Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will discuss foreign currency transactions get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, foreign currency transactions. So remember when we’re thinking about foreign currency transactions, we’re thinking about them from the perspective of the US company in US dollar. So we’re have our currency that we’re making our financial statements in, we’re measuring all the stuff on our financial statements with the measuring tool that we need to be using, that’s going to be the US dollar, that’s going to be our standardization. And then anytime we have foreign currency transactions with something other than US dollars, then we want to see them from that perspective, right? Because when we put them on our financial statements, just like anything else, just like inventory, if we were to value units of inventory, or to value stocks and whatnot, we need to value them in terms of our measure into a which of course is the US dollar.
Posts with the financial statements tag
Foreign Currency Exchange Rates
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we’re going to discuss foreign currency exchange rates get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, foreign currency exchange rates, let’s first define foreign currency transactions. So what are from foreign currency transactions? When are we going to need to account for foreign currency transactions. So from our perspective, we’re going to be looking at this from the perspective of a US company US company that is having their books then accounted for or measured in dollars. And when you think about the foreign currency transaction, it’s just like anything else, but it can be a little bit more confusing. So you want to remember, of course, that the dollar is basically the measuring tool.
Consolidation – Interim Acquisition
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss consolidation and interim acquisition. In other words, we have a parent subsidiary relationship that parent owning a controlling interest over 51%. However, that controlling interest took place for a purchase of the common stock of the subsidiary that happened in the middle of the year. So prior to this, we’ve been talking about situations where we are doing consolidations for an entire year. And you may have question probably popped up in your head at some point in time as well what would happen if the purchase took place in the middle of the year now we have that mid year kind of purchase worse, especially concerned with that first year where the consolidation didn’t really happen. I mean, there wasn’t a consolidated ownership until sometime in the middle of the year, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting. So we’re talking about a situation where we have a consolidation but the consolidation happened in the middle of the years. We’re thinking about that first year, primarily What would happen? Well, if the consolidation didn’t take place in January in other words, the parent didn’t purchase the controlling interest in the subsidiary at the beginning of the year but happened at some point in the middle of the year what’s going to be the impact on the year in consolidation, which typically happens for the entire year? Well, the subsidiary is seen as being part of the consolidated entity from the time the stock is acquired, even if acquired in the middle of the year.
Remeasure Financial Statement of Foreign Subsidiary
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss the remeasurement process for financial statements of a foreign subsidiary. Get ready to account with advanced financial accounting remeasurement financial statement of foreign subsidiary remeasurement overview so we’re going to go through the process of the remeasurement. As you think of the measurement process, you want to be comparing and contrasting it to the translation process. So you’re envisioning basically you got a parent company. The parent company has a subsidiary the subsidiary is a foreign subsidiary. The subsidiary then conducts their books. Typically we’re thinking in a foreign currency right, that subsidiary is conducting their books in a foreign currency. If we need to consolidate the subsidiary into the parents financial statements, the parent uses dollars to measure their books subsidiary uses a foreign currency on the bookkeeping side, how do we get them over $2 so we can do the consolidation process. two methods generally we can use a translation method or a remeasurement method, and we have to determine which method we’re going to use by determining what the functional currency is. And once we know what the functional currency is, then we can determine whether we need to use the translation method or the remeasurement method. And they’re going to be slightly different. Now note, there’s also a third kind of option where we might have to use translation and remeasurement if there was a situation where the foreign currency has the financial statements, and something other than the US dollars and then the functional currency was not the currency that their bookkeeping was in, and it’s not the US dollar.
Translate Financial Statements of Foreign Subsidiary
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will discuss translate financial statements of foreign subsidiary, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, translate financial statements of foreign subsidiary. So we’ll go through the general process of the translation process for the revenue and expenses, the average exchange rate for the period covered by the statement is the rate that is generally going to be used. And again, this would make sense, because if we’re talking about the revenue and expenses, we can’t really pick one rate, because that is a statement of how the performance did over time from beginning to the end. And therefore we need to use some kind of rate that would be representative and it wouldn’t really make sense to use the rate at the end of the timeframe but possibly some average of it. So a single material transaction is translated using the rate in effect on the translation date. So then there could be an argument that could be made we could say okay, so We’re not going to use just one rate, like at the end of the time period like we’re using on the balance sheet generally, because that would make more sense on the balance sheet because it’s reported as of a point in time. But on the income statement, yeah, it makes more sense for us to use some rate that’s kind of reflective of the timeframe. So possibly we’ll use an average rate. But what if we have this really material type of transaction that’s really large transaction, maybe in that case, we should we should deviate from just an average rate and use the rate as of that point in time or like a historical rate at that point in time. assets, liabilities and equity. So now we’re talking about the balance sheet. So for the most part on the balance sheet, you would think all right, it would make more sense then for us to be using the current exchange rate, which would be as of the date of the balance sheet date. So which says as of the end of the time period, if we’re talking for the for 1231 income statements or financial statements for the year ended 1231 then we’re talking 1231. The end of the time period is when all the balance sheet accounts are reporting as Oh, As of that point in time, and therefore, for the most part, you would think that the current exchange rate, the rate as of that point in time would work. However, you can also think that the historical exchange rate might be used for some items, some, again, some kind of large items power, possibly for the property, plant and equipment.
