In this presentation, we’re going to introduce the internal controls related specifically to cash, cash internal control goals, these are going to be the objectives of the internal control system over cash, we want to have the cash handling separate from the record keeping. So whoever is handling the cash, we would like to have them not be the same person doing the record keeping. And therefore we have that separation of duties. We have the person that is entering the data, not having as much of an incentive to steal the cash because they’re not the ones handling the cash, the people handling the cash, know that if they do steal it, the record keeping should pick that up, and they are a separate person. cash receipts are deposited to the bank. We want to make sure that the cash receipts are going to the bank as soon as possible, hopefully on a daily basis, so that we’re not actually emulating cash. We don’t want a cash to be piling up, because if it is then we have a greater risk of theft to happen and greater loss if that does happen.
Posts in the QuickBooks category:
Internal Controls
In this presentation we will introduce the topic of internal controls. Internal Controls been policies within an organization in order to achieve certain objectives those objectives including the safeguarding of assets, having reliable accounting records, efficient operations, and company policy alignment. We’ll get further into what each of these categories mean in detail. However, first we want to discuss the fact that internal controls will change from organization to organization and industry to industry will have similar objectives between organization to organization industry to industry, however, the customization of the internal controls will differ in order to have an optimal amount depending on size of company and type of industry. For example, a small company often one run by one individual will have very much fewer internal controls for multiple reasons. One that that individual can really monitor A lot more of the transactions for a small company and have direct contact with the transactions that are taking place.
Average Inventory Method Explained
Hello in this lecture we’re going to be talking about the average inventory cost method we will be selling our coffee mugs again we will not be using a specific identification but rather a cost flow assumption VAT assumption being the average method, we will be using the same worksheet I highly recommend working on a worksheet such as this when when doing any cost flow assumption for inventory, which will include a purchases section, a cost of merchandise section and an ending inventory section in which pieces we can then calculate the unit cost times the quantity to give the total cost for each of the sections. This can answer the most amount of questions that can be asked for this top. If we take a look at a trial balance, we can see that the inventory on the trial balance is at 5000.
Last In First Out LIFO Inventory Method Explained
Hello in this lecture we’re gonna be talking about the lastin first out inventory method, we will once again be selling our coffee mugs. Here, we will not be specifically identifying the coffee mugs that we sell, but rather using a cost flow method, that method been a lastin. First out this time, whenever doing a cost flow method, I do recommend setting up a worksheet such as this with three parts to it having the purchases, the cost of the merchandise and the ending inventory, and then calculating the units that we’re going to sell the unit cost and the total cost for those particular categories. As we will do here. This will answer the most amount of questions in any format that those questions could be asked. What we are trying to do here is of course, say that the inventory that is reported on the trial balance needs to be backed up in terms of a worksheet Why? Because on the trial balance, it’s reported in terms of dollars.
First In First Out FIFO Explained
Hello in this lecture we’re going to be taking a look at first in first out inventory method, we will be selling coffee mugs and we won’t be specifically identifying the coffee mugs. In this case, as we’ve talked about in a prior lecture of this time, we’re going to be using a cost flow assumption VAT cost flow assumption being the first in first out assumption this time to set up this problem in any cost flow assumption, I highly recommend putting together a worksheet that worksheet including headers of purchases columns, and then we got the cost of merchandise columns, then we have the ending inventory. I highly recommend setting up a worksheet like this, whether it’s by hand or in a computer or in Excel because it answers all the types of questions that could come up with an inventory cost flow type of assumption within those sections, we will then have the quantity and then the unit cost and the total cost we’re gonna have, if we sell something, we’re calculating the cost of that sale.
