Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss requirements for management reporting laws. We’ll discuss major laws and the reporting requirements related to them get ready to account with advanced financial accounting requirements for management reporting laws, we’re going to be starting off with the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977. The fcpa Congress passed it as a major amendment to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, which we’ve discussed in prior presentations. It has two primary sections first section Part One prohibits bribing foreign governmental or political officials for the purpose of securing a contract or otherwise increasing the company’s business and part two requires publicly held companies to maintain accurate records. It also requires an adequate system of internal control. So internal controls again, taking more of a central point focus a lot of times with the regulations related to large companies, we have then the Sarbanes Oxley act of 2002, also known as s o x Sox signed to law July 30 2002. So July 30 2002, Sarbanes Oxley gained traction after the accounting and financial mismanagement of Enron, WorldCom and other large companies. So there’s there’s big large scandals that were happening. And it was feared that and I think rightly so to a large extent that there was going to be faith lost in the financial reporting system. And once again, that’s the foundation really, that’s a huge component to why people invest in US companies because they have some more measure of trust than many other areas where they can put their money in. So if the financial statements are going to lose, lose that trust, that’s going to be a very big problems. So Sarbanes Oxley was a reaction to some of these large scandals which were reflecting missed. statements in the financial statements that looked like deceptive misstatements in the financial statements in an attempt to regain security to people who are investing and users of the financial statements to have faith in the contents of them, they’ll help the law has many implications for accountants. So there’s going to be a lot of changes. accounting firms have many implications related to it. We’ll go through it in some detail here. Not a whole lot of detail, but some detail we’ll go through some of the major parts of it. It was intended to minimize corporate governance, accounting and financial reporting abuses, resulting in restoration of investor confidence in the financial reporting of publicly traded companies.
Posts with the financial statements tag
Periodic Reporting Requirements
Advanced financial accounting PowerPoint presentation. In this presentation we will discuss periodic reporting requirements for publicly traded companies get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, periodic reporting requirements, companies that have more than 10 million in assets and whose securities are held by over 500. Persons must file annual and other periodic reports to provide updates on their economic activities. So remember the general rule here we’re talking about publicly traded companies that have a benefit of being able to be publicly traded to the public on the exchanges. And in exchange for that we want to see some more basically transparency, and therefore you’ve got the filing process that needed to take place. We see some regulation by the SEC that we talked about in prior presentations. And then going forward, we want to keep and maintain the transparency the information so that there’s both the investors and the companies have the information necessary in order to enter into a agreements. And therefore we’re going to need some continuing reporting, what are the what’s going to be the requirements in terms of the continuing reporting. So once again, companies that have more than 10 million in assets and whose securities are held by over 500 persons must file annual and other periodic reports to provide updates on their economic activities. And that’s going to increase that transparency so that investors know what is happening and they can invest with full information to do so. three basic periodic reporting forms used for this updating our form 10 k form 10 Q and form eight K. Let’s start with the form 10 k form 10 k is the annual filing to the SEC the Security and Exchange Commission.
Allocate Expenses to Classes
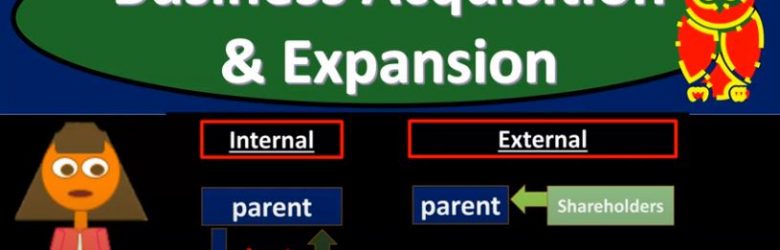
This presentation we’re going to take a closer look at external business expansion, which includes things like mergers and business combinations, get ready to act, because it’s time to account with advanced financial accounting. Before we move into the external expansion, you want to give a review and keep your mind on what our focus is we’re talking about a business that is expanding. When we think of it about expansion, we can break that expansion into internal and external expansion. So we have a business expanding into new areas do segments, we can think of it as an internal or external expansion. In a prior presentation, we talked a little bit more on the internal expansion, in which case you might have a situation where a parent creates a subsidiary or a parent basically just creates another division possibly, and expands in that format. Now we’re going to be going to the external expansion, in which case we’re talking about two entities. So we have two separate legal entities that in some or two separate entities in some case in some way, shape reform are coming together. So now we’re going to have an expansion where we have an external expansion. So if we’re thinking of thinking about this, from the from the standpoint of one company, we’re thinking about ourselves as one company and we are expanding, then we’re thinking about the expansion externally, that we are going to be combining in some way shape or form with another company. Now, the format and form in which that combination can take place can be various we can have various forms of that combination, it could result in a parent subsidiary type of relationship, or it could result in the parent basically consuming that another company and bringing them into the overarching parent company.
Business Acquisition & Expansion
In this presentation, we’re going to discuss an Introduction to Business acquisition and expansion, get ready to act, because it’s time to account with business, Advanced Accounting, advanced financial accounting will have to do with the concept of expansion and the accounting related to it. So first we need to know well, what is expansion? What are the types of expansion that can take place? What are the problems with regards to the accounting for it? And then what type of accounting principles can we apply in order to deal with the accounting related to those problems? So when we think about expansion in general of a business, we’re thinking about the growth of a business, typically, you have either internal expansion or external expansion. So those are two categories of expansion. We want to start to visualize in our mind and we got our mind our mind is visualizing a business that is trying to expand how are they going to do that? Are they going to do it with some type of internal growth or some type of external growth? Then we want to think about the legal structure of the of the expansion for example, an expansion often results in a parent subsidiary type of relationship. So, we have different legal entities that are associated in some way shape or form.
