In this presentation, we will take a look at business combination accounting methods, both historic methods and the current methods get ready to act, because it’s time to account with advanced financial accounting. We’re going to start off with business combinations from the past, these are not the current method that we’re going to be using. However, it’s good to have some historical context so that if you hear these methods, you know what you’re talking about. We also want to think about these concepts in terms of just a logistical standpoint. If you were to make these laws, then how would you do it? What are some of the challenges that have happened? And by looking through the historical process, you can kind of think about, okay, these are what were put in place, I see why those were put in place here that changes that are happening, we could see why the changes are happening, therefore have a better understanding of what we are doing, and how the current process is being put in place and why the decisions were made to put it in place. So in the past, we had combinations methods that included the purchase method and the pooling of interest. method. So they then what happened is the pooling of interest method was taken away by faz B. So faz B said, Hey, we’re not going to allow anymore, the pooling of interest method, and then the purchase method has been replaced with the acquisition method. So if you hear the purchase method, that in essence is what we’re currently doing. However, we changed the name from the purchase method to the acquisition method.
Posts with the purchase tag
Financial Reporting After a Business Combination
In this presentation, we will discuss financial reporting, after a business combination, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, financial reporting, after a business combination, show the combined entity starting on the date of combination and going forward. So in other words, we probably when we’re imagining this type of scenario, we’re going to say, Okay, I see how this all works out here. And then we imagine this happening if we have a calendar year in a calendar, fiscal year, January through December, we say, Alright, the purchase happens, it will just apply it to January out through December. But obviously, that’s not always the case here. What happens when we have that interim kind of transaction where the purchase happened sometime in the middle of the of the fiscal year then that adds some bit of a complication. So you want to think about this in terms of a clean, you know, year, if it happened at the beginning of the fiscal year in combination, and then you know, what would happen if it did not happen at the beginning of the fiscal year, so if a combination of During a fiscal period, revenue earned by the acquire II before the combination is not reported in revenue for that combined enterprise. So you can see that can add a bit of complication with regards to that reporting
Acquisition Accounting Bargain Purchase
This presentation we’re going to continue on with our discussion of acquisition accounting, and this time focusing in on a bargain purchase, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. First off, we can basically think of the bargain purchase as the opposite of goodwill. So in a prior presentation, we talked about the concept of goodwill within an acquisition, which would be resulting if the fair market value of the amount that was given like basically the purchasing price was greater than the fair market value of the net assets. So in other words, we take we look at the books of the company that’s being acquired, we’ve revalue their assets and liabilities to be on a fair market value, then assets minus liabilities, the equity section, the net assets now at a fair market value, we take a look at that. And if there’s a consideration that’s given that is greater than that amount, that then would result in goodwill. Now goodwill is quite common, because it’s unlikely even if you even if you re assess all the assets and liabilities to their fair value. Then you would typically think that the price would either be that that would be given the the amount that would be exchanged, the fair market value of the consideration would be the same as the assets minus the liabilities at fair market value, or more, because there’s some type of goodwill, that’s going to be that’s going to be in the organization. Now, you might be thinking, Well, what what if it was the opposite? What if you took the fair market value of the net assets, and the amount that was given the exchange amount was less than the fair market value? Now that could happen, but just note that that’s a lot more unusual.
Statement of Cash Flow Non Cash Items
In this presentation, we will take a look at the statement of cash flows non cash items. First question, why would we be looking at non cash items when considering a statement of cash flows? We’re gonna go through a list of non cash items first and see if you can recognize a trend in these and why we might be linking them to a statement of cash flows discussion, then we will explain more fully on the idea of looking at non cash items when considering a statement of cash flows. So, some examples of non cash items would be the purchase of long term assets by issuing a note the purchase of non cash assets by issuing equity or debt, the retirement of debt by issuing equity stock, lease of assets in a capital lease transaction and exchange non cash asset for other non cash asset. Consider these examples and note some of the common features including the deal with investing and financing activities. and think through why we might be linking them to a statement of cash flows. We’ll go more fully through this by giving an example of the purchase of long term assets by issuing a note, an example that we can then apply out to the rest of these items. So what are we going to do with these non cash items, we’re going to report them at the bottom of the statement of cash flows or report them in a note related to the statement of cash flows. So we’re going to have to say in some format, or other, hey, look, these are some non cash items that we’re linking to, for some reason, the statement of cash flows.
