In this presentation, we will record a transaction related to salaries expense into our accounting system. Get ready, because here we go with aplos. Here we are in our not for profit organization dashboard, we’re going to jump on over to our Excel file to see what our objective will be here, we’re going to be in tab number six, tab number six, where we have our transaction. Here we are in our not for profit organization dashboard, we’re going to be jumping on over to Excel to see what our objective will be, we’re going to be in tab number six. So we’re in tab number six, we’re going to be recording the salaries expense.
Posts with the record tag
Cash Donation 130
In this presentation, we’re going to record a cash donation or contribution into our not for profit organization. Get ready because here we go with aplos. Here we are in our not for profit organization dashboard, we’re going to be jumping on over to Excel first to see what our objective will be. So here we are in Excel, we’re on tab two in our Excel worksheet, we’re going to be recording a cash donation. Now note, we’re going to be recording this as a one lump sum donation. But you can imagine we have multiple donations, that would be of a similar format.
Office Space Donated 125
This presentation, we’re going to record a transaction related to the contribution or donation of office days to our not for profit organization. Get ready because here we go with aplos. Here we are in our not for profit organization dashboard, we’re going to jump on over to Excel to see what our objective will be, we’re going to be on tab one. So I’m on tap one here, and number one says it’s going to be office space donated. So it’s going to be a bit of a tricky transaction for the first transaction here we got a contribution, but that contribution isn’t cash and which would be the normal type of contribution what was contributed instead, the use of the facilities the use of office space.
Cash Budget 415
Corporate Finance PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will be discussing the cash budget Get ready, it’s time to take your chance with corporate finance, cash budget, as we consider the cash budget, let’s take a step back and think about the budgeting process. So we can think about where the cash budget will fit in it. So we got to start off with the sales projection, that’s going to be our first step. So we can think about the production plan if we manufacture inventory, or we think about the purchasing plan. If we purchase and sell inventory, then we can think about the pro forma income statement. Now the pro forma income statement is going to be on an accrual basis. But we also want to be considering the cash budget. So obviously, once we have once we start to construct the income statement, on an accrual basis, we can also think about what the cash flows will be.
Parent Sale to Sub & Sub Resold
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to discuss an intercompany transaction where a parent makes a sale to a subsidiary and then the subsidiary resells it. In other words, we have this intercompany transaction, we want to think about how that is constructed. And then how we can do the reversing entry for it or a consolidation entry in the case of a consolidation of a parent and subsidiary in a consolidated financial statements, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. So within a situation where we have a sale from P to s, and then S sells it to an outsider remember that as it goes to the outsider, that’s going to be the legitimate type of so that’s the arm’s length transaction, the sale from PETA is not so and therefore we kind of have to eliminate that. Now if it’s been sold to an outsider, then we have a situation where the inventory is still gone. There has been a sale being taken place. And so we so that’s good, but we still have to do the reversal of part of that intercompany transfer and it’s gonna boil down At the end of the day, basically debiting, the revenue account reversing revenue, and reversing the cost of goods sold. So this is the boiled down version. Now if you think about it, you might say what happy because if p sales to s, then you’re going to like debit cash credit, you know, you’re going to credit the sales, and then you debit cost of goods sold, and credit inventory and then asked is going to be recorded cash, and then they’re gonna be recording, then the other side go into inventory, and then right, there’s more, and then they made the sale to the outsider. So how do we boil this down? How does the intercompany boil down to just this right? We kind of kind of have an idea of that in our mind.
Push Down Accounting
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we will discuss push down accounting as it relates to parent subsidiary relationships controlling interest interest over 51%, where we have consolidation accounting taking place, we’re going to be applying pushdown accounting to it, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. So the concept of pushdown accounting will take place when we have the parent subsidiary type of relationship and we have a situation where the purchase price when the parent purchased the subsidiary, the purchase price was more than the book value of the subsidiary, which could complicate of course the consolidation process as we’ve talked about in prior presentations. So we have a couple different options that we could do.
