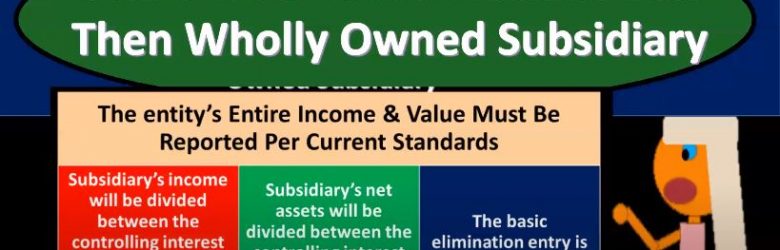
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to talk about consolidation calculations for less than wholly owned subsidiaries. So we have a parent subsidiary relationship, we’re going to be looking at the consolidation process to put the financial statements of the parents and the subsidiaries as if they are one entity, but we don’t have a wholly owned subsidiary. In other words, the parent does not own 100% of the subsidiary. How do we do the consolidation? in bad case, consolidation calculations less than wholly owned subsidiaries, that entities entire income and value must be reported per the current standards? So in other words, once again, we might think, well, on the income statement, maybe we would just report the part of the subsidiary that belongs to or is controlled by the parent, but that’s not typically the case. That’s not the case under generally accepted accounting principles.
Posts with the control tag
Direct & Indirect Control
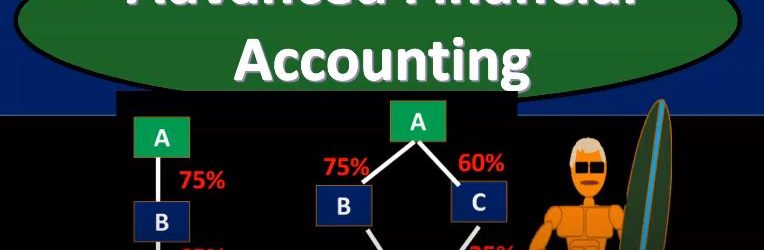
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to talk about the concepts of direct and indirect control. If you’re ready to account with advanced financial accounting, we want to consider these concepts within the context of financial statements and consolidation. So you’ll recall that when we have consolidated financial statements, the idea is to put two financial statements together when one company has basically control over another company that being defined typically by having more than 51% interest because if you have more than 51%, then you have basically a voting share for you to vote on anything, then of course, you would win the vote at that point in time. So let’s consider then direct control and indirect control direct control when one company has a majority of another company’s stock common stock. So that would be a situation where you got a and b, one company has a majority interest over 51% control is pretty easy to see at that point. When you start to get into indirect control. This can get more complicated things can get more confusing here. So indirect control, one company’s common stock is owned by one or more other companies that are under common control. So this can get a lot more detailed structure in terms of what is going to constitute control. So for example, if we have direct control, then you have just simply a parent subsidiary type of relationship. And, you know, the parent has more than 51% of the subsidiary, interest common stock. So and that could happen if we have to, we could still have a little bit more complexity here, where we have two subsidiaries, right. But they’re both going to be consolidated in this case, because there’s 75% over 51% direct control is parent over as one direct control over as to here because it’s over the 51%. So both of these cases would be direct control.
Usefulness of Consolidated Financial Statements
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to take a look at the usefulness of consolidated financial statements. In other words, consolidated financial statements taking two or more companies where there’s a parent subsidiary relationship, putting them together representing financial statements as if those entities were one entity. What are the pros and cons of using consolidated financial statements? Get ready to account with advanced financial accounting idea of consolidated financial statements? In other words, why did we come up with the consolidated financial statements? So remember, we’re talking about a situation where there’s a parent subsidiary relationship, there’s a controlling interest, we have one company that has a controlling interest in over 51 interest in the other company. And then we’ve come up with this concept of showing the Consolidated Financial Statements showing the entity the parent and the subsidiary entities of which there’s a controlling interest as if they were one entity. Why do that? So when company creates or gets controlled Another company, that’s going to be the scenario we have. So we have a parent subsidiary relationship due to that fact due to one company having control than another company. You can think of that, of course in a stock situation owning for more than 51%. The result is a parent subsidiary relationship. So if we just have the two entities, it would look something like this.
