here with a comparative balance sheet, the income statement and some added information, working primarily at this time from a worksheet that was made from the comparative balance sheet. So here is our worksheet. Here’s what we have. So far, we basically have a comparative balance sheet in a trial balance type format, where we have the current year, the prior year, and then the difference. Our goal is to find a home for all of these differences are in number that we’re looking for, is basically the 61 900 change in cash. So we’ve gone through this, from top to bottom, we’re working through basically the operating cash flows from operating First, the indirect method. So we started off with the net income, then we made our adjustments. And then now we’re going through basically The accounts receivable to inventory. Now once we get into the current assets, we’re going to group those into this change in current assets under the cash flows from operations. Once we know the theme here on what’s going to happen with these current assets, it’s it’s always going to be the same.
Statement of Cash Flow Indirect Method Change In Accounts Receivable
In this presentation, we will continue putting together the statement of cash flows using the indirect method focusing here on the change in accounts receivable. The information will be a comparative balance sheet, the income statement and some added information we will be focusing in on a worksheet that was composed from the comparative balance sheet. So here is our worksheet. So our worksheet that we can pay that we made from the comparative balance sheet, current period, prior period change. So we have all of our balances here for the current period, the prior period and the change, we have put in this change. And this is really the column that we are focusing in on we’re trying to get to this change in cash by finding a home for all other changes. Once we find a home for all other changes. We will get to this change in cash the bottom line here 61,900. The major thing we’re looking for is right here. We’ve already taken a look at the change in the retained earnings. And the change in the accumulated depreciation. Now we’re going to look at the changes in current assets and current liabilities.
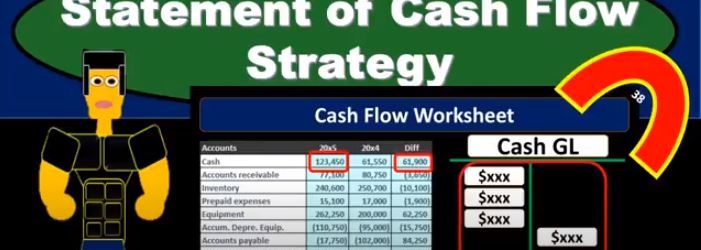
Statement of Cash Flow Strategy
In this presentation, we will take a look at strategies for thinking about the statement of cash flows and how we will approach the statement of cash flows. When considering the statement of cash flows, we typically look at a worksheet or put together a worksheet such as this for my comparative balance sheet, that given the balance sheet accounts for the current year and the prior year or the current period, and the prior period, and then giving us the difference between those accounts. So we have the cash, we’ve got the accounts receivable inventory, we’re representing this in debits and credits. So this is in essence going to be a post closing trial balance one with just the balance sheet accounts, the debits represented with positive and the credits represented with negative numbers in this worksheet, so the debits minus the credits equals zero for the current year, the prior year. And then if we take the difference between all the accounts, and we were to add them up, then that’s going to equal zero as well. This will be the worksheet that we’re thinking about. Now. When can In the statement of cash flows, we can think about the statement of cash flows in a few different ways. We know that this, of course, is the change in cash, this is the time period in the current time period, the prior year, in this case, the prior period, the difference between those two is the difference in cash.
Cash Flow Category Thought Process
In this presentation, we will think about the thought process to know which category a cash flow should be entered into whether it should be operating, investing or financing activity. When putting together the statement of cash flows, we’re usually going to have a worksheet, which will typically have a comparison of balance sheet accounts. And we also might just have test questions that will ask us, where should this cash flow go? And that’s going to be a common kind of question that we’re going to have whether we build the entire cash flow statement from scratch, or whether we’re just asking test test questions and trying to know what types of Cash Flows we’re talking about. It’s also important for practice as well so that we can understand when we’re thinking about cash flows, where do they belong? What are these cash flows mean? What are they doing for us? What are they doing for the company? Are they part of the operations? Are they part of investing? Are they part of financing? If we look at a worksheet like this to build the statement of cash flow, typically we’re going to look at a balance sheet for two periods. So here our balance sheet for these two periods. And we’ll have the difference between the two periods in terms of the balance for these balance sheet accounts. So we’ve got cash, accounts receivable, inventory, prepaid expenses.
01:13
Now what we’re going to do is we’re going to take the change in cash, that’s going to be the end result on our statement of cash flows. And we’re going to kind of back in to that end result by looking at the change in the other balance sheet accounts and tried to figure out what’s causing this change. So we’re going to go through all the other balance sheet accounts, look through these changes. And we know that if we look if we add them all up, they add up to zero. Why? Because the debits and credits for one year, add up to zero the debits and credits for the other year add up to zero. In other words, the debits minus the credits equals zero. And therefore the difference between the two years debits and credits the change will add up to zero. So we know that’s the case and we know that if we add up then everything except cash Then the result will be the difference in cash. So that’s how we’re going to kind of work and put together our statement of cash flows. So what we need to do then is we’re going to take a look at these changes in receivables, changes in inventory changes in prepaid expenses, and then try to determine where does that change belong? Before we get into any other question is, is the change of inventory and operating, investing or financing activity? And is the change in long term notes payable? Is that going to be an operating investing or financing activity? Our goal here is to go through a thought process to see if we can think through more clearly which category these these should be belong to. So what’s the most common journal entry in this account? It’s going to be our first question.