Consolidation When There is a Book & Fair Value Difference
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to take a look at a consolidation process when there is a book and fair value difference. In other words, we’ll have a consolidation. We have two companies, we have a parent subsidiary type of relationship, and the parent has a controlling interest of the subsidiary. Therefore consolidation is what we’re going to be doing. That means we’re going to take two separate sets of books combine them together as if they were one. And we had some complications with the fact that when the purchase took place, there was a difference between the book value and the fair value, what will be the effect of that difference on the consolidation process, elimination entry example. So when we consider this difference, we want to think about what’s going on with the parents books and the subsidiaries books and then what would be the process to consolidate them and what type of problems would be caused if there was a difference between the book and fair value of the net assets so the parents books investment accounts starts out containing the acquisition costs at the fair market value of net assets and goodwill, so we have, that’s basically what’s going to be on the parents books, right. And we’re thinking here typically have an equity method being used. So we have the parents books, we have the subsidiary books that we’re gonna have to consolidate together, and then do our elimination entries. And on the parents books, you’re accounting for the subsidiaries.
Securities Carried at Fair Value Accounting
In this presentation, we’re going to focus in on situations where we have securities carried at fair value using fair value accounting, this will typically be the case if one company is investing in another company, and they do not own above the 20%. That’s going to be basically the general rule. In other words, they don’t have significant influence, and therefore, we’re going to be using the fair value accounting method for them get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. In a prior presentation, we discussed in general different accounting methods we were going to use depending on the level of control or influence that one company has on another company we set what can be kind of arbitrary kind of points, which means zero to 20%. We’re going to use one method that they carried value 20% to 50%, the equity method and then 51 through to 100. We might be having a consolidation at that point. So now let’s break that down and concentrate on each of these in a little bit more detail This time, let’s focus in on this first category. Now this would be the category where typically most of the time you would be you would be accounting for something as in most cases, if you’re just investing if one company is just investing like a normal type of investment, just like an individual’s investing, they don’t expect to have really influence over the decision making process, because they have, they don’t have a controlling interest in order to do so it’s just a normal type of investment type of situation, that’s going to be the norm kind of here. And then once once the ownership gets over to a certain percentage 20% 20% being quite large, I mean, if you think about the number of shares that are out there for a large company or something like that, like apple or something like that, you would need a lot of shares to basically be constituting 20% ownership.
Investments Using the Equity Method
This presentation we’re going to focus in on investments using the equity method. In other words, we’re going to have a situation where we have one company that’s investing in another company, this time they have significant influence. And therefore, we will be using the equity method to account for that investment, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. In prior presentations, we gave an overview about different accounting methods that could be used based on different levels of influence and control those general rules being that if there is 20, or zero to 20%, ownership, we use the carried value 20 to 50%, which is where we’re going to focus in on now, the equity method, idea of there being that there is now significant influence. So in other words, if we own zero to 20%, that would be kind of like you investing in a large company like apple or whatnot. We’re the assumption being, we don’t have significant influence, even though we do have a vote of what happens However, when our vote gets to be 20% Have the total, that’s kind of a shady line or not completely solid line. But that’s kind of an arbitrary line that’s been drawn, then you’re thinking, Okay, now there’s pretty much significant influence. And therefore, we’re going to use a different method equity method, then if we’re over 51%, which is a more solid line, if you have more than 51%, and you’re voting on things, and you have like more than 51%, then you pretty much win. And that would mean control for that situation typically. And then we may use a different method, such as a consolidation. So we’re going to be focusing in here on the middle method, where we have significant influence where we have that lower line that’s a little bit fuzzy that 20% arbitrarily drawn. And then if you’re over the 51%, then it’s more likely that then you do have control and may be using the consolidated method. In that case. So equity method we’re focusing in on investments using the equity method, the equity method will reflect the investors changing interest in the investi. So we’re going to try to basically reflect what’s going on on the investor side with the change investment in the investi, the company that we are investing in that company, we have a significant influence over investment is recorded at the starting purchase price.