Consolidation Process 100% Owned Subsidiary
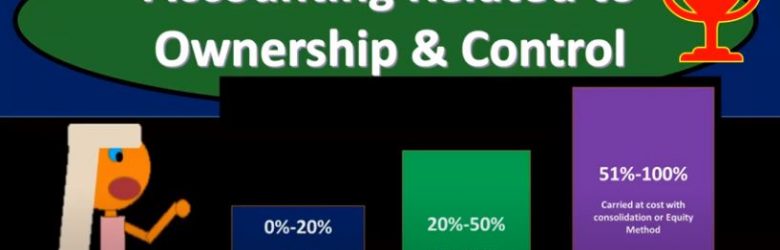
This presentation we’re going to take a look at the consolidation process for a 100% owned subsidiary. In other words, when we’re thinking about one company owning another company in advanced financial accounting, we’re usually looking at the situation and spending most of our time where we have some kind of consolidation process. So we want to Vin take the consolidation process and look at it in levels of complexity. So we’re going to start with a level of complexity, that’s going to be an easier setting where we will have 100% owned subsidiary, and then we’ll go from there and add more complications to it. Get ready to account with advanced financial accounting to ownership and control and prior presentations, we took a look at different methods based on different levels of ownership and control. We said in general, if we had zero to 20%, we use the carried value and then 20 percents kind of an arbitrary number, but if we’re over that amount, we’re really looking at the term of significant influence it for over the 20% from 20 to 50% then The assumption is that we would be using the equity method because the assumption would be if over 20% unless spoken otherwise, unless some unreal, some reason, otherwise, we would then have this significant influence and therefore be justified to use the equity method. And then if you’re over 51%, then you may have the consolidation. Now, when we think about these two methods that they carried value in the equity method, we can basically explain those as we go, you know, if you got anything from zero to 20%, then we could just basically say, yeah, then you fall into this category, let’s talk about the accounting in general.
Other Foreign Operations Issues
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss other foreign operations issues, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, other foreign operations issues. So we’re going to start off with an issue related to the parent company having a foreign subsidiary. Typically when that is the case, they’re going to have to consolidate. In other words, you’re going to have to get the foreign subsidiary books in some way to the US dollar and then do the consolidation process. However, you might have a situation where that wouldn’t take place under certain conditions. So, parent generally consolidates a foreign subsidiary except when certain conditions are so severe that the US company owning the foreign company may not be able to exercise the necessary level of economic control. So notice when we think about the consolidation process, we’ll typically think about, we need to consolidate the entities if there’s control right over the 51% is that going to be a general rule but the overarching concept is that there is control. Now if there are certain conditions even though it’s the ownership is over the 51%, we would think there would be control, but there are certain conditions in the foreign subsidiary that are restricting that economic control, then then they might not meet you know that condition and therefore in that situation you might not have the consolidation process. So in that situation then you might have a parent company that has basically a controlling interest you would think in terms of the stock, the stock but you’re not having a consolidation due to the due to one of these factors limiting the actual economic control. So, those include restrictions on foreign exchange in foreign country. So severe strict restrictions, there could be one of the items that would stop the basically consolidation process possibly restrictions on transfers of property in foreign country.
Other Foreign Operations Issues
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss other foreign operations issues, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, other foreign operations issues. So we’re going to start off with an issue related to the parent company having a foreign subsidiary. Typically when that is the case, they’re going to have to consolidate. In other words, you’re going to have to get the foreign subsidiary books in some way to the US dollar and then do the consolidation process. However, you might have a situation where that wouldn’t take place under certain conditions. So, parent generally consolidates a foreign subsidiary except when certain conditions are so severe that the US company owning the foreign company may not be able to exercise the necessary level of economic control. So notice when we think about the consolidation process, we’ll typically think about, we need to consolidate the entities if there’s control right over the 51% is that going to be a general rule but the overarching concept is that there is control. Now if there are certain conditions even though it’s the ownership is over the 51%, we would think there would be control, but there are certain conditions in the foreign subsidiary that are restricting that economic control, then then they might not meet you know that condition and therefore in that situation you might not have the consolidation process. So in that situation then you might have a parent company that has basically a controlling interest you would think in terms of the stock, the stock but you’re not having a consolidation due to the due to one of these factors limiting the actual economic control. So, those include restrictions on foreign exchange in foreign country. So severe strict restrictions, there could be one of the items that would stop the basically consolidation process possibly restrictions on transfers of property in foreign country.
