In this presentation, we will expand on the logistics of internal expansion, get ready to act, because it’s time to account with advanced financial accounting. We’re going to take a look now at the steps of the internal expansion. So note we have the two categories of expansion, the internal expansion and the external expansion, internal expansion with a company growing, we’re imagining the company growing, they can either grow internally make it another sub subsidiary, possibly, that would be owned by the parent company creating a parent subsidiary relationship internally, or has some kind of external expansion where we have two separate entities that are going to be together in some way, shape or form. So here, we’re talking about the internal expansion. So we have one company that is then thinking about expanding how are they going to put that expansion together? We’re thinking about the setting up then in this case of another legal entity such as a subsidiary, what steps for that? Well, first, you’re going to have a sub sub subsidiary B. created. So you get the parent company is going to be creating the subsidiary, then we have assets and liabilities are transferred to the new entity. So we’re imagining we have one company that wants to expand possibly have another division or another location that they will be expanding into. They make this subsidiary so they another legal entity created, we typically will think of another corporation that is owned by the prior Corporation, parent subsidiary relationship, the assets and liabilities that are going to be controlled or be part of that new segment are going to be transferred from the parent company now to the subsidiary company. And the key point here is that it’s going to be transferred at book value. And you might be thinking after looking at the external expansion, where you have two separate entities that are coming together and the need for us to then use the basically the acquisition method treat it basically like a sale happening.
Posts with the Liabilities tag
Business Combinations Methods
In this presentation, we will take a look at business combination accounting methods, both historic methods and the current methods get ready to act, because it’s time to account with advanced financial accounting. We’re going to start off with business combinations from the past, these are not the current method that we’re going to be using. However, it’s good to have some historical context so that if you hear these methods, you know what you’re talking about. We also want to think about these concepts in terms of just a logistical standpoint. If you were to make these laws, then how would you do it? What are some of the challenges that have happened? And by looking through the historical process, you can kind of think about, okay, these are what were put in place, I see why those were put in place here that changes that are happening, we could see why the changes are happening, therefore have a better understanding of what we are doing, and how the current process is being put in place and why the decisions were made to put it in place. So in the past, we had combinations methods that included the purchase method and the pooling of interest. method. So they then what happened is the pooling of interest method was taken away by faz B. So faz B said, Hey, we’re not going to allow anymore, the pooling of interest method, and then the purchase method has been replaced with the acquisition method. So if you hear the purchase method, that in essence is what we’re currently doing. However, we changed the name from the purchase method to the acquisition method.
Measurement Period and Contingent Considerations
In this presentation, we will discuss measurement period and contingent considerations within an acquisition process, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. At this point with the discussion of the acquisition process, you’re probably thinking, Okay, I kind of see how this fits together. I’ve see how this works. But logistically, it could still be a little bit tough. If you were to apply this in practice, you’re probably saying, Hey, there could be some problems. In practice. If we were to apply this out. For example, if we’re saying, okay, we’re going to revalue the assets and the liabilities. And we’re going to value the consideration we’re going to make a comparison of the value of the assets and liabilities to the consideration that’s being given for the company that in essence is being acquired in the acquisition process. Well, then what about that valuation process? That’s going to be difficult because how do we revalue the assets and liabilities because normally, when you value something, you value it from a market perspective, which means there’s actually a transaction a sale that’s taking place. So note obviously that valuation process is going to be somewhat of a tedious process for us to go through and revalue. And how long do we have for that to take? I mean, if this isn’t happening basically instantly with regards to this process, this is going to be taking some time.
Acquisition Accounting Bargain Purchase
This presentation we’re going to continue on with our discussion of acquisition accounting, and this time focusing in on a bargain purchase, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. First off, we can basically think of the bargain purchase as the opposite of goodwill. So in a prior presentation, we talked about the concept of goodwill within an acquisition, which would be resulting if the fair market value of the amount that was given like basically the purchasing price was greater than the fair market value of the net assets. So in other words, we take we look at the books of the company that’s being acquired, we’ve revalue their assets and liabilities to be on a fair market value, then assets minus liabilities, the equity section, the net assets now at a fair market value, we take a look at that. And if there’s a consideration that’s given that is greater than that amount, that then would result in goodwill. Now goodwill is quite common, because it’s unlikely even if you even if you re assess all the assets and liabilities to their fair value. Then you would typically think that the price would either be that that would be given the the amount that would be exchanged, the fair market value of the consideration would be the same as the assets minus the liabilities at fair market value, or more, because there’s some type of goodwill, that’s going to be that’s going to be in the organization. Now, you might be thinking, Well, what what if it was the opposite? What if you took the fair market value of the net assets, and the amount that was given the exchange amount was less than the fair market value? Now that could happen, but just note that that’s a lot more unusual.