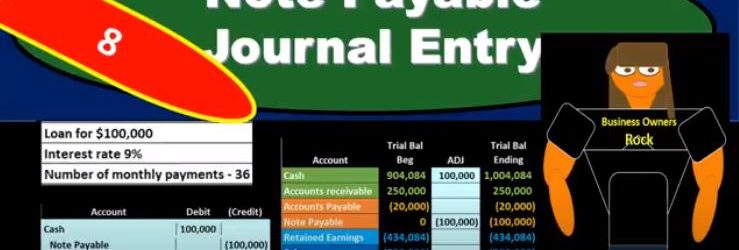
Note Payable Journal Entry
In this presentation, we will record the journal entry related to a note payable related to taking out a new loan from the bank. Here’s going to be our terms. We’re going to record that here in our general journal and then we’ll post that to our worksheet. The trial balances in order assets, liabilities, equity, income and expenses, we have the debits being non bracketed or positive and the credits being bracketed or negative debits minus the credits equaling zero net income currently at 700,000 income, not a loss, revenue minus expenses. The difficult thing in terms of a book problem, when we record the loan is typically that we have too much information and this is the difficult thing in practice as well. So once we have the terms of the loan, and we have the information, we’ve already taken the loan out, then it’s the question of well, how are we going to record this thing? How are we going to put it on the books and if we have this information here, if we have a loan for 100,000, the interest is 9%. And then the next number of payments that we’re going to have, we’re going to pay back our 36. Then how do we record this on the books? Well, first, we know that we can ask our question is cash affected? We’re going to say, Yeah, because we got a loan for 100,000. That’s why we got the loan.
01:14
So cash is a debit balance, it’s going to go up with a debit, so we’ll increase the cash. And then the other side of it is going to be something we owe back in the future. And that’s going to be note payable. And that’s as easy as it is to record the initial loan. The problem with this the thing it’s difficult in practice, and in the book question is that we’re often given, of course, the other information, like the interest in the number of payments, and possibly more information that can cloudy up the what we’re doing, and the reason these are needed, so that we calculate interest in the future, but they’re not really We don’t even need that information to record the initial loan. All we need to know is that we got cash and we owe it back in the future. And you might be asking, Well, what about the interest we owe interest in the future as well? We do, but we don’t know it yet. And that that’s the confusing thing interest, although we we will pay interest and we know exactly how much interest we’re going to pay in the future. We don’t owe it yet. Why don’t we owe it yet? Because we’re going to pay back more than 100,000. Why don’t we Why don’t we record something greater than 100,000? You might say, because we know we’re going to pay more than 100,000. And that’s because the interest is something that it’s like rent. So we’re paying rent on the use of this 100,000. And just like if we if we had a building that we rented, that we’re using for office space, we’re not even though we know we’re going to pay rent in the future. We’re not going to record the rent now. Because we haven’t incurred it until we use the building.
02:41
So the same things happening here. We know we’re going to pay interest in the future we’re no we know we’re going to pay more than 100,000 but it hasn’t happened yet. We haven’t used up we haven’t gotten the use of this hundred thousand and therefore haven’t incurred the expense of it yet. So the interest and is something we need to negotiate when making To turn off the loan, but once the loan has been made, and we’re just trying to record it, it’s not going to be in the initial recording. It will be there when we calculate the payments need and the amortization table. So the initial recording is pretty straightforward. We’re just going to say okay, cash is going to go up by 100,000. And then the notes payable is going to go up from zero in the credit direction to 100,000. So what we have here is the cash increasing the liability increasing, although we got cash, there’s no effect on net income because we haven’t incurred any expenses. We’re going to use that cash most likely to pay for expenses possibly or pay for other assets or pay off liabilities in order to help us to generate revenue in the future. But as of now, we’ve gotten we increase an asset and we increase the liability