02:48
Whatever account they’re given us here, we’re going to say it let’s think about the most common journal entry that’s related to this account, there’s typically going to be one or two journal entries that are going to be very common and we want just right down first, once we know the most common journal entry, then we’re going to ask is an income statement account involved? So when we think about whatever account we’re dealing with, we’d write down the journal entry and say, Okay, is there an income statement account involved? Is there a revenue account or an expense account involved? If the answer is yes, then it’s probably the change that we’re dealing with is probably something that should be in the operating activities. Because remember, the operating activities is kind of like the income statement on a cash basis. So if we’re dealing with something that’s this change has something to do with the income statement, then it’s going to be something on the operating activities. Typically, if the journal entry has nothing to do with the income statement, there’s no revenue or expense accounts involved in the normal journal entries related to these accounts, then we’re going to ask the question, are we purchasing or selling an asset? Because it’s so if it’s not operating, this means that it’s not operating therefore, We’re trying to see if it’s going to be investing activity. And that typically means we’re purchasing or selling an asset. If it has to do with, for example, property, plant and equipment, or some other type of investment, then it’s going to be an investing activity. And then if it’s not, then it’s going to be financing. And of course, financing is going to be dealing with notes, something that we’re dealing with that doesn’t deal with operating activities in terms of the income statement, no revenue and expenses, and typically doesn’t have assets involved either, because what we’re doing is funding the company. So that’s typically going to be something that deals with cash and subtype of liability or the equity section. So this is going to be our thought process if we go through each of those line items, and think about each account on the balance sheet.
04:46
And then try to go through this thought process and think okay, which category are we going to be putting this change to? Now, this looks a little less intuitive than we might think at first glance here because no one We’re doing we’re looking at the balance sheet accounts. And we’re trying to see what category these things are going to fit into. And remember that the operating activities I’m keep on comparing that to the income statement. And you might be thinking, well, these are all balance sheet accounts. Why do you keep mentioning the income statement. And note, what we’re doing here is we’re really kind of backing into the activity is happening by looking at the change in two points in time. So we’re kind of still looking at the income statement activity type of accounts, we’re looking at change, we’re looking at activity, even though we’re doing that by looking at the change in two points in time to balance sheet accounts, which are points in time. So when we look at the change in accounts receivable for example, if we go through our thought process, we’re going to say okay, accounts receivable was at 80,007 50. In the prior year, end of the current year, it’s at 77,100.
05:51
That means it went down by 3650. So our goal here is just to determine which category That change belongs to it’s an operating, investing or financing. And if we think about that, then we could think Well, what’s the normal journal entry related to accounts receivable? We’re going to have a debit to accounts receivable and a credit to sales. That’s going to be our normal journal entry that we’ll have related to accounts receivable. And we can see there that sales is an income statement account. So we know that it is an income statement account involved, we’re going to say yes, therefore, it’s an operating activity. So note what we’re doing here, we’re looking at the change in a balance sheet account. We’re looking at the change in the balance sheet account, then ask yourself, what’s the normal journal entry related to this account? And if we think about the normal journal entry related to accounts receivable, that’s a sale of something on account. So accounts receivable goes up when we make a sale on account, and we credit revenue and revenue is clearly an income statement account. So this Change, then that’s what we’re going to think through, we’re going to say that change looks like it belongs somewhere in the operating activities. Because we’re dealing, we’re really kind of backing into sales. That’s what we’re really looking at. And we’re going to do that by writing down the journal entry. Let’s look at another account. We’re going to pick equipment now. So we’re just going to go through all these changes. And we just got to find a home for all these changes.
07:21
When we when we make the statement of cash flows. We got to find a home for them in either operating, investing or financing. And we’ll end up with the change in cash, which is kind of like the bottom line. The bottom line will be cashed at the end of the day. So we’re going to find a home for the equipment. Where’s that going to go that change? Well, if we think about the journal entry for equipment, then if we buy equipment, we’re going to debit equipment, and credit cash and possibly credit like a note payable, some type of financing. But if we pay cash for it, this would be the most simplified journal entry. Even if we had a note there’d be no Part of it that would be on the income statement, one asset went up, the other asset is going down. So therefore, is the is an income statement account involved? No. So we’re purchasing or weren’t, so it’s not going to be an operating activity. And then the next question is, are we purchasing or selling an asset? In this case, yeah, we’re purchasing an asset. And that means that it’s going to be an investing activity. So and this was the confusing thing for me when I first started learning this thing, because investing activities, I had a different conception of what investing is to invest in something like any asset any anything we purchase in the business that we’re not consuming now is an investment to the future. In terms of the cash flow statement, we’re trying to spend our cash in order to put our money somewhere that’s going to help us make money in the future. That’s going to be some type of investment. So in this case, it’s going to be an investing activity.