Statement of Cash Flow Investing Activities Cash Paid for Purchase of Equipment
In this presentation, we will continue on with our statement of cash flows. Taking a look at the investing activities, specifically the purchase of equipment, we’re going to be using the comparative balance sheet, the income statement and additional information focusing here on the comparative balance sheet, which we use to make this worksheet. So this worksheet is our comparative balance sheet. We’ve been going through this worksheet and really looking for the differences. We’re finding a home for all the differences. Once we do that, we’re feeling pretty good. We have done this all the way through the operating activities. So are the cash flows from operations. So we’ve gone through here we’ve kind of picked and choose the items that are going to be cash flows from operations, which is probably the way most people approach this. But just note that as we’ve done that, we’ve tried to pick up the exact differences here. We haven’t gone to the income statement and thought about it separately outside of this worksheet, and then we’re going to go back and make adjustments. So we found a home for the difference in cash because that’s Kind of like our bottom line. And then we’ve got accounts receivable, inventory prepaid expenses, and then we skipped equipment and went down to accounts payable.
Statement of Cash Flow Tools For Completion
This presentation we will take a look at the tools needed in order to complete a statement of cash flows. to complete a statement of cash flows, we are typically going to need a comparative balance sheet that’s going to include a balance sheet from the prior period, whether that be the prior month or the prior year and a balance sheet from the current period, then we’re going to have to have an income statement. And then we’ll need some additional information in a book problem, it’ll typically give us some additional additional information often having to do with things like worth an equipment purchases, whether equipment purchases or equipment sales, were their investments in the company where their sales of stocks, what were the dividends within the company. In practice, of course, we would have to just know and recognize those types of areas where we might need more detail. And we would get that additional information with General Ledger we’d go into the general ledger, look at that added information. Now once we have this information, our major component we’re going to use is going to be the comparative balance sheet. That’s where we will start. So that comparative balance sheet is going to be used to make a worksheet such as this.
Cash Disbursements Internal Controls
In this presentation, we’re going to talk about Cash Disbursements, internal controls. Now we’re going to talk about a voucher system for the payment process. But before we get too into the voucher system, note that the systems will change depending on the type of organization and what industry we’re in and how large the organization is. So if we just have a small organization, then we probably just want to have some internal controls for the owner of the company, the owner, being a key component of the internal control system and having a lot more oversight over many of the things that happened. For example, for the payments that happen, we may have someone that requests something on an employee that wants to request a payment may even you know, enter the payment into this system. However, we want to make sure that the owner still has some control over such as the cheque signing.
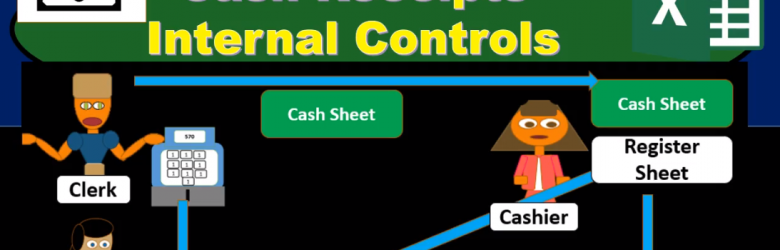
Cash Receipts Internal Controls
In this presentation, we will talk about cash receipts, internal controls. Now we’re going to talk about a voucher system for the payment process. But before we get too into the voucher system, note that the systems will change depending on the type of organization and what industry we’re in and how large the organization is. So if we just have a small organization, then we probably just want to have some internal controls for the owner of the company, the owner, being a key component of the internal control system and having a lot more oversight over many of the things that happen. For example, for the payments that happen, we may have someone that requests something on an employee that wants to request the payment may even you know, enter the payment into the system.
Average Inventory Method Explained
Hello in this lecture we’re going to be talking about the average inventory cost method we will be selling our coffee mugs again we will not be using a specific identification but rather a cost flow assumption VAT assumption being the average method, we will be using the same worksheet I highly recommend working on a worksheet such as this when when doing any cost flow assumption for inventory, which will include a purchases section, a cost of merchandise section and an ending inventory section in which pieces we can then calculate the unit cost times the quantity to give the total cost for each of the sections. This can answer the most amount of questions that can be asked for this top. If we take a look at a trial balance, we can see that the inventory on the trial balance is at 5000.
Last In First Out LIFO Inventory Method Explained
Hello in this lecture we’re gonna be talking about the lastin first out inventory method, we will once again be selling our coffee mugs. Here, we will not be specifically identifying the coffee mugs that we sell, but rather using a cost flow method, that method been a lastin. First out this time, whenever doing a cost flow method, I do recommend setting up a worksheet such as this with three parts to it having the purchases, the cost of the merchandise and the ending inventory, and then calculating the units that we’re going to sell the unit cost and the total cost for those particular categories. As we will do here. This will answer the most amount of questions in any format that those questions could be asked. What we are trying to do here is of course, say that the inventory that is reported on the trial balance needs to be backed up in terms of a worksheet Why? Because on the trial balance, it’s reported in terms of dollars.