QuickBooks Online 2021 products and services list or item list, let’s get into it with Intuit QuickBooks Online 2021. Here we are in the free QuickBooks Online test drive file, which you can find by typing into your favorite browser, QuickBooks Online test drive, we’re in Craig’s design and landscaping services. So we’re looking at the another item that can be classified under the category of lists. So one way to get there would be go to the cog up top. And then under the lists, here, we’re looking at the products and services. So that’s one way you can get into this particular list. fairly quick way to get into it, I think more often, or at least more often for me,
Posts with the purchase tag
Enter Purchase Order P.O. 7.17
QuickBooks Online 2021, enter purchase order, or P OE. Let’s get into it with Intuit QuickBooks Online 2021. Here we are in our get great guitars practice file, we’ll be entering a purchase order, we’re not going to be opening up the financial statements because if I opened this plus button or the New button, unlike any of the other forms here in the customers, vendors or employee cycles, the purchase order does not have an impact on the financial statements. In order to see that, let’s review it with our flowchart which is on the desktop version.
Inventory Tracking Options 6.55
QuickBooks Online 2021 inventory tracking options. Let’s get into it with Intuit QuickBooks Online 2021. Here we are in our get great guitars practice file. Last time we entered some items for our service items, we can check those out by going to the sales tab on the left hand side, then the products and services up top. These are the service items that we entered that would then be helpful or used to populate things like invoices and sales receipts.
Pro Forma Income Statement 410
Corporate Finance PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will discuss the pro forma income statement, get ready, it’s time to take your chance with corporate finance pro forma income statement. Let’s first take a step back and think about the pro forma financial statements in general, remembering the fact that we got to do them in some type of order in order to do them in a logical fashion. And that would mean that we would first need the sales projection information, the production plan, we can use those in order to create the pro forma income statement.
Push Down Accounting
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we will discuss push down accounting as it relates to parent subsidiary relationships controlling interest interest over 51%, where we have consolidation accounting taking place, we’re going to be applying pushdown accounting to it, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. So the concept of pushdown accounting will take place when we have the parent subsidiary type of relationship and we have a situation where the purchase price when the parent purchased the subsidiary, the purchase price was more than the book value of the subsidiary, which could complicate of course the consolidation process as we’ve talked about in prior presentations. So we have a couple different options that we could do.
Consolidation When There is a Book & Fair Value Difference
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to take a look at a consolidation process when there is a book and fair value difference. In other words, we’ll have a consolidation. We have two companies, we have a parent subsidiary type of relationship, and the parent has a controlling interest of the subsidiary. Therefore consolidation is what we’re going to be doing. That means we’re going to take two separate sets of books combine them together as if they were one. And we had some complications with the fact that when the purchase took place, there was a difference between the book value and the fair value, what will be the effect of that difference on the consolidation process, elimination entry example. So when we consider this difference, we want to think about what’s going on with the parents books and the subsidiaries books and then what would be the process to consolidate them and what type of problems would be caused if there was a difference between the book and fair value of the net assets so the parents books investment accounts starts out containing the acquisition costs at the fair market value of net assets and goodwill, so we have, that’s basically what’s going to be on the parents books, right. And we’re thinking here typically have an equity method being used. So we have the parents books, we have the subsidiary books that we’re gonna have to consolidate together, and then do our elimination entries. And on the parents books, you’re accounting for the subsidiaries.
Foreign Currency Transactions
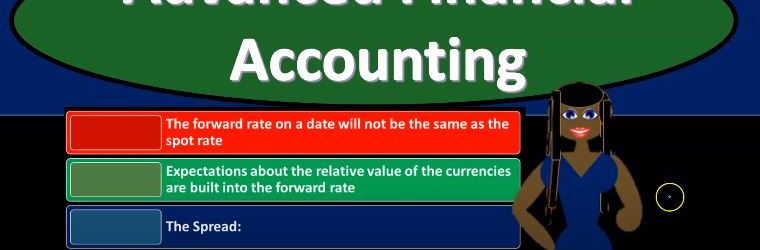
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will discuss foreign currency transactions get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, foreign currency transactions. So remember when we’re thinking about foreign currency transactions, we’re thinking about them from the perspective of the US company in US dollar. So we’re have our currency that we’re making our financial statements in, we’re measuring all the stuff on our financial statements with the measuring tool that we need to be using, that’s going to be the US dollar, that’s going to be our standardization. And then anytime we have foreign currency transactions with something other than US dollars, then we want to see them from that perspective, right? Because when we put them on our financial statements, just like anything else, just like inventory, if we were to value units of inventory, or to value stocks and whatnot, we need to value them in terms of our measure into a which of course is the US dollar.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rates
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we’re going to discuss foreign currency exchange rates get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, foreign currency exchange rates, let’s first define foreign currency transactions. So what are from foreign currency transactions? When are we going to need to account for foreign currency transactions. So from our perspective, we’re going to be looking at this from the perspective of a US company US company that is having their books then accounted for or measured in dollars. And when you think about the foreign currency transaction, it’s just like anything else, but it can be a little bit more confusing. So you want to remember, of course, that the dollar is basically the measuring tool.
Consolidation – Interim Acquisition
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss consolidation and interim acquisition. In other words, we have a parent subsidiary relationship that parent owning a controlling interest over 51%. However, that controlling interest took place for a purchase of the common stock of the subsidiary that happened in the middle of the year. So prior to this, we’ve been talking about situations where we are doing consolidations for an entire year. And you may have question probably popped up in your head at some point in time as well what would happen if the purchase took place in the middle of the year now we have that mid year kind of purchase worse, especially concerned with that first year where the consolidation didn’t really happen. I mean, there wasn’t a consolidated ownership until sometime in the middle of the year, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. So we’re talking about a situation where we have a consolidation but the consolidation happened in the middle of the years. We’re thinking about that first year, primarily What would happen? Well, if the consolidation didn’t take place in January in other words, the parent didn’t purchase the controlling interest in the subsidiary at the beginning of the year but happened at some point in the middle of the year what’s going to be the impact on the year in consolidation, which typically happens for the entire year? Well, the subsidiary is seen as being part of the consolidated entity from the time the stock is acquired, even if acquired in the middle of the year.
Forms of Business Combinations
This presentation we’re going to talk about forms of business combinations, which is basically external expansion, two types of entities that are going to be related in some way, shape or form, get ready to act because it’s time to account with advanced financial accounting, forms of business combinations. Now remember, we’re talking about expansion. Here, we’re thinking about expansion. We’ve got the two categories, we’ve got the internal expansion and external expansion. We’re considering here, the external expansion, we have an organization that now wants to expand and they’re going to be consolidated in some way or have two separate entities that will be combining. So now we’re talking about two separate legal entities typically separate legal entities that are now going to be combined in some way shape or forms. The forms of business combinations can be the statutory merger, the statutory consolidation, and the stock acquisition. So if you think about, in other words to separate legal entities and say, Alright, well how can these two separate legal entities be combined in some type of way, you can imagine some different Kind of scenarios in which that could take place. So and when you’re imagining those different types of scenarios, you’re going to be thinking about, okay, well, what’s going to be the key factor here, it’s going to be the controlling interest. So what’s going to be a situation where you had two separate legal entities, and now they’re they’re going to be have some controlling relationship, which could be that they’re combined together under one entity at some point or they are having a parent subsidiary type of relationship, in which case the control would be over the 50%. So that control concept is what you want to keep in mind here.