Acquisition Accounting Goodwill
In this presentation, we’re going to continue on with our discussion of acquisition accounting, this time focusing in on the concept of goodwill. Get ready, because it’s time to account with advanced financial accounting. First question is, what is goodwill. So it’s an intangible factors that allow a business to earn above average profits. So the way you might want to think about that is the first thing about a business that isn’t being purchased and sold. If you just got one business that started from scratch, they just started doing business, they started earning revenue, then you can look at their financial statements, they got the they got the balance sheet, assets minus liabilities is the book value of the company, and then the income statement, which is their performance. Now, if you were to say, Hey, is this company worth more than their equity than their assets minus the liabilities than their net assets? In other words, if it is, then you’re saying hey, there must be some intangible factor that’s not really on the balance sheet that would explain the reason why the you know the value of them because most likely through Profit generation, after the the perceived ability, the likely ability to earn profit in the future is greater than just what’s on the balance sheet assets minus liabilities. So you would think then that many companies, if a company is doing well, then there’s going to be some kind of intangible factor there. That’s not basically on the balance sheet that basically explains why the company is doing better than then just the value of the company being assets minus liabilities. So in other words, if we were to purchase the company, you would think that you would purchase it for their assets minus the liabilities, that’s what they consist of, that’s breaking them down to their parts.
Post Closing Trial Balance & financial statements
Hello in this presentation we will discuss the post closing trial balance and financial statements. When considering the financial statement relationship to the trial balance, we typically think of the adjusted trial balance that being used to create the financial statement. It’s important to note, however, that any trial balance that we use can be generated into financial statements. It’s just that the adjusted trial balance is the one that we have totally completed and prepared and ready. In order to create the financial statements to be as correct as possible as of the date we want them, which is usually the end of the month or the end of the year. Note that the names of the unadjusted trial balance the adjusted trial balance and the post closing trial balance are really a convention they’re all basically trial balances.
Closing Process Explained
Hello in this lecture we’re going to talk about the objectives of the closing process the closing process will happen after the financial statements have been created. So we will have done the journal entries where we will have compiled those journal entries into a trial balance, and then we will have made the financial statements. And then as of the end of the period in this case, we’re going to say as of December, when we move into the next time period, January, what we need to do is close out some of the temporary accounts those accounts including the income statement and the draws account so that we can start the new period from start in a similar way as if we were trying to see how many miles we could drive say in a month. If we wanted to Vince in December, and then see how many miles we’re going to drive in January of next year.
Accounting Building Blocks
Hello in this lecture we will discuss the accounting building blocks and the double entry accounting system. At the end of this we will be able to define and describe the double entry accounting system, write down the accounting equation and define each individual part of it, define and describe debits and credits, define a balance sheet and list its parts define an income statement list its parts and explain the relationship between the balance sheet and the income statement. Okay, so starting off every business and accounting software uses the double entry accounting system. So the double entry accounting system, it’s kind of like the math behind the calculator, every software is going to use it. In order to understand what the system is doing, we need to understand the double entry accounting system.
Statement of Cash Flow Indirect Method Change In Accounts Receivable
In this presentation, we will continue putting together the statement of cash flows using the indirect method focusing here on the change in accounts receivable. The information will be a comparative balance sheet, the income statement and some added information we will be focusing in on a worksheet that was composed from the comparative balance sheet. So here is our worksheet. So our worksheet that we can pay that we made from the comparative balance sheet, current period, prior period change. So we have all of our balances here for the current period, the prior period and the change, we have put in this change. And this is really the column that we are focusing in on we’re trying to get to this change in cash by finding a home for all other changes. Once we find a home for all other changes. We will get to this change in cash the bottom line here 61,900. The major thing we’re looking for is right here. We’ve already taken a look at the change in the retained earnings. And the change in the accumulated depreciation. Now we’re going to look at the changes in current assets and current liabilities.
Financial Statement Relationships 18
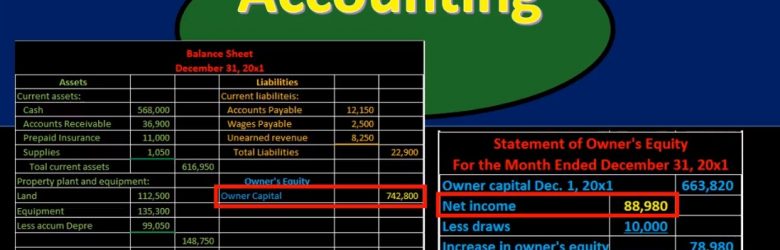
Hello in this presentation we’re going to take a look at financial statement relationships. In other words, how do these financial statements fit together? How do these financial statements represent the double entry accounting system in the format of the accounting equation that have assets equal liabilities plus equity? First, we’ll take a look at the balance sheet. Note that most textbooks will talk about this relationship and constructing the financial statements by first saying to construct the income statement, then the statement of equity and then the balance sheet. If you’re constructing things by hand with a paper and pencil, that does reduce the number of calculations that you would need to do, however, if you’re using something like Excel, then it’s a lot easier to sum up columns of numbers and it might be useful to take a look at the balance sheet. In any case, the relationships will be the same when we consider the relationships between the financial statements.