Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to talk about consolidation calculations for less than wholly owned subsidiaries. So we have a parent subsidiary relationship, we’re going to be looking at the consolidation process to put the financial statements of the parents and the subsidiaries as if they are one entity, but we don’t have a wholly owned subsidiary. In other words, the parent does not own 100% of the subsidiary. How do we do the consolidation? in bad case, consolidation calculations less than wholly owned subsidiaries, that entities entire income and value must be reported per the current standards? So in other words, once again, we might think, well, on the income statement, maybe we would just report the part of the subsidiary that belongs to or is controlled by the parent, but that’s not typically the case. That’s not the case under generally accepted accounting principles.
Posts with the Equity tag
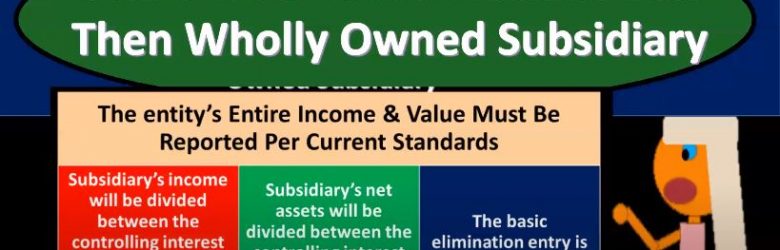
Consolidation for Non Wholly Owned Subsidiary
Advanced financial accounting. In this presentation we’re going to talk about a consolidation for a non wholly owned subsidiary. So in other words, we have a parent subsidiary relationship, but the parent doesn’t own 100% of the outstanding common stock of the subsidiary but something other than 100%. In other words, over 51% controlling interest less than 100% get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. Non controlling interest often will be represented NCI non controlling interest. So notice if we have a parent subsidiary relationship we’re talking about there is some controlling interest, the controlling interest is the interest that’s going to be over 51%. However, if we don’t have 100% ownership, then we have the amount that’s not in control and that of course is going to be the non controlling interest. So non controlling interest. NCI controlling interest is needed for consolidation. Obviously, if we’re going to consolidate this thing, that means typically that A parent has some controlling interest over 51% a 100% is not needed. So 100% of ownership, in other words, by one parent to the other is not necessary for a consolidation to take place control is necessary, which is typically over 51% less than 100% ownership will result in a non controlling shareholder, those other than the parent.
Consolidation Process 100% Owned Subsidiary
This presentation we’re going to take a look at the consolidation process for a 100% owned subsidiary. In other words, when we’re thinking about one company owning another company in advanced financial accounting, we’re usually looking at the situation and spending most of our time where we have some kind of consolidation process. So we want to Vin take the consolidation process and look at it in levels of complexity. So we’re going to start with a level of complexity, that’s going to be an easier setting where we will have 100% owned subsidiary, and then we’ll go from there and add more complications to it. Get ready to account with advanced financial accounting to ownership and control and prior presentations, we took a look at different methods based on different levels of ownership and control. We said in general, if we had zero to 20%, we use the carried value and then 20 percents kind of an arbitrary number, but if we’re over that amount, we’re really looking at the term of significant influence it for over the 20% from 20 to 50% then The assumption is that we would be using the equity method because the assumption would be if over 20% unless spoken otherwise, unless some unreal, some reason, otherwise, we would then have this significant influence and therefore be justified to use the equity method. And then if you’re over 51%, then you may have the consolidation. Now, when we think about these two methods that they carried value in the equity method, we can basically explain those as we go, you know, if you got anything from zero to 20%, then we could just basically say, yeah, then you fall into this category, let’s talk about the accounting in general.
Consolidation & Subsidiary Stock Dividends
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss the consolidation process and a situation where the subsidiary issues stock dividends we have stock default dividends issued by the subsidiary what will be the effect on the consolidation process get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. We’re talking about a consolidation process where the subsidiary then issued stock dividends. So we have stock dividends are issued to all common stockholders proportionally, therefore, the relative interest of the controlling and non controlling stockholders is not changed. So that relative interest isn’t changed, so we don’t have to worry about that which is nice. The carrying amount on the parents books is also not changed. So we’re not going to have to change anything on the books of the parent with basically an adjustment to the investment account using you know, typically the equity method, which is nice stockholders equity accounts for the subsidiary do change. So we do have a change to the stock There’s equity on the subsidiary, but total stockholders equity does not. So in other words, if we take stockholders equity as a whole, there’s no change there, even though there’s changes within the stockholders equity of the subsidiary. So we’re here we’re going to say this stock dividends represent a permanent capitalization of retained earnings. That’s basically what is happening, permanent capitalization of the retained earnings.