Forms of Business Combinations
This presentation we’re going to talk about forms of business combinations, which is basically external expansion, two types of entities that are going to be related in some way, shape or form, get ready to act because it’s time to account with advanced financial accounting, forms of business combinations. Now remember, we’re talking about expansion. Here, we’re thinking about expansion. We’ve got the two categories, we’ve got the internal expansion and external expansion. We’re considering here, the external expansion, we have an organization that now wants to expand and they’re going to be consolidated in some way or have two separate entities that will be combining. So now we’re talking about two separate legal entities typically separate legal entities that are now going to be combined in some way shape or forms. The forms of business combinations can be the statutory merger, the statutory consolidation, and the stock acquisition. So if you think about, in other words to separate legal entities and say, Alright, well how can these two separate legal entities be combined in some type of way, you can imagine some different Kind of scenarios in which that could take place. So and when you’re imagining those different types of scenarios, you’re going to be thinking about, okay, well, what’s going to be the key factor here, it’s going to be the controlling interest. So what’s going to be a situation where you had two separate legal entities, and now they’re they’re going to be have some controlling relationship, which could be that they’re combined together under one entity at some point or they are having a parent subsidiary type of relationship, in which case the control would be over the 50%. So that control concept is what you want to keep in mind here.
Allocate Expenses to Classes
This presentation we’re going to take a closer look at external business expansion, which includes things like mergers and business combinations, get ready to act, because it’s time to account with advanced financial accounting. Before we move into the external expansion, you want to give a review and keep your mind on what our focus is we’re talking about a business that is expanding. When we think of it about expansion, we can break that expansion into internal and external expansion. So we have a business expanding into new areas do segments, we can think of it as an internal or external expansion. In a prior presentation, we talked a little bit more on the internal expansion, in which case you might have a situation where a parent creates a subsidiary or a parent basically just creates another division possibly, and expands in that format. Now we’re going to be going to the external expansion, in which case we’re talking about two entities. So we have two separate legal entities that in some or two separate entities in some case in some way, shape reform are coming together. So now we’re going to have an expansion where we have an external expansion. So if we’re thinking of thinking about this, from the from the standpoint of one company, we’re thinking about ourselves as one company and we are expanding, then we’re thinking about the expansion externally, that we are going to be combining in some way shape or form with another company. Now, the format and form in which that combination can take place can be various we can have various forms of that combination, it could result in a parent subsidiary type of relationship, or it could result in the parent basically consuming that another company and bringing them into the overarching parent company.
Accounting Related to Ownership & Control
In this presentation, we will take a look at accounting methods which will relate to and depend on ownership and control, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. Accounting related to ownership and control methods used to account for investments in common stock will depend on the extent of influence or control, the investor can exercise over the investi. So in other words, we’re gonna have different methods depending on the level of control. Now, if we’re going to use different methods, we need to have some kind of definition we need to have some lines in terms of when we’re going to apply these different methods. What does it mean to have different levels of control? And then how do we apply those in practice so we can have some kind of standardization for that.
Consolidation Process Overview
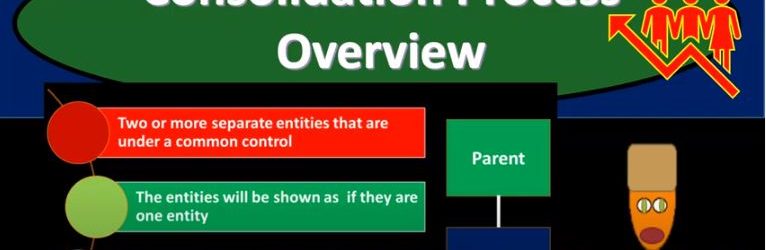
In this presentation, we will take a look at an overview of the consolidation process, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, consolidation process overview we’re talking about a situation where we have two or more separate entities that are under a common control. So the basic kind of format of that you’re imagining here, then you have a parent and a subsidiary, these are going to be connected in some way shape or form because the parent has control over the subsidiary, we can imagine more complex situations, for example, having one parent and multiple subsidiaries as well. The entities will be showing as if they are one entity. So if we have a situation like this, if there’s a control type of situation, it’s quite possible then we’re going to have the the subsidiary and the parent These are two separate companies have a consolidated basically a financial statement. So the financial statement the idea of that being we’re going to take these two financials and represent them as if these two separate entities in this case, two or more can be more than two are one entity. This means two or more sets of books are merged into one set of financial statements. So obviously, what does that look like from a practical standpoint, we have the parent company, we have this subsidiary company, they have two sets of books, we’re gonna have to take those two sets of books and put them together for the financial statements. Here is an example of a slightly more complex situation where we still have parent subsidiary relationships but multiple pole subsidiaries in this case, so we have the parent subsidiary one where there’s a 75% ownership. So we’re over we have a controlling interest, we’re over that 51, we’re going to say there’s a controlling interest here, therefore there’s going to be a consolidation. So we’re gonna have a consolidation subsidiary to is owned 52%. So we’re still over the 51.