Translation vs Remeasurement
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss translation versus remeasurement. Get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, translation versus remeasurement methods to restate to foreign entities statements to US dollar. So the most straightforward methods can be translation of foreign entities functional currency statement to US dollars. So the translation is what we’ll use the most straightforward method when the entity statement is using the functional currency. So typically, if the if the entity is using the functional currency, and we need to translate it, then we’ll simply translate it from the functional currency to the US dollars. And then there’s remeasurement of foreign entities statement into its functional currency. So remeasurement means that the entity is running their bookkeeping in a currency that is not the functional currency. Right? So then we’re going to have to re measure we’re going to use this term re measure rather than translate the To the functional currency, so after we remeasure to the functional currency, after remeasurement statements need to be translated to the reporting currency if the functional currency is not the US dollar. So in other words, if we’re assuming, in this case, in the case of the remeasurement, or let’s say, we have an entity that we’re going to be consolidating a subsidiary entity in another country, and we’re in the US and we need to basically consolidate these data together in terms of US dollars at the end of the day, if the entity is using the functional currency as as their financial statements, their bookkeeping is in the functional currency, then we can simply use the term translate it to the US dollars, which will be the parent currency that we’re talking about here. If however, the foreign entity is having their books in some currency, that is not the functional currency, then what we’re going to have to do is re measure it. We want to use remeasurement To the functional currency, we want to make remeasure at first to the functional currency rather than straight to the US dollar. So we’re going to use remeasure to the functional currency. And after we re measure to the functional currency, if the functional currency is the US dollar, then then we should be able to stop there. That’s okay. If however, the functional currency is not the US dollar, then we would have to go from the functional currency and then translate to the US dollar. So we’ll talk a little bit more about that as we go. So let’s think about translation.
Functional Currency
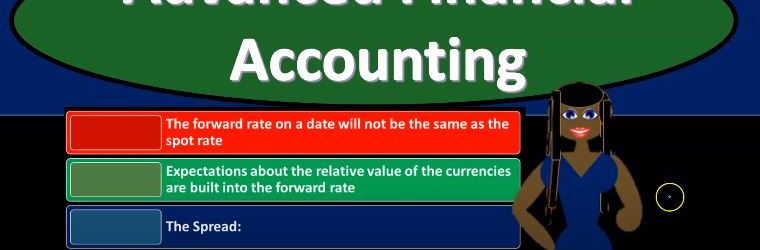
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss functional currency get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, functional currency. When financial statements are restated from a foreign currency into US dollars, we must consider which exchange rate should be used to translate the foreign currency amounts to the domestic currency. So, when we translate the foreign currency to the domestic currency, we’ll have to determine what our exchange rate Are we going to be using in order to do so how will we account for translation gains and losses? So if there’s going to be a translation gain or loss, what are we going to do with that? In other words, should we put the translation gains and losses as part of the income statement reporting it on the income statement, the gains and losses that are due to the translation process exchange rates that may be used? So what kind of exchange rates might we use during this exchange process? Well, we could use the current rates probably the first thing that comes to mind you say, Hey, we got the financial status. As of the year ended of this time period, why don’t we just use the current rate. And that’s typically what we will do for the balance sheet amounts. And that typically makes sense for the balance sheet amounts, because remember, the financial statements, of course on the balance sheet represents where we are at a particular point in time. So simply converting them makes some sense on the balance sheet. But you also might think, Well, what about those things, you know, that we purchased, like fixed assets at a point in time, maybe we should use the point in time that we had the purchase took place. So you could argue on that on the balance sheet, but the current rate on the balance sheet and makes the most sense, but if you’re looking at the income statement, the current rate might not make as much sense because we’re measuring a timeframe that from a year will, let’s say, for a year’s timeframe from the beginning to the end, so maybe it doesn’t seem quite right to use simply the current rate, which would be the rate as of the end of the financial statements if we’re talking like December 31, rather than using some type of race. That would be representative of the period that would covered being January through December, we could use the historical rate, that’s gonna be the rate that exists at the time the initial transaction took place. And again, this one is often would make sense to us if we’re talking about a situation like if we bought equipment or something like that fixed assets, property, plant and equipment, large purchases that are on the books, we might say, well, maybe we should be putting those on the books at the rate that we should be using at the time, basically, the transaction took place. So maybe we would argue for the historical right there. And then we have the average rate for the period, generally a simple average for a period of time, usually the exchange rate used to measure revenues and expenses.