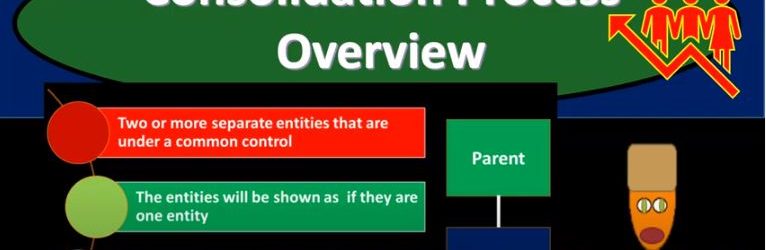
Consolidation Process Overview
In this presentation, we will take a look at an overview of the consolidation process, get ready to account with advanced financial accounting, consolidation process overview we’re talking about a situation where we have two or more separate entities that are under a common control. So the basic kind of format of that you’re imagining here, then you have a parent and a subsidiary, these are going to be connected in some way shape or form because the parent has control over the subsidiary, we can imagine more complex situations, for example, having one parent and multiple subsidiaries as well. The entities will be showing as if they are one entity. So if we have a situation like this, if there’s a control type of situation, it’s quite possible then we’re going to have the the subsidiary and the parent These are two separate companies have a consolidated basically a financial statement. So the financial statement the idea of that being we’re going to take these two financials and represent them as if these two separate entities in this case, two or more can be more than two are one entity. This means two or more sets of books are merged into one set of financial statements. So obviously, what does that look like from a practical standpoint, we have the parent company, we have this subsidiary company, they have two sets of books, we’re gonna have to take those two sets of books and put them together for the financial statements. Here is an example of a slightly more complex situation where we still have parent subsidiary relationships but multiple pole subsidiaries in this case, so we have the parent subsidiary one where there’s a 75% ownership. So we’re over we have a controlling interest, we’re over that 51, we’re going to say there’s a controlling interest here, therefore there’s going to be a consolidation. So we’re gonna have a consolidation subsidiary to is owned 52%. So we’re still over the 51.
Statement of Cash Flow Non Cash Items
In this presentation, we will take a look at the statement of cash flows non cash items. First question, why would we be looking at non cash items when considering a statement of cash flows? We’re gonna go through a list of non cash items first and see if you can recognize a trend in these and why we might be linking them to a statement of cash flows discussion, then we will explain more fully on the idea of looking at non cash items when considering a statement of cash flows. So, some examples of non cash items would be the purchase of long term assets by issuing a note the purchase of non cash assets by issuing equity or debt, the retirement of debt by issuing equity stock, lease of assets in a capital lease transaction and exchange non cash asset for other non cash asset. Consider these examples and note some of the common features including the deal with investing and financing activities. and think through why we might be linking them to a statement of cash flows. We’ll go more fully through this by giving an example of the purchase of long term assets by issuing a note, an example that we can then apply out to the rest of these items. So what are we going to do with these non cash items, we’re going to report them at the bottom of the statement of cash flows or report them in a note related to the statement of cash flows. So we’re going to have to say in some format, or other, hey, look, these are some non cash items that we’re linking to, for some reason, the statement of cash flows.
Post Closing Trial Balance & financial statements
Hello in this presentation we will discuss the post closing trial balance and financial statements. When considering the financial statement relationship to the trial balance, we typically think of the adjusted trial balance that being used to create the financial statement. It’s important to note, however, that any trial balance that we use can be generated into financial statements. It’s just that the adjusted trial balance is the one that we have totally completed and prepared and ready. In order to create the financial statements to be as correct as possible as of the date we want them, which is usually the end of the month or the end of the year. Note that the names of the unadjusted trial balance the adjusted trial balance and the post closing trial balance are really a convention they’re all basically trial balances.
Closing Process Step 4 of 4 Closing Journal Entry Draws or Withdraws
Hello in this lecture we’re going to continue on with the closing process with step four, the final step of the process which will be to close out the draws. Remember that the objective is to have the adjusted trial balance be converted to the post closing trial balance. adjusted trial balance is what we use to create the financial statements. And the difference between the adjusted trial balance and the post closing trial balance will be that we want to have all temporary accounts including draws revenue and expense accounts to be converted to zero and have all that be in the owner capital account meaning the owner capital account will now be including all these accounts underneath it crunched into basically one number, we’re going to do that with a four step process.
One Step Closing Process
Hello in this presentation, we will be looking at a one step closing process. In other words, we will be closing out temporary accounts using one journal entry. There’s a few different ways that we can perform the closing process. And there’s benefits and cons to each way of doing it. The one step closing process is the simplest way to do it. And it’s also a way that we can imagine what is happening within the closing process as easily as possible a skill useful when considering what’s happening from time period to time period, and how the financial statements are working. So here we’re going to look at a one step closing process. Remember what the closing process is, it’s going to be a process at the end of the time period that we will be performing.
Closing Process Explained
Hello in this lecture we’re going to talk about the objectives of the closing process the closing process will happen after the financial statements have been created. So we will have done the journal entries where we will have compiled those journal entries into a trial balance, and then we will have made the financial statements. And then as of the end of the period in this case, we’re going to say as of December, when we move into the next time period, January, what we need to do is close out some of the temporary accounts those accounts including the income statement and the draws account so that we can start the new period from start in a similar way as if we were trying to see how many miles we could drive say in a month. If we wanted to Vince in December, and then see how many miles we’re going to drive in January of next year.