Subsidiary Sells Additional Shares to Nonaffiliate
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss a consolidation process where we have a parent subsidiary relationship and the subsidiary sells additional shares to a non affiliate. So we have the subsidiary selling shares not to the parent, but to a non affiliate what will be the effect on the consolidation process? Get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. We are talking about a situation here where the subsidiary is selling more stock or additional stock to someone outside of the organization, someone who is not affiliated not to the parent or some other subsidiary, what will be the effect in the consolidation process? It’s going to increase the total stockholders equity of the consolidated entity by the amount received by the subsidiary in the sale. That of course would make sense because if you imagine the transaction taking place, then if they got cash for it, for example, cash would be going up the other side going to the equity so it’s going to be increasing the total stockholders equity will increase total shares outstanding for the subsidiary reducing the percent ownership of the parent company. So if the subsidiary then issues more shares and they didn’t go to the parent, then that means there’s going to be more shares outstanding. That means the shares that the parent owns will go down, therefore, their percentage ownership will typically go down. In that case, we’ll increase the amount assigned to the non controlling interest.
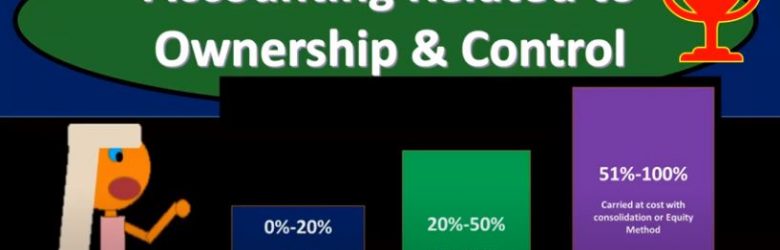
Accounting Related to Ownership & Control
In this presentation, we will take a look at accounting methods which will relate to and depend on ownership and control, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. Accounting related to ownership and control methods used to account for investments in common stock will depend on the extent of influence or control, the investor can exercise over the investi. So in other words, we’re gonna have different methods depending on the level of control. Now, if we’re going to use different methods, we need to have some kind of definition we need to have some lines in terms of when we’re going to apply these different methods. What does it mean to have different levels of control? And then how do we apply those in practice so we can have some kind of standardization for that.
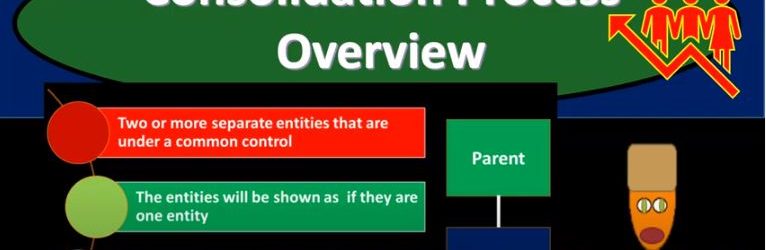
Consolidation Process Overview
In this presentation, we will take a look at an overview of the consolidation process, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, consolidation process overview we’re talking about a situation where we have two or more separate entities that are under a common control. So the basic kind of format of that you’re imagining here, then you have a parent and a subsidiary, these are going to be connected in some way shape or form because the parent has control over the subsidiary, we can imagine more complex situations, for example, having one parent and multiple subsidiaries as well. The entities will be showing as if they are one entity. So if we have a situation like this, if there’s a control type of situation, it’s quite possible then we’re going to have the the subsidiary and the parent These are two separate companies have a consolidated basically a financial statement. So the financial statement the idea of that being we’re going to take these two financials and represent them as if these two separate entities in this case, two or more can be more than two are one entity. This means two or more sets of books are merged into one set of financial statements. So obviously, what does that look like from a practical standpoint, we have the parent company, we have this subsidiary company, they have two sets of books, we’re gonna have to take those two sets of books and put them together for the financial statements. Here is an example of a slightly more complex situation where we still have parent subsidiary relationships but multiple pole subsidiaries in this case, so we have the parent subsidiary one where there’s a 75% ownership. So we’re over we have a controlling interest, we’re over that 51, we’re going to say there’s a controlling interest here, therefore there’s going to be a consolidation. So we’re gonna have a consolidation subsidiary to is owned 52%. So we’re still over the 51.