Note Receivable Example
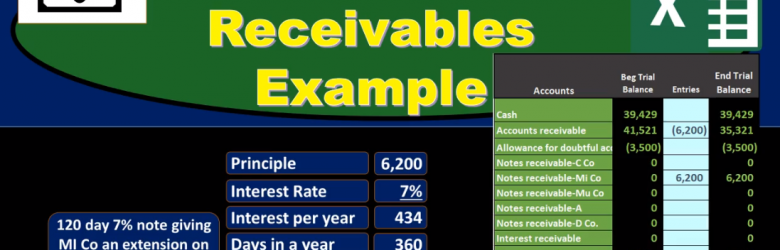
In this presentation we will discuss notes receivable, giving some examples of journal entries related to notes receivable and a trial balance so we can see the effect and impact on the accounts as well as the effect on net income of these transactions. first transaction, we’re gonna have 120 day 7% note giving the company EMI and extension on past due AR or accounts receivable of 6200. When considering book problems and real life problems, one of our challenges is to interpret what is actually happening what is going on, which party are we in this transaction in? Therefore, how are we going to record this transaction when we’re looking at notes receivable? A common problem with notes receivable is the conversion of an accounts receivable to a notes receivable. So in this case, that’s what we have. We have an accounts receivable here that includes an amount of Due to us by this particular company in AI so these are our books, we have a receivable people owing us money for prior transactions goods or services provided in the past and they owe us in total, all customers owe us 41,521 this customer in particular owes us 6200 of this amount in the receivable that could be found not in the general ledger which would give backup of transactions by date.
Notes Receivable
In this presentation, we will take a look at notes receivable. We’re first going to consider the components of the notes receivable. And then we’ll take a look at the calculation of maturity and some interest calculations. When we look at the notes receivable, it’s important to remember that there are two components two people, two parties, at least to the note, that seems obvious. And in practice, it’s pretty clear who the two people are and what the note is and what the two people involved in the note our doing. However, when we’re writing the notes, or just looking at the notes as a third party that’s considering the note that has been documented. Or if we’re taking a look at a book problem, it’s a little bit more confusing to know which of the two parties are we talking about who’s making the note who is going to be paid at the end of the note time period? We’re considering a note receivable here, meaning we’re considering ourselves to be the business who is going to be receiving money. into the time period, meaning the customer is making a promise, the customer is in essence, we’re thinking of making a note in order to generate that promise, that will then be a promise to pay us in the future.
Allowance Method % Accounts Receivable vs % Sales Method
In this presentation, we will be taking a look at the allowance method for accounts receivable focusing in on the calculation of the allowance for doubtful accounts. There are two methods that can be used in order to calculate the allowance for doubtful accounts accounts. One being the percentage of accounts receivable, the other is the percentage of sales, we will take a look at them both and look at the pros and cons of them. First, we’re going to look at the accounts receivable method. We’re going to start off with the percentage of accounts receivable method for a few different reasons. One, it’s the one that’s most often tested. And two is the one that may be most often used in practice often making the most sense to people that are looking at the two methods. It’s also a bit more complicated. So when we’re looking at test questions, they typically would focus on this method in order to have a bit more complicated process to do the calculation.
Allowance Method VS Direct Write Off Method
In this presentation, we will take a look at a comparison between the allowance method and the direct write off method. When considering both the allowance method and the direct write off method, we are considering the accounts receivable account. Remember that the accounts receivable account represents some money that is owed to the company, typically from sales made in the past, on account haven’t yet received the funds for sales made in the past and therefore, the company is owed money. We see this amount on the trial balance in this case 1,000,001 91. We then want to know information about that, including who owes us that money. We can’t find that typically in the GL as we have a GL for every account the GL only giving us the information by date. Typically, we want to see that information also broken out in the subsidiary ledger saying who owes us this money.
Allowance Method Accounts Receivable-financial accounting
Hello in this presentation we’re going to take a look at the allowance method which is of course related to the accounts receivable account, we will be able to define the allowance method record transactions related to recording bad debt recording the receivable account that has been determined to be uncollectible recording every single account that has been collected after being determined that it was uncollectible. So we’re going to take a look at some different transactions, the most common transactions when dealing with the allowance method and see what those look like and why we use the allowance method. We’re going to work through a problem. So what we’re going to have here is we’ve got our accounting equation, of course we have our trial balance, I do suggest working problems to take a look at a trial balance because it can give you the context in which to work problems. So here’s what we have. We’ve got the assets in green, the liabilities are going to be orange, the light blue is the capital account and the equity section.