Attempts to Converge to One Set of Global Accounting
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation, we will take a look at attempts to converge to one set of global accounting standards get ready to account with advanced financial accounting attempts to converge to one set of global accounting standards. When preparing financial statements of global companies, accounting firms must think about differences and accounting principles across national boundaries. So obviously, if we’re a large company, and we have places of business across national boundaries, then we got to think about well, what are the accounting principles and standards in those different locations? And what are the requirements for us to prepare financial statements if doing business in you know, different countries across boundaries that have different accounting standards, differences in currencies that are used to measure the operations of companies in different countries. So again, this is something of course we have to think about it for a large company. We have places of business in our company that are across different different areas. Different countries that have different currencies, that it’s possible that we could be measuring parts of the books and whatnot in different currencies. We need to know what the standards are in different places so that we can meet those standards if we’re a large company. International Financial Reporting Standards IFRS published by the International Accounting Standards Board is ay ay ay ay SB, as the name indicates International Financial Reporting Standards. The goal here or one of the goals is have one set of standards that will go across different areas, different countries, different nations, which could make it easier to do business in different companies or across borders. So it is accepted widely the set of standards and permitted or required in over 100 countries.
Requirements for Management Reporting Laws
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss requirements for management reporting laws. We’ll discuss major laws and the reporting requirements related to them get ready to account with advanced financial accounting requirements for management reporting laws, we’re going to be starting off with the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977. The fcpa Congress passed it as a major amendment to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, which we’ve discussed in prior presentations. It has two primary sections first section Part One prohibits bribing foreign governmental or political officials for the purpose of securing a contract or otherwise increasing the company’s business and part two requires publicly held companies to maintain accurate records. It also requires an adequate system of internal control. So internal controls again, taking more of a central point focus a lot of times with the regulations related to large companies, we have then the Sarbanes Oxley act of 2002, also known as s o x Sox signed to law July 30 2002. So July 30 2002, Sarbanes Oxley gained traction after the accounting and financial mismanagement of Enron, WorldCom and other large companies. So there’s there’s big large scandals that were happening. And it was feared that and I think rightly so to a large extent that there was going to be faith lost in the financial reporting system. And once again, that’s the foundation really, that’s a huge component to why people invest in US companies because they have some more measure of trust than many other areas where they can put their money in. So if the financial statements are going to lose, lose that trust, that’s going to be a very big problems. So Sarbanes Oxley was a reaction to some of these large scandals which were reflecting missed. statements in the financial statements that looked like deceptive misstatements in the financial statements in an attempt to regain security to people who are investing and users of the financial statements to have faith in the contents of them, they’ll help the law has many implications for accountants. So there’s going to be a lot of changes. accounting firms have many implications related to it. We’ll go through it in some detail here. Not a whole lot of detail, but some detail we’ll go through some of the major parts of it. It was intended to minimize corporate governance, accounting and financial reporting abuses, resulting in restoration of investor confidence in the financial reporting of publicly traded companies.
Disclosure Requirements
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss disclosure requirements get ready to account with advanced financial accounting disclosure requirements. We have the management discussion and analysis that’s often referred to as the M D and A discusses a company’s financial condition and results from operations. The MD and a are part of the basic information package required in major filing with the SEC, the Securities and Exchange Commission. Items currently required in the MD and a the management discussion and analysis include liquidity, capital resources, results of operations, off balance sheet arrangements, tabular disclosure of contractual obligations, disclosure requirements, pro forma disclosures, pro forma disclosures, financial presentations generally taking the form of summarized financial statements. demonstrate the effect of major transactions that happen after the end of the fiscal period or that happened during the year, but are not fully reflected in the company’s historical cost financial statements.