Acquisition Accounting Bargain Purchase
This presentation we’re going to continue on with our discussion of acquisition accounting, and this time focusing in on a bargain purchase, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. First off, we can basically think of the bargain purchase as the opposite of goodwill. So in a prior presentation, we talked about the concept of goodwill within an acquisition, which would be resulting if the fair market value of the amount that was given like basically the purchasing price was greater than the fair market value of the net assets. So in other words, we take we look at the books of the company that’s being acquired, we’ve revalue their assets and liabilities to be on a fair market value, then assets minus liabilities, the equity section, the net assets now at a fair market value, we take a look at that. And if there’s a consideration that’s given that is greater than that amount, that then would result in goodwill. Now goodwill is quite common, because it’s unlikely even if you even if you re assess all the assets and liabilities to their fair value. Then you would typically think that the price would either be that that would be given the the amount that would be exchanged, the fair market value of the consideration would be the same as the assets minus the liabilities at fair market value, or more, because there’s some type of goodwill, that’s going to be that’s going to be in the organization. Now, you might be thinking, Well, what what if it was the opposite? What if you took the fair market value of the net assets, and the amount that was given the exchange amount was less than the fair market value? Now that could happen, but just note that that’s a lot more unusual.
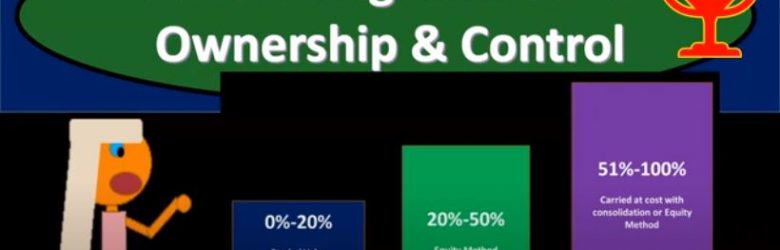
Accounting Related to Ownership & Control
In this presentation, we will take a look at accounting methods which will relate to and depend on ownership and control, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. Accounting related to ownership and control methods used to account for investments in common stock will depend on the extent of influence or control, the investor can exercise over the investi. So in other words, we’re gonna have different methods depending on the level of control. Now, if we’re going to use different methods, we need to have some kind of definition we need to have some lines in terms of when we’re going to apply these different methods. What does it mean to have different levels of control? And then how do we apply those in practice so we can have some kind of standardization for that.
Investments Using the Equity Method
This presentation we’re going to focus in on investments using the equity method. In other words, we’re going to have a situation where we have one company that’s investing in another company, this time they have significant influence. And therefore, we will be using the equity method to account for that investment, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. In prior presentations, we gave an overview about different accounting methods that could be used based on different levels of influence and control those general rules being that if there is 20, or zero to 20%, ownership, we use the carried value 20 to 50%, which is where we’re going to focus in on now, the equity method, idea of there being that there is now significant influence. So in other words, if we own zero to 20%, that would be kind of like you investing in a large company like apple or whatnot. We’re the assumption being, we don’t have significant influence, even though we do have a vote of what happens However, when our vote gets to be 20% Have the total, that’s kind of a shady line or not completely solid line. But that’s kind of an arbitrary line that’s been drawn, then you’re thinking, Okay, now there’s pretty much significant influence. And therefore, we’re going to use a different method equity method, then if we’re over 51%, which is a more solid line, if you have more than 51%, and you’re voting on things, and you have like more than 51%, then you pretty much win. And that would mean control for that situation typically. And then we may use a different method, such as a consolidation. So we’re going to be focusing in here on the middle method, where we have significant influence where we have that lower line that’s a little bit fuzzy that 20% arbitrarily drawn. And then if you’re over the 51%, then it’s more likely that then you do have control and may be using the consolidated method. In that case. So equity method we’re focusing in on investments using the equity method, the equity method will reflect the investors changing interest in the investi. So we’re going to try to basically reflect what’s going on on the investor side with the change investment in the investi, the company that we are investing in that company, we have a significant influence over investment is recorded at the starting purchase price.