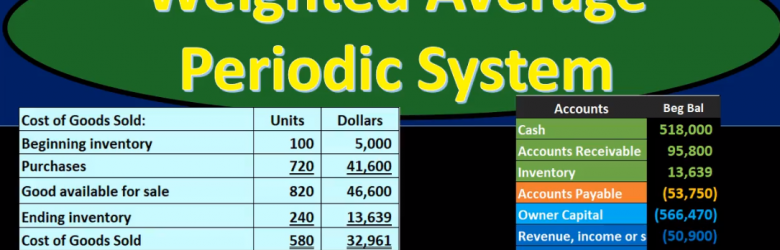
Weighted Average Periodic System
In this presentation we will discuss the weighted average inventory method using a periodic system. The weighted average method as opposed to a first in first out or last In First Out method, the periodic system as opposed to a perpetual system. We want to keep the other systems in mind as we work through this comparing and contrasting. We’re going to be working with this worksheet entering this information here. It’s important to note that this worksheet is a worksheet that can typically be used with any of these inventory flow type problems of which there are many. We have first out last in first out the average method. And then we have a perpetual and periodic system which can be used with any of those methods. It’s also possible for questions to ask for just one component such as cost of goods sold or Indian inventory, and therefore it can seem like there’s more types of problems that we can have in that format as well. If we set up everything in a standard way, even if that weighs a little bit longer for some types of problems, it may be easier because we can just memorize that one format to set things up, this would be a format to do that.
Last In First Out LIFO Periodic
In this presentation we will discuss the lastin first out inventory system on a periodic basis rather than a perpetual basis. As we go through this process, we want to always be comparing those to one, the LIFO or lastin first out system to other systems such as first in first out and average, as well as comparing the perpetual system to the periodic system. We’re going to go through this by looking at a problem the problem going into a worksheet such as this, I do recommend learning this worksheet. This worksheet should look repetitive if you seen the first in first out presentation as well as presentations for the perpetual system.
First In First Out (FIFO) Periodic System
In this presentation we will discuss first in first out or FIFO using a periodic system as compared to a perpetual system. As we go through this, we want to keep that in mind all the time that been that we are using first in first out as opposed to some other systems lastin first out, for example, or average cost, and we’re doing so using a periodic system rather than a perpetual system. Best way to demonstrate is with examples. So we’ll go through an example problem. We’re going to be using this worksheet for our example problem. It looks like an extended worksheet or large worksheet, but it really is the best worksheet to go through in order to figure out all the components of problems that deal with these cost flow assumptions, including a first in first out lastin first out, or an average method, and using a periodic or perpetual for any of them.
Perpetual & Periodic Inventory Systems
In this presentation, we will compare and contrast the perpetual and periodic inventory systems as we track inventory through the accounting process. First, we’re going to look at the perpetual system, the system we typically think of when recording transactions that deal with inventory. So if a transaction doesn’t say it’s using a periodic or perpetual system, you probably want to default to the perpetual system. We have here the owner, we have the customer, we’re saying that we’re selling this inventory this Inc for a cost of 8450. To the customer, the customer is not paying cash but pain, an IOU to the owner. Typically, under a perpetual system. We break this out into two components one, the IOU, or the accounts receivable or sales component. The component similar to what would be seen if we were not selling merchandise but a service company.
Lower of Cost or Market
In this presentation we will discuss the concept of lower of cost or market. We will define this concept first and then see it and talk about how it would apply to inventory. The definition of lower of cost or market according to fundamental accounting principles, while 22nd edition is required method to report inventory at market replacement cost when that market cost is lower than recorded cost. So, what we’re saying here is we have we’re talking about the inventory, of course, and we’re saying that we have to record it at the replacement cost. When that replacement cost that market cost is lower than the recorded cost, what we actually purchased it for. So this looks like a confusing type of definition. However, it’s pretty straightforward. What we’re applying here is going to be the conservative principle meaning that if our inventory has declined in value, we have to record it at the lower cost. We don’t want to be overstating our income mentoree obviously regulations are very concerned about us overstating something, when we’re talking about an asset, and making the financial statements look better than they would rather than understating it.